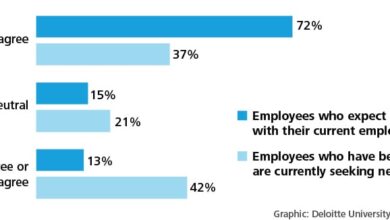
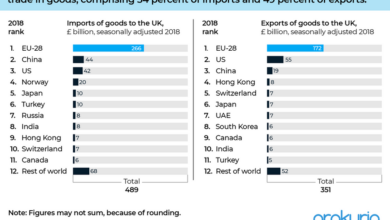
CIMA Recommendations UK Post-コロナ Recovery
CIMA recommendations to UK government post coronavirus recovery offer a roadmap for the nation’s economic resurgence. The document delves into the UK’s pre-pandemic economic standing, highlighting the challenges faced by various sectors during and after the pandemic. It explores diverse recovery models, potential government strategies emphasizing sustainability, and the crucial role of infrastructure investment. A detailed analysis of sector performance before and after the pandemic, alongside potential benefits and drawbacks of different recovery approaches, is presented.
This in-depth analysis, encompassing CIMA’s specific recommendations, their rationale, and potential impacts on different socioeconomic groups, provides a comprehensive perspective on the UK’s post-pandemic economic future. It also compares CIMA’s recommendations with other expert opinions and reports, showcasing a nuanced understanding of the complexities involved in the recovery process. The report underscores the importance of a well-defined implementation timeline and robust evaluation methods to ensure the success of the government’s recovery strategies.
Economic Recovery Strategies
The UK’s pre-coronavirus economic landscape was characterized by a mixed bag. While experiencing periods of growth, the nation faced persistent challenges, including regional disparities, skills gaps, and a reliance on specific sectors like finance and automotive. The pandemic’s impact has undeniably amplified these pre-existing issues, requiring a comprehensive and targeted recovery strategy.The economic disruption caused by the pandemic has created a complex and multifaceted challenge for the UK.
Obtain direct knowledge about the efficiency of cima ethics confidentiality rules through case studies.
Sectors like hospitality, tourism, and retail have been particularly hard-hit, facing reduced consumer spending and significant job losses. The need for swift and strategic intervention is crucial to mitigate the long-term economic consequences and ensure a robust recovery.
UK’s Pre-Coronavirus Economic Performance
The UK economy prior to the pandemic exhibited a fluctuating performance. Periods of growth were punctuated by economic uncertainties, including Brexit negotiations and global economic instability. Significant regional variations in economic prosperity existed, with some areas experiencing stronger growth than others. This disparity in growth highlights the need for tailored recovery strategies.
UK’s Economic Challenges Post-Coronavirus
The pandemic significantly impacted various sectors. The hospitality and tourism industries, heavily reliant on international travel, experienced substantial declines in revenue and employment. Retail, with its shift towards online shopping, faced significant challenges in adapting to the new consumer landscape. The manufacturing sector also felt the pressure of supply chain disruptions and reduced demand.
Economic Recovery Models and Their Application
Several economic recovery models exist, each with unique strengths and weaknesses. A Keynesian approach, focusing on government spending and stimulating demand, could be beneficial in jumpstarting the economy, particularly in sectors heavily impacted by the pandemic. A supply-side approach, emphasizing productivity gains and investment in infrastructure, could address long-term economic challenges and promote sustainable growth. A hybrid model combining elements of both approaches could offer a balanced and comprehensive recovery strategy.
Government Strategies to Stimulate Growth
Government strategies must prioritize sustainable practices. Investing in renewable energy infrastructure and promoting green technologies can stimulate growth while reducing the nation’s carbon footprint. Tax incentives and subsidies for businesses adopting environmentally friendly practices can accelerate the transition to a greener economy. Targeted support for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) is also essential, as they are vital drivers of job creation and innovation.
Infrastructure Investment in Post-Coronavirus Recovery
Investing in infrastructure is a critical component of economic recovery. Projects such as upgrading transportation networks, expanding broadband access, and modernizing energy grids can boost productivity, create jobs, and improve quality of life. This investment not only stimulates economic activity in the short term but also enhances the nation’s long-term competitiveness.
Comparison of Sector Performance Before and After the Pandemic
| Sector | Pre-Pandemic Performance | Post-Pandemic Performance |
|---|---|---|
| Hospitality | Strong, driven by tourism | Declining, significantly impacted by travel restrictions |
| Retail | Adapting to e-commerce | Facing challenges with the shift to online shopping |
| Manufacturing | Relatively stable | Affected by supply chain disruptions and reduced demand |
| Finance | Significant contributor to the economy | Demonstrating resilience but facing scrutiny |
Potential Benefits and Drawbacks of Economic Recovery Strategies
| Recovery Strategy | Potential Benefits | Potential Drawbacks |
|---|---|---|
| Keynesian | Rapid economic stimulus, job creation | Potential for inflation, increased government debt |
| Supply-side | Increased productivity, long-term growth | Potential for slower initial impact, uneven distribution of benefits |
| Hybrid | Balanced approach, mitigating risks | Complexity in implementation, potential for delays |
CIMA Recommendations for Government
The Chartered Institute of Management Accountants (CIMA) has released a comprehensive set of recommendations for the UK government’s post-coronavirus recovery strategy. These recommendations are built upon a thorough analysis of the economic impact of the pandemic and are designed to foster sustainable growth and resilience in the UK economy. CIMA’s proposals address crucial areas like financial support, skills development, and industry-specific interventions.
The aim is to create a recovery plan that benefits all sectors and social groups, ultimately driving a robust and equitable economic future.CIMA’s recommendations emphasize the importance of targeted interventions to address the unique challenges faced by different sectors and socioeconomic groups. This approach recognizes that a “one-size-fits-all” approach is unlikely to be effective in a post-pandemic recovery.
The focus is on tailoring policies to specific needs, promoting innovation, and fostering sustainable economic growth.
Specific Recommendations for Financial Support
CIMA recommends a multifaceted approach to financial support, focusing on targeted assistance for businesses, particularly SMEs, and job creation initiatives. This includes tailored financial aid packages, grants, and tax incentives, designed to stimulate investment and support job creation. The reasoning behind these recommendations is to help mitigate the long-term economic fallout of the pandemic, particularly for vulnerable businesses.
This strategy is designed to boost economic activity, stimulate innovation, and support employment.
- Targeted Grants and Loans: CIMA advocates for grant programs specifically designed for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). These grants should be structured to help them overcome cash flow problems and invest in new technologies. This would encourage business continuity and innovation.
- Interest Rate Support: CIMA suggests exploring measures to lower interest rates for businesses, making borrowing more affordable. This is crucial to stimulate investment and help firms weather the recovery period. This approach aligns with the goal of boosting business confidence and investment.
- Tax Reliefs: CIMA emphasizes the importance of tax relief programs for businesses. Such programs could include reduced corporate taxes or investment allowances, encouraging investment in new projects and stimulating economic activity.
Skills Development Initiatives
Addressing the skills gap is a key aspect of CIMA’s recommendations. Recognizing that the pandemic has accelerated the need for new skills and expertise, the institute suggests comprehensive training programs to equip workers with in-demand skills.
- Upskilling and Reskilling Programs: CIMA recommends investing in training programs that help workers transition into new roles and acquire the skills needed for emerging industries. This proactive approach to reskilling is essential for a smooth transition in the post-pandemic labor market.
- Digital Literacy Programs: The digital transformation accelerated by the pandemic has created a growing demand for digital skills. CIMA highlights the need for widespread digital literacy programs, aimed at all levels of the workforce.
- Collaboration with Businesses: CIMA stresses the importance of collaboration between educational institutions and businesses to ensure that training programs align with industry needs and prepare workers for the jobs of the future. This collaborative approach is vital for creating a skilled workforce that is relevant to the evolving needs of the market.
Prioritized Sectors
CIMA prioritizes sectors that have been particularly impacted by the pandemic, including the hospitality, tourism, and retail industries. The institute recognizes the significant job losses and economic disruption experienced in these sectors.
- Hospitality and Tourism: CIMA recommends targeted support for businesses in the hospitality and tourism sector, including financial aid and marketing campaigns to help attract tourists and revive the industry.
- Retail: The retail sector has also faced significant challenges. CIMA advocates for measures that help retailers adapt to changing consumer behaviors and embrace online sales and delivery options.
Comparison with Other Expert Opinions, Cima recommendations to uk government post coronavirus recovery
CIMA’s recommendations align with several other expert reports and opinions. The common thread is the need for a multi-pronged approach to recovery, encompassing financial support, skills development, and sector-specific interventions. Several independent reports have highlighted similar concerns and proposed similar solutions. These shared recommendations underscore the critical need for a coordinated approach to economic recovery.
Potential Impact on Socioeconomic Groups
| Socioeconomic Group | Potential Impact (Positive) | Potential Impact (Negative) ||—|—|—|| Low-income households | Increased access to financial support | Potential for limited impact on long-term income generation || SMEs | Increased access to capital and training | Potential for bureaucratic hurdles in accessing support || High-income earners | Limited direct impact | Potential for less focused support programs|| Young people | Increased access to training and jobs | Potential for competition for limited jobs || Unemployed | Increased job opportunities | Potential for long-term unemployment if the recovery is not sustainable|
Implementation and Evaluation: Cima Recommendations To Uk Government Post Coronavirus Recovery
The success of any economic recovery strategy hinges on its effective implementation and rigorous evaluation. Post-coronavirus recovery plans must go beyond mere recommendations; they require a practical roadmap for execution and a system for measuring progress. This section delves into the challenges of implementation, the crucial role of timelines, and the vital importance of evaluation metrics.A successful recovery demands a clear understanding of how the CIMA recommendations will translate into tangible action.
This necessitates a comprehensive implementation strategy that considers the diverse needs and constraints across different sectors of the UK economy. The government must also acknowledge that there will be challenges and potential roadblocks to overcome, from navigating bureaucratic processes to securing necessary resources.
Potential Challenges in Implementing CIMA’s Recommendations
Several factors could hinder the implementation of CIMA’s recommendations. These include resource constraints, resistance to change from vested interests, and the complexity of coordinating different government departments. Lack of sufficient funding for crucial initiatives, political disagreements on policy direction, and public skepticism about the government’s approach can also pose significant obstacles. Furthermore, adapting recommendations to the specific needs of different regions and sectors requires careful consideration and tailored implementation plans.
Importance of a Clear Timeline for Implementation
Establishing a clear timeline for the implementation of CIMA’s recommendations is essential for maintaining momentum and accountability. A well-defined schedule provides a framework for tracking progress, identifying potential delays, and making necessary adjustments. This structured approach ensures that the recovery plan is not just a theoretical document but a practical guide for action. Without a clear roadmap, the risk of losing focus and delaying crucial initiatives increases significantly.
Examples of countries that have successfully navigated economic crises often highlight the importance of time-bound action plans.
Importance of Evaluating the Effectiveness of Implemented Policies
Regular evaluation of the effectiveness of implemented policies is critical to adapting to unforeseen circumstances and ensuring that resources are allocated efficiently. This evaluation process must incorporate feedback from stakeholders, such as businesses, workers, and consumers. Monitoring key indicators and adjusting strategies as needed is vital for maximizing the impact of the recovery efforts. Thorough evaluations enable the government to understand what is working, what is not, and what needs to be improved.
Methods for Measuring the Success of the Government’s Post-Coronavirus Recovery Strategies
Various methods can be employed to measure the success of the government’s post-coronavirus recovery strategies. These include tracking economic growth rates, employment figures, and inflation levels. Assessing the performance of different sectors of the economy, like manufacturing, services, and retail, is also essential. Furthermore, evaluating the impact on vulnerable populations, including small businesses and low-income households, is crucial for a comprehensive assessment.
Structured Approach to Evaluating Financial Performance
A structured approach to evaluating the financial performance of different sectors involves setting specific targets and benchmarks for each sector. This enables a comparison of performance before and after the implementation of the CIMA recommendations. Using key financial ratios, such as return on equity (ROE) and debt-to-equity ratios, can provide a comprehensive view of the financial health of different businesses and industries.
Quantitative data analysis, combined with qualitative feedback from stakeholders, allows for a nuanced understanding of the recovery’s impact.
Indicators to Track the Progress of the Recovery
| Indicator | Description | Target/Benchmark |
|---|---|---|
| Gross Domestic Product (GDP) Growth Rate | Percentage change in the total value of goods and services produced in the UK. | 3% annual growth |
| Employment Rate | Percentage of the working-age population that is employed. | 75% |
| Inflation Rate | Percentage increase in the average price level of goods and services. | 2% |
| Small Business Confidence Index | Measure of optimism among small businesses. | Above 50 |
| Consumer Confidence Index | Measure of consumer optimism and spending intentions. | Positive trend |
Sector-Specific Impacts

The COVID-19 pandemic significantly disrupted various sectors, leaving lasting impacts on their operations and recovery trajectories. Understanding these sector-specific challenges is crucial for tailoring effective government policies and support measures. This analysis examines the impacts on key sectors, highlighting CIMA recommendations and their potential for stimulating growth and resilience.
Key Sectors Facing Challenges
Several sectors experienced substantial setbacks during the pandemic. These include tourism, small businesses, and technology, each facing unique hurdles in their respective recovery processes. The pandemic exposed vulnerabilities within these sectors, prompting a need for targeted interventions.
Tourism Sector Impact of Government Policies
The tourism sector, a vital component of many economies, suffered a severe downturn due to travel restrictions and consumer hesitancy. Government policies played a significant role in shaping the sector’s response. Policies focused on supporting businesses through grants, loans, and tax breaks were implemented. However, the effectiveness of these policies varied across countries and regions. For instance, some policies provided timely financial assistance, while others were perceived as slow or insufficient.
The long-term recovery of the tourism sector depends on rebuilding consumer confidence and restoring global travel networks.
CIMA Recommendations for Technology Sector Growth
The technology sector, while exhibiting resilience during the pandemic, could benefit from further support. CIMA recommendations focused on fostering innovation and attracting skilled talent. Examples include investments in digital infrastructure, promoting STEM education, and providing incentives for research and development. These measures would help maintain the sector’s growth trajectory and position it for future opportunities.
Learn about more about the process of finance departments evolving while bracing for coronavirus second wave in the field.
Challenges Faced by Small Businesses and CIMA Support
Small businesses, often the backbone of local economies, experienced substantial disruptions. They faced challenges in adapting to new operating models, managing supply chains, and maintaining cash flow. CIMA recommendations for small businesses emphasized access to finance, mentorship, and digital tools. These recommendations would help small businesses navigate the recovery period and rebuild their operations.
Recovery Prospects Comparison Table
| Sector | Challenges | CIMA Recommendations | Recovery Prospects (High/Medium/Low) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tourism | Travel restrictions, consumer hesitancy, and disruption to supply chains. | Targeted financial assistance, promoting safe travel, and rebuilding consumer confidence. | Medium |
| Technology | Maintaining growth momentum, attracting skilled talent, and fostering innovation. | Investment in digital infrastructure, promoting STEM education, and incentives for R&D. | High |
| Small Businesses | Adapting to new operating models, managing supply chains, and maintaining cash flow. | Access to finance, mentorship, and digital tools. | Medium |
International Comparisons

Post-pandemic economic recovery strategies are not a one-size-fits-all approach. Different countries have unique economic structures, social contexts, and political priorities, influencing their chosen paths. Understanding these diverse approaches is crucial for identifying potential best practices and adaptable solutions for the UK’s own recovery.
Recovery Strategies in Other Developed Nations
Numerous developed nations, including the US, Germany, and Japan, implemented diverse recovery strategies. The US, for instance, focused heavily on fiscal stimulus, while Germany prioritized supporting its export-oriented industries. Japan, with a longer history of economic challenges, often employed strategies that emphasized long-term structural reforms. Each approach reflected the specific economic vulnerabilities and strengths of each country.
Comparison of UK’s Approach with Other Nations
Comparing the UK’s approach with those of other developed nations reveals both similarities and marked differences. While all nations recognized the need for stimulus packages and support for businesses, the UK’s initial focus on furlough schemes differed significantly from the US’s emphasis on direct financial aid. Furthermore, the UK’s approach to addressing skills gaps and technological advancements varied compared to nations with more robust and targeted industry-specific support programs.
Successful International Strategies
Several nations exhibited success in specific aspects of their recovery strategies. For example, the German strategy of combining fiscal support with targeted investments in renewable energy technologies contributed to a relatively quick recovery and reduced reliance on fossil fuels. South Korea’s proactive use of digital technology in government services and business operations also facilitated a swift recovery. The key takeaway from these successes is the importance of adapting strategies to specific national contexts.
Policy Examples from Other Governments
Examining successful policies from other countries offers potential lessons for the UK. For instance, Canada’s approach to supporting small businesses through targeted loans and grants might provide insights for similar support mechanisms in the UK. Likewise, France’s emphasis on social safety nets and worker retraining programs could be relevant for the UK’s approach to long-term economic resilience.
Investigate the pros of accepting positive outlook financial services work in europe in your business strategies.
Lessons Learned from Other Countries’ Experiences
The experiences of other countries during previous economic crises, such as the 2008 financial crisis, provide valuable insights. These crises highlighted the importance of proactive fiscal and monetary policy responses, the necessity of supporting vulnerable sectors, and the long-term impact of inadequate social safety nets. Lessons from other countries’ experiences offer valuable insights for the UK.
Comparison Table of Recovery Strategies
| Nation | Key Focus | Primary Policy Tools | Success Factors | Weaknesses |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| United States | Fiscal stimulus, direct aid | Tax cuts, infrastructure spending | Rapid job creation | Inflationary pressures |
| Germany | Export-oriented industries, investments | Targeted subsidies, R&D funding | Strong export performance | Limited domestic consumption |
| Japan | Structural reforms, long-term investments | Public works, technological advancements | Sustainable growth | Slow initial recovery pace |
| UK | Employment support, business aid | Furlough schemes, grants | Preserved employment | Potential long-term economic impact |
Future Considerations
CIMA’s recommendations for the UK’s post-coronavirus recovery present a crucial roadmap, but their effectiveness hinges on anticipating future economic shifts. A robust plan must account for potential long-term impacts, the likelihood of further economic shocks, and the associated risks and opportunities. This section delves into the critical future considerations for the UK’s economic trajectory, guided by CIMA’s insights.The UK’s economic recovery, while promising, faces a complex landscape.
The recommendations are not a one-size-fits-all solution, but rather a framework. Understanding how these recommendations might fare in a shifting global market and a potential future economic downturn is essential for long-term success. The following analysis examines these future considerations.
Potential Long-Term Impacts of CIMA Recommendations
CIMA’s recommendations, if implemented effectively, can foster a more resilient and adaptable UK economy. This resilience is built on a foundation of strengthened financial institutions, a modernized infrastructure, and a skilled workforce. Positive long-term impacts include increased productivity, reduced economic inequality, and a more robust public sector. However, unforeseen circumstances or a lack of consistent implementation could diminish the anticipated benefits.
Importance of Considering Future Economic Shocks
The global economy is inherently volatile. The COVID-19 pandemic demonstrated the devastating impact of unexpected economic shocks. Failure to account for potential future shocks, such as geopolitical instability, supply chain disruptions, or unforeseen technological advancements, could render recovery strategies ineffective. Foresight and adaptability are crucial for mitigating the impact of future shocks.
Potential Risks and Opportunities Associated with the Recommendations
Implementing CIMA’s recommendations presents both risks and opportunities. Potential risks include resistance from certain sectors, bureaucratic hurdles in implementation, and a potential overreliance on specific strategies. Opportunities include a more diversified economy, enhanced international competitiveness, and a more resilient financial system. A thorough risk assessment and proactive mitigation strategies are essential.
Economic Outlook for the UK over the Next 5 Years
The UK’s economic outlook over the next five years is contingent on several factors, including global economic performance, government policy, and technological advancements. A positive outlook hinges on sustained investment in infrastructure, education, and innovation, alongside effective management of public debt. If these factors are addressed, the UK could achieve sustainable growth, potentially outpacing other developed economies. Conversely, if challenges remain unaddressed, the UK could face stagnation or even decline.
This prediction considers both positive and negative scenarios, and acknowledges the inherent uncertainty in forecasting long-term trends.
Preparing the UK for Future Economic Challenges
CIMA’s recommendations aim to equip the UK with the tools to navigate future economic challenges. Key strategies include fostering innovation, investing in education and skills development, and diversifying the economy. This will strengthen the UK’s ability to withstand future shocks and seize emerging opportunities. The focus on skills development and technological advancement is particularly crucial for long-term economic success.
Potential Challenges and Solutions Based on CIMA Recommendations
| Potential Challenges | Potential Solutions (Based on CIMA Recommendations) |
|---|---|
| Skills Gap in Specific Sectors | Investing in targeted training programs, upskilling initiatives, and collaborations between businesses and educational institutions. |
| Slow Adoption of Digital Technologies | Implementing incentives for businesses to adopt digital technologies, providing access to digital literacy training, and supporting the development of digital infrastructure. |
| Geopolitical Uncertainty and Trade Disputes | Diversifying trade relationships, fostering international partnerships, and strengthening the UK’s supply chains. |
| High Public Debt Levels | Implementing fiscally responsible policies, focusing on productivity improvements, and encouraging private sector investment. |
| Regional Disparities in Economic Development | Targeted investments in infrastructure, skills development, and innovation in underperforming regions. |
Closing Summary
Ultimately, CIMA’s recommendations for the UK government post-coronavirus recovery present a multifaceted approach to economic revitalization. The report considers sector-specific impacts, international comparisons, and future considerations, demonstrating a holistic view of the challenges and opportunities ahead. A crucial takeaway is the importance of adapting strategies to the unique needs of each sector, including tourism, technology, and small businesses.
The document concludes by outlining potential long-term impacts, future economic shocks, and the UK’s five-year economic outlook, highlighting how CIMA’s recommendations can position the UK for future economic resilience.