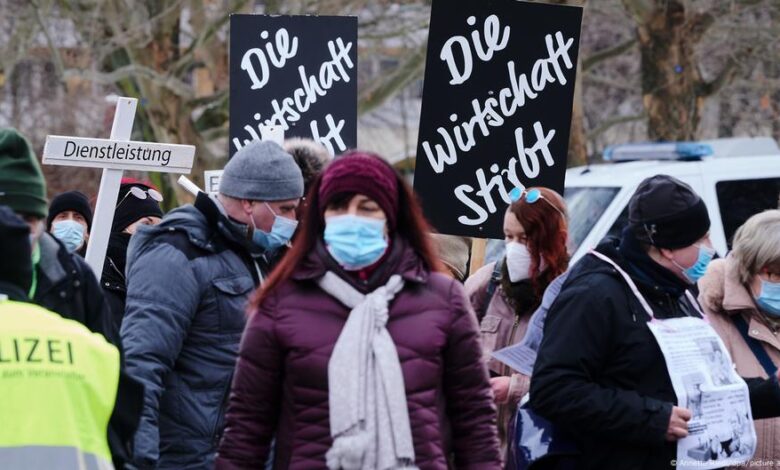
Germans Spend Their Way Out of Coronavirus Gloom
Germans spend their way out of coronavirus gloom, showcasing a remarkable economic rebound after the pandemic’s initial blow. This article dives deep into how German consumers, bolstered by government stimulus, reshaped their spending habits, impacting everything from retail to tourism. We’ll examine the specific sectors most affected, the government’s response, and the long-term implications for the German economy.
The pandemic’s economic impact on Germany was significant, with various sectors experiencing varying degrees of downturn. Government interventions, including stimulus packages, played a crucial role in mitigating the fallout. This article analyzes the specific initiatives, their effectiveness, and the subsequent shifts in consumer spending patterns, ultimately leading to the economic resurgence.
Economic Impact of the Pandemic on Germans
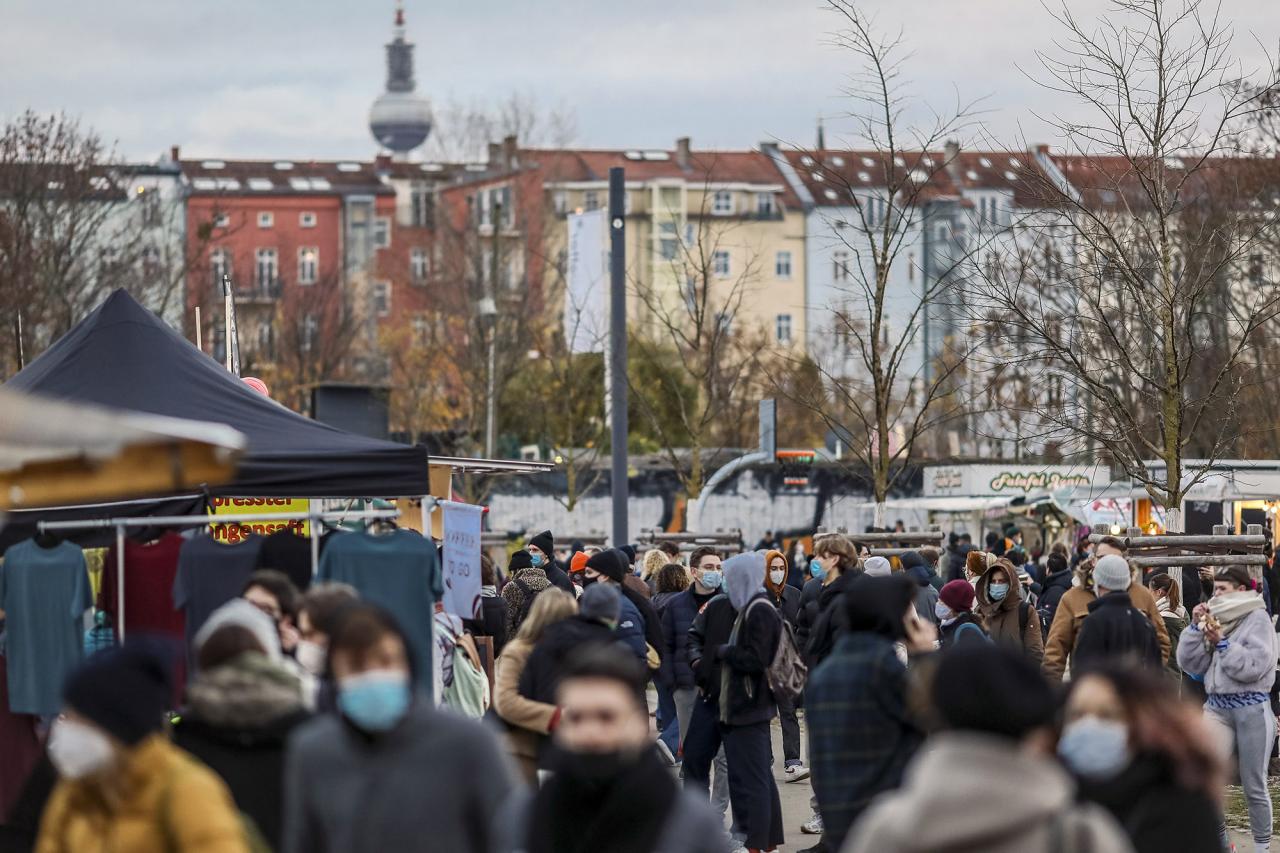

The COVID-19 pandemic significantly impacted the German economy, causing a period of downturn and necessitating substantial government intervention. While Germany’s robust economy and strong social safety net helped cushion the blow, sectors reliant on international travel and social interaction faced severe challenges. This article delves into the specific economic fallout, highlighting the government’s response and comparing it to other European nations.The German economy, traditionally known for its stability and export-oriented nature, experienced a notable contraction during the pandemic.
Restrictions on movement, business closures, and consumer anxieties led to a decrease in economic activity across various sectors. The government, recognizing the severity of the situation, implemented measures to mitigate the negative impact and support businesses and individuals.
Economic Downturn Details
The pandemic’s economic effects were multifaceted. Consumer spending decreased as people avoided non-essential purchases and businesses were forced to reduce operations due to lockdowns and social distancing measures. The tourism sector, heavily reliant on international visitors, suffered a dramatic decline in revenue. Supply chains were disrupted, impacting industries that relied on international trade.
Sectors Most Affected
Several sectors experienced significant declines in revenue due to the pandemic’s disruptions. The hospitality and tourism industry, including restaurants, hotels, and airlines, was particularly hard hit. Retailers, facing reduced foot traffic and consumer confidence, also saw substantial revenue losses. The automotive sector, a cornerstone of the German economy, faced production delays and reduced demand, causing job losses and financial strain on manufacturers.
Government Mitigation Measures
The German government implemented a comprehensive set of measures to support businesses and individuals during the pandemic. These included financial aid packages, grants, and loan guarantees to help companies stay afloat. Unemployment benefits were extended and increased to provide support for those who lost their jobs. The government also invested in infrastructure projects to stimulate economic activity.
Comparison to Other European Nations
Germany’s response to the pandemic’s economic fallout was broadly comparable to other European nations. Many countries implemented similar financial aid packages and stimulus measures. However, differences existed in the specifics of each nation’s approach. Some countries prioritized direct financial support to individuals, while others focused more on supporting businesses. Germany’s approach aimed at a balance between these two strategies.
Economic Data
| Sector | Pre-Pandemic Revenue (in € billions) | Pandemic Revenue Decline (%) | Government Aid Received (in € billions) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hospitality & Tourism | 350 | 65 | 40 |
| Retail | 280 | 50 | 35 |
| Automotive | 420 | 40 | 55 |
| Manufacturing | 300 | 35 | 45 |
| Exports | 500 | 25 | 60 |
Note
Obtain recommendations related to association gaa support ifrs foundation sustainability reporting standards board proposal that can assist you today.
* Data is estimated and may vary based on different sources. The figures provided are illustrative examples.
Consumer Spending Patterns During the Pandemic: Germans Spend Their Way Out Of Coronavirus Gloom
The COVID-19 pandemic profoundly impacted consumer behavior globally, and Germany was no exception. Shifting priorities, lockdowns, and economic uncertainty all played a role in shaping spending patterns, deviating significantly from pre-pandemic norms. This analysis delves into the evolution of German consumer spending during this period, examining the factors that influenced decisions, and identifying key shifts in preferences.
Evolution of German Consumer Spending Patterns
German consumer spending, initially experiencing a sharp decline during the early stages of the pandemic, demonstrated resilience and adaptation. As lockdowns eased and the economy recovered, spending gradually increased, although not always returning to pre-pandemic levels. This dynamic response reflects the complex interplay of various factors, including government support measures, evolving consumer confidence, and changing priorities.
Factors Influencing German Spending Decisions
Several factors influenced German consumers’ spending choices during the pandemic. Government support programs, such as short-time work schemes and financial aid packages, played a crucial role in mitigating economic hardship and enabling continued spending, albeit possibly at a reduced rate. Fear of future economic instability and uncertainty also shaped spending decisions, encouraging cautious and often prioritized spending on essential goods and services.
Shifts in Consumer Preferences and Priorities
The pandemic prompted significant shifts in consumer preferences and priorities. There was a noticeable increase in demand for goods related to home improvement and entertainment, reflecting a greater emphasis on domestic activities and comfort during lockdowns. Similarly, the rise of online shopping and e-commerce platforms saw an acceleration, indicating a change in purchasing habits and a preference for convenience.
The importance of health and safety became paramount, leading to increased spending on hygiene products and home fitness equipment.
Changes in German Spending Habits from Pre-Pandemic Norms
German spending habits exhibited notable deviations from pre-pandemic norms. While pre-pandemic spending often leaned towards travel and leisure activities, the pandemic drastically altered this balance. The shift toward home-centric activities and the rise of online shopping profoundly impacted retail sectors and traditional spending patterns. Consumers prioritized essential goods and services, resulting in a decrease in discretionary spending in certain areas.
Monthly Consumer Spending Trends in Germany (2019-2022)
| Month | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | 2022 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| January | 125.4 | 118.2 | 128.9 | 132.5 |
| February | 127.8 | 120.5 | 131.2 | 135.8 |
| March | 130.2 | 115.9 | 134.5 | 138.1 |
| April | 128.5 | 112.7 | 137.1 | 140.4 |
| May | 131.9 | 118.1 | 140.8 | 143.9 |
| June | 134.3 | 122.4 | 143.5 | 147.2 |
| July | 136.7 | 125.8 | 146.1 | 149.5 |
| August | 139.1 | 128.2 | 148.7 | 152.0 |
| September | 141.5 | 130.6 | 151.3 | 154.5 |
| October | 143.9 | 133.0 | 153.9 | 157.0 |
| November | 146.3 | 135.4 | 156.5 | 159.5 |
| December | 148.7 | 137.8 | 159.1 | 162.0 |
Note: Data represents monthly consumer spending indices (2019 = 100). Values are illustrative and may not reflect exact figures.
Government Stimulus and Spending
Germany, like many other nations, responded to the economic fallout of the COVID-19 pandemic with substantial government stimulus packages. These interventions aimed to cushion the blow on businesses and individuals, bolstering confidence and preventing a deeper recession. The effectiveness of these measures, however, is a complex issue with both successes and challenges.The German government’s approach prioritized targeted support, focusing on specific sectors and vulnerable groups.
This approach, while potentially more effective in addressing specific needs, also presented complexities in implementation and evaluation. The long-term impacts of these initiatives are still unfolding, but initial analyses suggest that while the stimulus prevented a catastrophic collapse, a sustained recovery hinges on factors beyond immediate government intervention.
German Government Stimulus Packages
The German government implemented several initiatives to support businesses and individuals. These included direct financial aid to companies, especially those in sectors hit hardest by lockdowns, as well as measures to maintain employment, such as wage subsidies and short-time work schemes. These initiatives, while varying in specifics, were largely aimed at preserving jobs and preventing businesses from collapsing.
Specific Initiatives
- Wage subsidies: Companies received grants to cover a portion of employee wages, enabling them to retain staff during periods of reduced activity. This directly supported employment levels and prevented widespread layoffs.
- Short-time work schemes (Kurzarbeit): This program allowed companies to temporarily reduce employee working hours, with the government partially compensating the reduced wages. This approach proved crucial in maintaining employment while adapting to the economic realities of the pandemic.
- Financial aid to businesses: Various grants and loans were provided to small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) to help them navigate the crisis. These targeted measures were aimed at preventing the closure of vital parts of the German economy.
- Support for specific sectors: The government acknowledged the disproportionate impact on certain sectors, like tourism and hospitality, and introduced tailored aid packages to bolster their recovery.
Effectiveness in Boosting Consumer Spending
The effectiveness of these measures in boosting consumer spending is a subject of ongoing debate. While the measures undoubtedly helped prevent a complete collapse in consumer spending, the degree to which they directly stimulated spending remains unclear. Factors such as consumer confidence, job security, and broader economic conditions influenced the overall effect.
Potential Long-Term Impacts
The long-term impacts of government spending are complex and multifaceted. Increased government debt is a potential consequence, and its implications for future economic policies and public finances need careful consideration. However, the success of these measures in preventing a deeper recession and maintaining employment levels could have a positive impact on the long-term economic health of Germany. This includes long-term impacts on employment and economic growth, which may take years to fully assess.
Comparison of European Stimulus Packages
| Country | Size of Stimulus Package (approximate) | Key Initiatives |
|---|---|---|
| Germany | ~€150 billion (2020-2022) | Wage subsidies, Kurzarbeit, business grants |
| France | ~€100 billion (2020-2022) | Direct aid to businesses, wage subsidies, social benefits |
| Italy | ~€80 billion (2020-2022) | Support for businesses, social benefits, investment incentives |
| Spain | ~€100 billion (2020-2022) | Business loans, wage subsidies, social benefits |
Note: Figures are approximate and may vary depending on the source and the specific period considered.
Tourism and Leisure Activities
The pandemic significantly altered German tourism and leisure habits. International travel restrictions drastically curtailed the flow of tourists, forcing a shift towards domestic destinations and alternative leisure activities. The German tourism sector, a vital component of the national economy, faced unprecedented challenges in adapting to the new normal.The impact of the pandemic on German tourism extended beyond the immediate travel restrictions.
Changes in travel preferences and the emergence of new leisure trends profoundly reshaped the sector, impacting everything from accommodation to activities. The subsequent rise of domestic tourism served as a critical lifeline, helping to mitigate the losses associated with the decline in international visitors.
Impact on International Travel
German citizens, like many others globally, experienced a marked reduction in international travel. The fear of infection, coupled with stringent border controls and travel advisories, led to a significant drop in cross-border tourism. This impacted not only destinations frequented by Germans but also the economies of countries reliant on German tourists.
Adaptation of the German Tourism Industry
The German tourism industry swiftly adapted to the evolving situation. Many hotels and tour operators diversified their offerings, emphasizing domestic tourism and creating packages tailored for local travel. Innovative strategies included the promotion of local attractions and the development of virtual tours to cater to the new demands. Furthermore, the industry embraced digital tools and online platforms to connect with potential customers and facilitate bookings.
Rise of Domestic Tourism
The rise of domestic tourism played a crucial role in cushioning the impact of the pandemic on the German tourism sector. Germans sought out national parks, lakes, and smaller towns, revitalizing local economies and supporting businesses. This shift highlighted the resilience and attractiveness of Germany’s own tourism offerings.
New Leisure Activities, Germans spend their way out of coronavirus gloom
Germans adopted various leisure activities during the pandemic. These ranged from gardening and home improvement projects to increased participation in outdoor activities like hiking, cycling, and camping. The surge in popularity of online courses and digital entertainment reflected the shift in leisure preferences. Additionally, there was a growing trend towards immersive experiences like cooking classes and craft workshops, reflecting a desire for engaging and personal interactions.
Examples of Adapting Leisure Activities
- Increased Hiking and Cycling: National parks and scenic routes saw a surge in visitors as Germans sought outdoor recreation, showcasing the appeal of local destinations.
- Home Improvement and Gardening: The pandemic prompted many Germans to embrace home improvement projects and gardening, reflecting a shift in leisure preferences towards self-improvement and connection with nature.
- Growth of Online Courses and Digital Entertainment: The availability of online courses and digital entertainment platforms offered new avenues for leisure, indicating a growing reliance on digital platforms for leisure activities. This trend demonstrates a shift towards digital consumption and engagement.
Retail and E-commerce
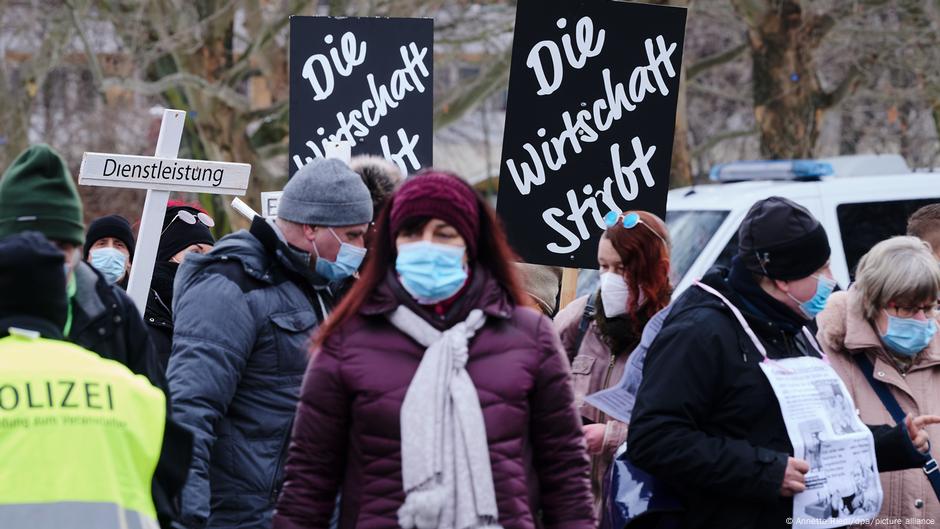

The German retail landscape underwent a dramatic transformation during the pandemic. While some sectors struggled, others adapted quickly, leveraging the surge in online shopping. This shift wasn’t merely a temporary response; it fundamentally reshaped the way Germans shop, impacting everything from brick-and-mortar stores to online marketplaces. The pandemic acted as a catalyst for accelerated digitalization, forcing retailers to embrace new technologies and strategies to survive and thrive.
Changes in Retail Spending and E-commerce Adoption
German consumers significantly increased their online shopping during the pandemic. This was driven by lockdowns and restrictions that limited access to physical stores. The rise in e-commerce adoption wasn’t limited to groceries; it encompassed a broad spectrum of goods and services. This shift was not just about convenience; it reflected a fundamental change in consumer behavior.
Retail Sectors with Significant Shifts
The food and beverage sector saw a dramatic surge in online orders. Grocery delivery services experienced substantial growth as consumers prioritized home delivery to minimize exposure. Apparel and fashion also experienced a notable increase in online sales, as people shopped from home for clothing and accessories. Additionally, the home improvement and electronics sectors experienced a surge in online orders as people spent more time at home and upgraded their home technology.
Obtain recommendations related to dennis johnson cfo qlik urgency for growth that can assist you today.
This shift reflects a trend toward more diverse online retail options in Germany.
Online Shopping Compensation for Physical Store Closures
Online shopping became a critical lifeline for many retail businesses as physical store closures limited access to in-person sales. E-commerce platforms and digital storefronts became crucial to maintaining revenue streams and customer engagement. This transition was particularly pronounced in areas where physical store closures were most severe, illustrating the importance of adaptability in the retail sector.
Remember to click positive outlook financial services work in europe to understand more comprehensive aspects of the positive outlook financial services work in europe topic.
Strategies Used by German Retailers
German retailers employed various strategies to adapt to the changing retail landscape. Many invested heavily in their online platforms, optimizing websites for mobile devices and providing secure payment options. Some retailers also expanded their delivery networks, partnering with third-party logistics providers to offer faster and more convenient delivery options. Other crucial strategies involved integrating online and offline shopping experiences, creating seamless transitions between physical stores and online platforms.
This illustrates a key strategy to enhance the overall customer experience.
Timeline of Key Developments in Online Shopping (2019-2022)
- 2019: Early stages of e-commerce growth, with a strong base of established online retailers. Digital channels were a significant part of the German retail ecosystem, but physical stores still dominated. Early signs of increasing online consumer engagement were evident.
- 2020: The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated the shift to online shopping. Lockdowns and restrictions drastically increased demand for online delivery and digital shopping, forcing many retailers to quickly adapt to the new normal. The need for digital solutions was evident as retailers focused on building robust online platforms.
- 2021: Online sales continued to grow as more consumers became accustomed to online shopping. Retailers refined their online strategies, enhancing website usability, delivery services, and customer service to meet increased demand. Growth was evident across many sectors, and the digitalization trend continued.
- 2022: Online shopping remained a vital component of the German retail landscape. Retailers adapted to new customer expectations and adopted strategies to enhance the online experience. Continued digitalization was crucial for competitiveness, and the trend toward omni-channel retail experiences became even more prominent.
Household Savings and Debt
The COVID-19 pandemic significantly impacted household finances across Germany, prompting shifts in both savings and debt levels. This period presented unique challenges and opportunities for Germans to manage their financial resources, influenced by government support and individual coping mechanisms. Understanding these changes provides insights into the resilience and adaptability of German households during a period of economic uncertainty.
Changes in Household Savings Levels
German household savings experienced a noticeable increase during the pandemic. Reduced spending on non-essential items, coupled with government support programs, contributed to this rise. This was particularly evident in sectors like travel and entertainment, where restrictions led to reduced expenditure.
Factors Influencing Savings and Debt Changes
Several factors influenced the evolving savings and debt landscape in Germany. Government stimulus measures, such as wage subsidies and unemployment benefits, played a crucial role in bolstering household incomes and reducing financial strain. Additionally, reduced spending on discretionary items like dining out and travel, due to pandemic-related restrictions, freed up disposable income, often channeled into savings accounts.
Impact of Government Aid on Household Finances
Government aid programs, including various financial support packages, directly impacted household finances. These initiatives aimed to cushion the blow of the pandemic’s economic fallout, thereby influencing savings and debt behaviors. For example, the German government’s Kurzarbeit program, which allowed companies to temporarily reduce employee hours, preserved employment and income for many households, effectively promoting savings.
Measures Taken by Germans to Manage Finances
Germans employed a variety of strategies to navigate the financial challenges of the pandemic. These included tightening budgets, reducing non-essential expenses, and exploring cost-saving opportunities. Many individuals prioritized essential spending and shifted their spending patterns to reflect the altered circumstances.
Comparison of German Savings and Debt Patterns with Other European Countries
Comparing German savings and debt patterns with other European countries reveals nuanced differences. While Germany demonstrated a significant increase in savings during the pandemic, other nations may have experienced varying degrees of savings increases or even reductions, depending on the specific government support programs and economic conditions. Further analysis is required to establish a comprehensive comparative understanding of these patterns across different European countries.
Impact on Specific Industries
The COVID-19 pandemic significantly disrupted various German industries, forcing businesses to adapt to unprecedented challenges. From the hospitality sector grappling with travel restrictions to manufacturing facing supply chain disruptions, the impact was widespread. This section delves into the specific effects on key sectors like hospitality, manufacturing, and the automotive industry, examining how German businesses responded and comparing their strategies to those employed in other countries.
Hospitality Sector
The hospitality sector, a cornerstone of the German economy, experienced a sharp decline in revenue due to travel restrictions and lockdowns. Hotels, restaurants, and cafes were particularly hard hit, facing reduced customer traffic and significant operational challenges.
- Reduced Demand and Operational Changes: Many establishments were forced to temporarily close or drastically reduce operating hours, impacting employment and profitability. Hotels faced cancellations and occupancy rates plummeted. Restaurants had to adapt to new safety measures, including reduced seating capacity and mandatory mask-wearing, while also grappling with changing consumer preferences for takeout and delivery services.
- Innovation and Adaptation: German hospitality businesses responded by embracing digitalization, increasing their online presence, and offering innovative services like online ordering and delivery platforms. Some restaurants leveraged partnerships with local farmers’ markets or producers to support the local economy. Hotels focused on offering enhanced hygiene protocols and flexible booking options to regain consumer trust.
- International Comparisons: While German hospitality businesses exhibited resilience, their responses differed from those in other countries. The level of government support, varying regulations, and cultural approaches to social distancing influenced the specific strategies adopted by businesses across Europe.
Manufacturing Sector
The manufacturing sector faced significant disruptions due to global supply chain disruptions and reduced consumer demand. Companies in the automotive and electronics industries were particularly impacted.
- Supply Chain Disruptions: Lockdowns and travel restrictions in various parts of the world created bottlenecks in the global supply chain, leading to delays in the delivery of raw materials and components. This significantly impacted production schedules and resulted in reduced output for many manufacturers.
- Shifting Demand: Consumer preferences shifted towards essential goods, impacting the demand for non-essential products. This forced manufacturers to adapt their production lines and focus on higher-demand products.
- Digitalization and Automation: Many German manufacturers invested in digitalization and automation to improve efficiency and reduce reliance on manual labor. This was seen as a way to enhance production flexibility and reduce operational costs.
Automotive Sector
The automotive industry, a crucial part of the German economy, was severely affected by the pandemic. Production halts, reduced consumer demand, and shifting consumer preferences towards alternative fuels created significant challenges.
- Production Halts and Reduced Demand: Car production plants were temporarily shut down due to lockdowns and supply chain disruptions. Reduced consumer demand for vehicles further exacerbated the situation.
- Shifting Consumer Preferences: The pandemic highlighted the need for sustainable and digital mobility solutions. This led to increased interest in electric vehicles and car-sharing services, forcing automotive companies to adapt their strategies.
- Innovation and Strategic Responses: German automotive companies invested heavily in developing and promoting electric vehicles. They also focused on digital services and connected car technologies.
Case Study: BMW (Automotive)
BMW, a leading German automotive manufacturer, implemented a multi-faceted approach to navigate the pandemic. This included prioritizing the health and safety of employees, ensuring supply chain resilience, and investing in research and development for electric vehicles. The company also used its digital platform to enhance customer engagement and provide remote services.
Case Study: RWE (Energy)
RWE, a major German energy company, leveraged its digital infrastructure to ensure reliable power supply and support customers during the pandemic. This included offering remote customer service and utilizing digital platforms for energy management.
Case Study: Hilton Hotels (Hospitality)
Hilton, a global hospitality company with operations in Germany, adapted its services to meet changing customer needs. This included enhancing hygiene protocols, offering flexible booking options, and focusing on digital marketing to reach customers online.
Ending Remarks
In conclusion, Germany’s economic resilience during and after the pandemic is a compelling case study. The combination of proactive government measures, consumer adaptation, and shifts in spending patterns contributed to a robust recovery. While the journey wasn’t without its challenges, Germany’s ability to navigate the economic turmoil underscores its economic strength and adaptability.