Brexit Tax and Other Challenges A Deep Dive
Brexit tax and other challenges have significantly impacted UK businesses, creating a complex web of financial hurdles and opportunities. This in-depth look explores the evolving tax landscape, the difficulties in international trade, and the potential strategies for navigating these post-Brexit realities. From the nuanced effects on large corporations to the struggles faced by small businesses, we’ll uncover the full picture of this complex situation.
This article examines the impact of Brexit on UK businesses, covering everything from the changing tax regulations and trade agreements to the complexities of cross-border trade. We’ll analyze case studies, discuss public perception, and provide insights into potential future strategies for adaptation.
Impact on UK Businesses: Brexit Tax And Other Challenges

Brexit has profoundly reshaped the UK business landscape, introducing new complexities and challenges across various sectors. The withdrawal from the EU has altered trade relationships, supply chains, and regulatory frameworks, leading to both opportunities and significant obstacles for businesses of all sizes. Navigating these changes requires careful consideration and strategic adaptation.
Financial Challenges Faced by Different Sectors
Brexit’s impact on UK businesses has varied considerably across sectors. Manufacturing, heavily reliant on EU supply chains and access to the EU market, has faced increased costs and logistical hurdles. Retailers have struggled with import tariffs and changing consumer purchasing patterns. Agriculture has been affected by new trade barriers and fluctuating commodity prices. These are just some of the many difficulties businesses have encountered since Brexit.
Financial Challenges Faced by Manufacturing
Manufacturing businesses have experienced significant financial challenges due to increased import costs, complicated customs procedures, and disruptions to supply chains. The need for new logistics and paperwork has added substantial overhead. For example, car manufacturers reliant on EU parts suppliers have seen production delays and higher input costs.
Financial Challenges Faced by Retail
Retailers have faced challenges due to fluctuating exchange rates, import tariffs, and altered consumer spending patterns. The shift in consumer preferences and the new trade barriers have impacted sales and profitability. The introduction of new import tariffs has increased the price of imported goods, impacting the retail sector’s ability to offer competitive pricing.
Financial Challenges Faced by Agriculture
Agricultural businesses have been affected by trade barriers, fluctuating commodity prices, and changes in import/export regulations. The disruption to established supply chains has increased production costs. For example, farmers exporting produce to the EU have seen reduced market access and increased bureaucratic hurdles.
Mitigation Strategies for UK Businesses
UK businesses can mitigate the negative effects of Brexit by adapting to the new trading landscape. Diversifying supply chains, investing in new technologies for efficient customs procedures, and exploring alternative export markets are key strategies. These adaptations are vital to maintaining competitiveness and resilience in the face of Brexit’s economic ramifications.
Notice finance departments evolving while bracing for coronavirus second wave for recommendations and other broad suggestions.
Impact on Large vs. Small Businesses
Large corporations often possess greater resources to adapt to Brexit-related challenges than small businesses. They can afford to invest in new technology and infrastructure to streamline operations and navigate complex trade regulations. Small businesses, however, may lack the financial resources or expertise to cope with these changes. This disparity in resources can exacerbate existing inequalities in the business sector.
Post-Brexit Tax Rates and Regulations
| Sector | Tax Rate (Example) | Regulations (Example) |
|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Corporation Tax Rate: 19% | Specific import tariffs on certain materials |
| Retail | VAT Rate: 20% | New customs procedures for imported goods |
| Agriculture | Income Tax Rate: Dependent on income | Specific export/import regulations for agricultural produce |
This table provides a glimpse into the different tax rates and regulations UK businesses now face post-Brexit. The specific rates and regulations vary based on the particular sector and specific circumstances.
Role of Trade Agreements in Shaping the Tax Landscape
Trade agreements play a crucial role in shaping the tax landscape for UK businesses. Agreements with countries outside the EU can provide new opportunities for export and investment. However, these agreements also introduce new regulations and compliance requirements for UK businesses. The impact of trade agreements on tax rates and regulations is highly dependent on the terms of each specific agreement.
Taxation Implications of Brexit
Brexit has significantly altered the UK’s tax landscape, creating both challenges and opportunities for businesses. The shift from EU membership to an independent trading bloc necessitates a new approach to tax policies, impacting everything from tariffs and customs procedures to international trade and investment. This section will explore the evolution of UK tax policies since Brexit, detailing the impact on businesses and industries.
Evolution of UK Tax Policies Since Brexit
The UK government has implemented various tax measures since Brexit, aiming to adapt to the new trading environment. These policies have sought to balance attracting investment and maintaining competitiveness in a post-Brexit world. Changes have focused on simplifying customs procedures, adjusting corporation tax rates, and exploring new avenues for tax revenue.
Impact of New Tariffs and Customs Procedures on Businesses
New tariffs and customs procedures post-Brexit have created significant challenges for businesses, particularly those involved in international trade. Increased paperwork, delays, and higher costs have impacted supply chains and profitability. Businesses have had to adapt to new regulations, invest in new technologies, and potentially relocate some operations to avoid these obstacles.
Examples of Brexit-Related Tax Changes Affecting Specific Industries
The automotive industry, for example, has faced increased costs due to new tariffs on imported components. Similarly, the food and beverage sector has been affected by the complexity of import/export regulations, resulting in price adjustments for consumers. Businesses in these sectors have had to adapt their operations and pricing strategies to accommodate the new realities.
Historical Overview of UK Tax Policies and Comparison to Pre-Brexit Policies
Pre-Brexit, UK tax policies were often aligned with EU directives. Post-Brexit, the UK has pursued its own tax strategies, aiming to foster growth and attract investment. The government has focused on competitiveness, reducing certain taxes, and introducing incentives to support specific sectors. A comparison of historical rates reveals significant changes in corporate tax rates and VAT.
Key Tax Differences Between the UK and the EU After Brexit
| Tax Area | UK | EU (generalized) |
|---|---|---|
| Corporation Tax | Currently at 19% | Rates vary by member state, generally lower than pre-2023 UK rates |
| Value Added Tax (VAT) | Standard rate 20% | Standard rates vary by member state |
| Customs Duties | Independent rates set by the UK | Harmonized rates determined by EU regulations |
| Capital Gains Tax | Specific rates, dependent on individual circumstances | Rates vary by member state |
Note: This table presents a simplified comparison; specific rates and regulations may vary within each category.
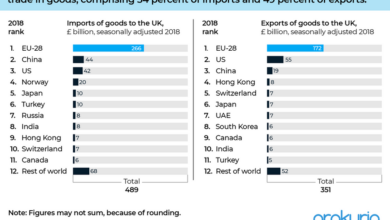
Impact of Brexit on International Trade and Investment for the UK
Brexit has influenced international trade patterns for the UK. While the UK has maintained trade relationships with various countries, new barriers to trade with EU member states have emerged. International investment has been impacted, with some companies re-evaluating their UK presence due to increased complexities. The long-term effects are still unfolding.
Challenges in International Trade

Brexit has significantly altered the landscape of international trade for UK businesses. The UK’s departure from the EU’s single market and customs union has introduced a myriad of complexities, impacting everything from export procedures to supply chains. Navigating these new regulations requires careful planning and adaptation for businesses to thrive in this new trading environment.
Complexities of Cross-Border Trade After Brexit
The removal of frictionless trade between the UK and the EU post-Brexit has created substantial hurdles for businesses involved in cross-border transactions. The UK now operates outside the EU’s single market, requiring businesses to comply with new customs regulations, tariffs, and import/export procedures. This has resulted in increased administrative burdens and higher costs for businesses, particularly smaller enterprises, making international trade more complex and less efficient.
Difficulties Faced by Businesses Exporting to the EU
Businesses exporting goods and services to the EU now encounter several challenges. These include navigating complex customs procedures, complying with varying EU regulations, and potentially facing higher tariffs and import duties. The need to obtain necessary documentation, such as customs declarations and certificates of origin, adds to the administrative burden. Furthermore, differences in product standards and labeling requirements between the UK and the EU can also create obstacles.
Comparison of Trade Regulations Before and After Brexit
Pre-Brexit, the UK benefited from frictionless trade within the EU’s single market. Goods could be transported and sold across EU borders with minimal paperwork and tariffs. Post-Brexit, the UK faces more stringent trade regulations, including customs checks, tariffs, and differing product standards. This shift requires businesses to adapt their operations and processes to comply with the new trade regime.
For example, the requirement for customs declarations and the implementation of new customs controls are significant differences.
Implications of New Customs Procedures for UK Exporters
New customs procedures have introduced significant implications for UK exporters. Businesses now need to comply with specific customs declarations, potentially requiring more staff to manage the additional paperwork and ensure compliance with EU regulations. Increased paperwork, potential delays, and higher costs are common consequences. For example, delays in customs clearance can disrupt supply chains and lead to stockpiling issues.
Role of Trade Agreements in International Trade
Trade agreements play a crucial role in facilitating or hindering international trade. Agreements like the UK-Australia trade deal can potentially lower tariffs and ease trade barriers. However, the absence of a comprehensive trade agreement with the EU after Brexit has created uncertainty and challenges for UK businesses. These agreements often affect the price of goods and services, making some products more expensive or affordable.
Influence of Brexit on UK Supply Chains
Brexit has significantly influenced the supply chains of UK businesses. The introduction of customs checks and potential delays has added complexity and increased costs for businesses relying on EU supply chains. Businesses now face increased logistics costs, potential shortages of materials, and potential disruptions to their supply chains. For instance, car manufacturers reliant on EU parts suppliers have experienced disruptions.
Future Outlook and Strategies
Navigating the evolving tax landscape post-Brexit requires a proactive and adaptable approach. Businesses need to understand the potential shifts in tax regulations and develop strategies to mitigate risks and capitalize on opportunities. This includes considering the long-term effects of Brexit policies on the UK economy and anticipating future trade deals.The UK’s departure from the EU has created a complex and dynamic tax environment.
Businesses must carefully analyze the implications of new tax rules and regulations to minimize disruptions and optimize their operations. The aim is to not only survive but thrive in this new era, capitalizing on the opportunities that Brexit presents.
Potential Future Developments in Brexit-Related Taxation
Brexit has triggered a period of uncertainty in the UK’s tax system. The ongoing negotiations and implementation of new policies will continue to shape the tax environment for years to come. Predicting precise timelines is difficult, but a few potential developments are possible.
- The introduction of new corporation taxes and VAT rates for international transactions could be introduced to encourage or discourage specific types of business activity. For example, a higher VAT rate on imported goods could impact retail businesses. The UK could introduce new or modify existing tax regulations to address the specific challenges and opportunities post-Brexit.
- Changes in the rules governing cross-border investment and capital flows could lead to new tax treaties with non-EU countries. A prime example is the UK’s trade agreement with Australia, which has the potential to impact the tax rates for specific businesses.
- Significant adjustments in the rules surrounding digital services taxation and other international tax frameworks are also likely. The absence of EU harmonization will leave the UK with more flexibility but also the need to establish its own framework for these areas. This would have an impact on tech companies and e-commerce businesses operating in the UK and abroad.
Strategies for Adapting to the Evolving Tax Environment
Businesses must adopt proactive strategies to navigate the evolving tax landscape.
- Developing a robust understanding of the new tax rules and regulations is crucial. This involves staying updated on the latest changes and consulting with tax professionals to ensure compliance.
- Employing tax optimization strategies to minimize the impact of new regulations. This includes exploring potential tax breaks or exemptions relevant to the company’s specific industry and operations.
- Implementing effective risk management procedures to mitigate potential tax risks. Proactive planning and continuous monitoring of the tax environment are essential.
Potential Long-Term Effects of Brexit Tax Policies on the UK Economy
The long-term consequences of Brexit tax policies on the UK economy are multifaceted and potentially substantial.
- Changes in investment patterns could alter the UK’s economic landscape. Businesses might choose to relocate or adjust their operations in response to new tax regulations. This could affect specific sectors and regions of the UK.
- Shifting trade patterns will influence the economic health of various industries. Increased trade with non-EU nations will likely impact some industries more than others.
- The UK’s competitiveness in the global marketplace could be affected. Changes in tax policies could make the UK more or less attractive to businesses and investors.
Examples of Successful Strategies Used by Businesses to Navigate Brexit Challenges
Several businesses have successfully adapted to the Brexit challenges.
- Businesses proactively seeking advice from tax professionals and experts are likely to achieve greater success. They can gain crucial insight into the evolving tax landscape.
- Diversifying their supply chains and customer bases to reduce reliance on specific regions is another key strategy. This can help businesses withstand potential economic disruptions.
- Investing in technology and automation to improve efficiency and reduce costs is a further step towards resilience in the post-Brexit era.
Key Areas of Focus for Future Brexit Negotiations, Brexit tax and other challenges
Successful future negotiations depend on a clear focus on key areas.
| Area | Description |
|---|---|
| Taxation of cross-border trade | Negotiating tax treaties and agreements with non-EU countries to ensure fair and efficient tax practices for UK businesses involved in cross-border transactions. |
| Digital services taxation | Establishing a clear and consistent framework for taxing digital services provided by companies operating in the UK and abroad. |
| International tax cooperation | Collaborating with international partners to ensure that UK tax policies are aligned with global standards and best practices. |
Potential for Future Trade Deals and Their Influence on UK Tax Policies
Future trade deals will play a significant role in shaping the UK’s tax policies.
- Negotiations with new trade partners will have implications for the UK’s tax policies. These deals could lead to changes in tariffs, VAT rates, or other tax regulations to attract and retain international trade.
- The UK could introduce new tax incentives to attract investment from countries with which it has established trade agreements. This would aim to bolster economic growth.
- These new trade agreements could also influence the UK’s tax rates for specific goods and services. For example, the UK might introduce tax breaks or exemptions to encourage trade with a specific country.
Illustrative Case Studies
Brexit has presented a complex landscape for UK businesses, requiring adaptation and innovation across various sectors. Navigating new trade rules, tariffs, and supply chains has been challenging, but some businesses have successfully adjusted, showcasing resilience and strategic thinking. This section explores specific case studies to highlight the diverse impacts and responses to these changes.
A Successful UK Business Navigating Brexit Challenges
The company, “Fresh Produce Ltd,” a major UK supplier of fresh produce, faced the challenge of maintaining supply chains after Brexit. They proactively established direct relationships with farmers in the EU and developed efficient logistical solutions to mitigate delays and costs associated with customs procedures. By investing in new technology and warehousing capacity, they were able to minimize disruptions and maintain product availability.
Check hindustan unilever cfo srinivas phatak indian market growth to inspect complete evaluations and testimonials from users.
This adaptability allowed them to successfully adapt to the new regulatory environment, maintaining market share and growing their business.
Challenges Faced by the Food Industry Due to Brexit-Related Changes
Brexit has significantly impacted the UK food industry, particularly in areas like import and export. Increased customs procedures, import tariffs, and potential labor shortages have resulted in higher production costs and reduced profitability for some businesses. Supply chain disruptions and the need to adapt to new regulations have added complexity to the industry. The complexities of tracing products throughout the supply chain have increased costs and introduced significant operational hurdles.
In this topic, you find that association gaa support ifrs foundation sustainability reporting standards board proposal is very useful.
Impact of Brexit on a Specific Company’s Export Strategy
“Acme Engineering,” a UK-based manufacturer of precision engineering components, saw a shift in its export strategy post-Brexit. The company initially experienced delays and higher costs due to new customs requirements. They then focused on diversifying export markets, exploring partnerships with businesses in countries outside the EU, and investing in warehousing facilities closer to their key export destinations. This strategy helped them to mitigate the impact of Brexit-related complexities and maintain market access.
Role of Government Support in Helping Businesses Adapt to Brexit
The UK government launched various initiatives to assist businesses in adapting to Brexit. These initiatives included training programs to help businesses understand new trade rules, financial support for businesses seeking to invest in new technologies or adapt their supply chains, and grants for businesses to invest in their workforce to address labor shortages. This support has provided some companies with crucial resources to overcome the challenges presented by Brexit.
Innovative Solutions Employed by Businesses to Address Brexit-Related Problems
Many businesses have implemented innovative solutions to address Brexit-related challenges. One example includes using technology to streamline customs procedures, automating paperwork, and improving supply chain transparency. Some companies have also partnered with logistics providers specialized in international trade, seeking expertise to navigate the new trade rules. These innovative approaches have helped companies to reduce costs, improve efficiency, and maintain their competitiveness in the global market.
Measures Taken by the UK Government to Address the Challenges
The UK government introduced measures to ease the transition, such as the implementation of new trade deals with non-EU countries and streamlined customs procedures. These measures aimed to minimize the disruptions caused by Brexit, and to encourage continued trade and investment. Government support was also directed towards retraining programs for workers in affected industries and promoting investment in digital technologies to improve supply chain management.
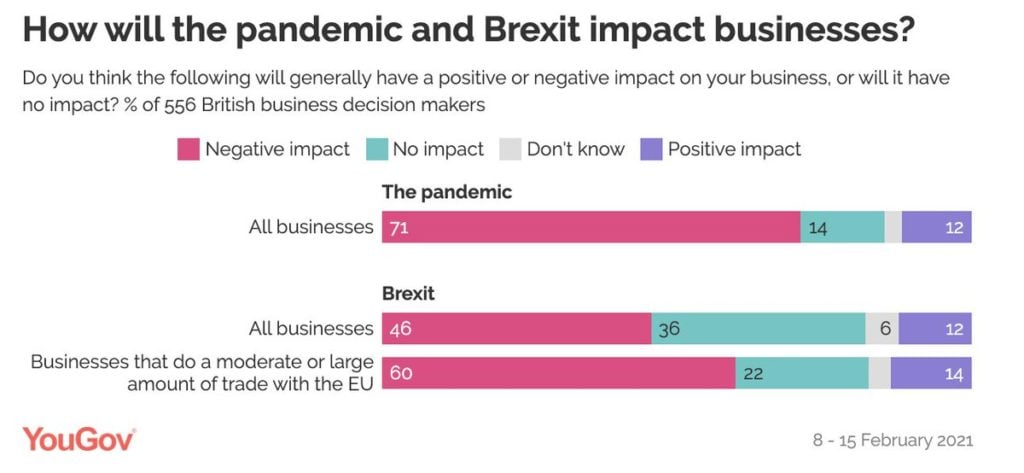
Public Perception and Policy Debates
Brexit’s impact on taxation has sparked considerable public debate, often reflecting differing economic perspectives and political ideologies. The shift in trade relationships, coupled with new tax policies, has created a complex landscape of public opinion and political maneuvering. Understanding these diverse viewpoints is crucial to comprehending the ongoing challenges and future trajectory of the UK economy.Public reaction to Brexit-related tax changes has been varied and often polarized.
Some segments of the population have welcomed certain tax measures as potentially beneficial, while others have voiced concerns about their impact on their livelihoods and the overall economy. The public’s perception is further influenced by media coverage and political narratives, which can sometimes distort or simplify complex economic issues.
Public Reaction to Tax Changes
Public opinion surveys reveal a mixed reaction to specific tax policies implemented after Brexit. Concerns often center on potential increases in living costs, job losses in specific sectors, and perceived inequities in the distribution of tax burdens. Some sectors, particularly those reliant on international trade, have reported significant challenges in adapting to the new tax regime. Conversely, proponents of certain tax policies argue that they promote economic growth or address specific societal needs.
Political Debates Surrounding Brexit Tax Policies
Political debates surrounding Brexit tax policies have been intense, reflecting the differing priorities and philosophies of political parties. Conservative politicians often argue for policies that promote economic growth and business investment, sometimes emphasizing tax cuts for specific sectors. Conversely, Labour and other opposition parties may highlight the need for social welfare programs and progressive taxation to address inequality and the potential negative consequences of specific tax policies.
The differing viewpoints of political parties often shape public discourse and influence policy outcomes.
Key Arguments for and Against Specific Tax Policies
Arguments for and against specific tax policies are often rooted in contrasting economic theories and societal values. Proponents of lower corporation taxes, for example, may argue that it attracts foreign investment and boosts economic output, while opponents may highlight the potential for reduced government revenue and increased inequality. Conversely, arguments for increased taxes on certain goods or services may center on social welfare or environmental concerns, while opponents may argue that it hinders economic activity and consumer choice.
Perspectives on the Future of the UK Economy After Brexit
Divergent perspectives exist on the future of the UK economy post-Brexit. Some economists predict a period of significant adjustment and potential economic contraction, citing the disruptions to trade and investment flows. Conversely, others argue that the UK economy will adapt and find new opportunities, emphasizing the UK’s historical resilience and entrepreneurial spirit. These differing projections highlight the uncertainty inherent in long-term economic forecasting.
Public Opinion Surveys on Brexit’s Impact
Public opinion surveys consistently demonstrate the complexity of public sentiment regarding Brexit’s economic impact. Surveys often reveal variations in opinions based on factors such as demographics, geographic location, and political affiliation. A nuanced understanding of the survey results is critical to identifying specific trends and concerns within the public.
Influence of Political Parties on Brexit Policies
Political parties wield significant influence on Brexit policies, particularly through their representation in the legislature and their ability to shape public discourse. For instance, a party’s stance on tax policy can significantly influence the direction of proposed legislation and the subsequent public debate. Political parties’ platforms often contain specific proposals related to taxation and their impact on various segments of the population.
Final Summary
In conclusion, Brexit tax and other challenges have created a dynamic and demanding environment for UK businesses. The complexities of new trade regulations, shifting tax policies, and evolving international trade relationships require careful consideration and strategic adaptation. The future will depend on the UK’s ability to navigate these challenges and capitalize on the opportunities presented by this new global landscape.
Further exploration of specific sector-specific impacts and government support programs will be crucial for a complete understanding.