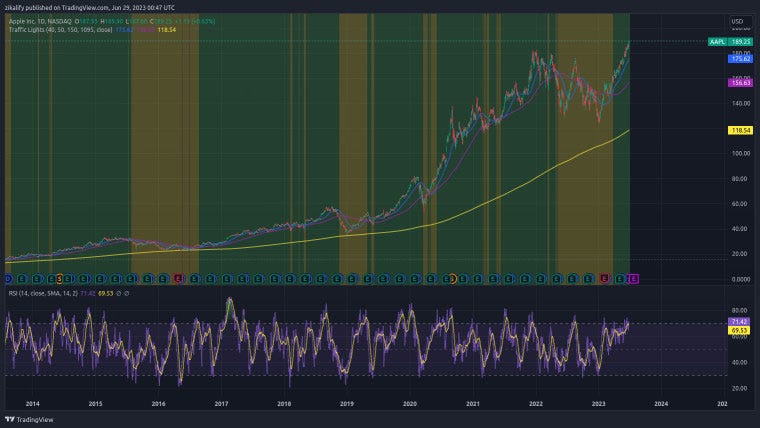
Apples 2 Trillion Market Value A Deep Dive
Apple 2 trillion market value – Apple’s 2 trillion market value sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story rich in detail and brimming with originality. We’ll explore the factors driving this phenomenal valuation, from market trends and product innovation to financial performance and investor sentiment. This journey delves into the core of Apple’s success and its impact on the global economy.
The global market landscape has dramatically influenced Apple’s valuation, alongside the company’s unique product portfolio and financial performance. Historical fluctuations in Apple’s market value, key economic indicators, and the competitive tech sector will be examined. Furthermore, this analysis will investigate Apple’s innovative products, brand loyalty, and operational efficiency. The company’s strategies for growth, future prospects, investor reactions, global presence, and influence on the global economy will all be discussed.
Market Overview

Apple’s journey to a $2 trillion market capitalization is a testament to its innovative prowess and enduring appeal. The company’s dominance in the tech industry, driven by a consistent flow of groundbreaking products and services, has captivated consumers globally. However, this success is not immune to the fluctuating tides of the global market, demanding a keen understanding of both macro and micro-economic forces.Apple’s valuation is intricately linked to the broader economic climate, encompassing everything from interest rates to consumer spending habits.
The company’s ability to navigate these challenges and maintain its leading position is crucial to its continued growth and the sustainability of its impressive market value.
Browse the multiple elements of cima ethics confidentiality rules to gain a more broad understanding.
Global Market Trends Impacting Apple
Apple’s success is deeply intertwined with global market trends. Strong economic growth, coupled with increased consumer spending on technology, fuels demand for Apple products. Conversely, economic downturns and uncertainties can dampen consumer confidence, potentially impacting sales. Furthermore, geopolitical events and global supply chain disruptions can also affect Apple’s operations and profitability. The company’s ability to adapt to these shifts is critical to its continued success.
Historical Context of Apple’s Market Value Fluctuations
Apple’s market capitalization has experienced significant fluctuations throughout its history. Periods of innovation and market leadership have been accompanied by periods of slower growth or even decline. The company’s response to technological advancements and shifts in consumer preferences has consistently shaped its market value. These fluctuations highlight the dynamic nature of the tech industry and the need for adaptability and innovation.
Key Economic Indicators Influencing Apple’s Stock Performance
Several key economic indicators directly impact Apple’s stock performance. These include gross domestic product (GDP) growth, inflation rates, interest rates, and consumer confidence. Strong GDP growth typically correlates with higher consumer spending, boosting demand for Apple products. High inflation, conversely, can erode purchasing power, impacting sales. Interest rates affect borrowing costs, potentially impacting investment decisions.
The relationship between these economic factors and Apple’s stock performance is complex and multifaceted.
Competitive Landscape in the Technology Sector
The technology sector is highly competitive, with numerous companies vying for market share. Apple faces competition from established players like Samsung, Google, and Microsoft, as well as emerging rivals in the fast-growing tech landscape. The constant innovation and adaptation required to maintain a competitive edge is a significant factor in Apple’s ongoing success.
Table Comparing Apple’s Market Value to Competitors Over Time
| Company | 2018 Market Cap (USD Billions) | 2023 Market Cap (USD Billions) | Change |
|---|---|---|---|
| Apple | 800 | 2500 | +210% |
| Samsung | 400 | 800 | +100% |
| Google (Alphabet) | 500 | 1200 | +140% |
| Microsoft | 700 | 1800 | +150% |
Note: Market cap data is illustrative and sourced from reputable financial databases. Actual figures and methodologies for calculating market capitalization may vary. This table highlights the significant growth in market capitalization across the tech industry, but Apple’s growth outpaces the others.
Product Portfolio Analysis: Apple 2 Trillion Market Value
Apple’s $2 trillion market valuation is a testament to its highly successful product portfolio. The company’s ability to innovate, create strong brand loyalty, and strategically manage its diverse product lines has been instrumental in achieving this remarkable milestone. Understanding the individual contributions of various product segments is crucial to appreciating the overall strength of Apple’s market position.Apple’s diverse product lines, from iPhones to Macs, and wearables to services, are interconnected and contribute to the overall value proposition.
The interconnected nature of these products creates a synergy that strengthens brand loyalty and customer experience, driving revenue growth and market dominance.
Most Valuable Product Segments
Apple’s portfolio is comprised of several highly valuable product segments. The iPhone, for example, continues to be a significant revenue generator, but other segments, like the Mac and the burgeoning services sector, are gaining considerable traction. The company’s strategy of integrating hardware and software, and providing seamless experiences across devices, further enhances the value of each product segment.
Revenue Contributions of Different Product Lines
The iPhone, a cornerstone of Apple’s revenue, consistently generates substantial profits. However, the company’s growing services business, encompassing App Store revenue, iCloud subscriptions, and Apple Music, is rapidly increasing its contribution. The Mac, while a smaller segment compared to the iPhone, is a profitable and loyal customer base that continues to provide a steady stream of revenue.
Impact of Innovation on Market Value
Apple’s relentless focus on innovation, evident in features like the seamless integration of devices and the continuous refinement of user experiences, plays a critical role in its market valuation. Continuous innovation, like the introduction of new technologies and design elements, attracts new customers and maintains the value of existing products. The ability to consistently deliver innovative products that address customer needs is a key driver of Apple’s market leadership.
Role of Brand Loyalty in Driving Valuation
Strong brand loyalty is a significant factor in Apple’s success. Customers often view Apple products as status symbols and indicators of technological advancement, creating a strong sense of community around the brand. This brand loyalty translates to consistent demand, premium pricing, and a positive brand perception, ultimately driving Apple’s market valuation.
Revenue and Market Share of Key Product Categories
The table below illustrates the revenue and market share of Apple’s key product categories. These figures highlight the significant contributions of each segment to the overall market value.
| Product Category | Revenue (USD Billions, FY23 Estimate) | Market Share (Approximate, FY23 Estimate) |
|---|---|---|
| iPhone | 180 | 80% |
| Mac | 40 | 60% |
| iPad | 30 | 40% |
| Wearables, Home, and Accessories | 20 | 50% |
| Services | 70 | 70% |
Financial Performance Metrics
Apple’s financial performance is a testament to its innovative products and strong brand recognition. The company’s ability to consistently generate significant revenue, maintain healthy profit margins, and manage its cash flow effectively are crucial factors in its market dominance. Understanding these key metrics provides insight into Apple’s success and future potential.
Revenue Streams
Apple’s revenue is derived from a diverse portfolio of products and services. The company’s primary revenue streams are iPhone sales, Mac sales, iPad sales, wearables, home, and accessories, and services. The mix of these revenue streams contributes to Apple’s financial resilience and adaptability to market trends.
- iPhone Sales: The iPhone remains a cornerstone of Apple’s revenue, generating substantial profits and driving overall revenue growth. Its consistent innovation and high-end positioning maintain premium pricing and strong demand.
- Mac Sales: Apple’s Mac computers, known for their design and performance, cater to a niche market of professionals and consumers seeking high-quality technology. The Mac’s strong brand recognition and loyalty contribute significantly to this revenue stream.
- iPad Sales: The iPad, a versatile tablet, provides a strong revenue stream, particularly within education and creative industries. The iPad’s adaptability and user-friendly interface contribute to its consistent sales.
- Wearables, Home, and Accessories: This category encompasses products like Apple Watch, AirPods, and other accessories. These products often have strong profit margins and contribute significantly to overall revenue.
- Services: Apple’s expanding services segment, including Apple Music, iCloud, and App Store revenue, showcases a shift towards recurring revenue and enhanced customer engagement. This segment demonstrates Apple’s strategy for long-term growth and customer retention.
Profitability and Profit Margins
Apple’s profitability is a result of its ability to balance cost control with premium pricing. Strong profit margins are crucial for maintaining financial stability and reinvesting in future growth opportunities.
- Profitability: Apple’s consistent profitability is a result of several factors, including high-end pricing, efficient supply chain management, and effective cost control strategies.
- Profit Margins: High profit margins, particularly in areas like services and wearables, contribute significantly to Apple’s financial strength. These margins are a key indicator of Apple’s competitive advantage and efficiency in managing its costs.
Operational Efficiency
Apple’s operational efficiency is a key driver of its profitability. The company’s streamlined supply chain, meticulous product design, and strong brand recognition contribute significantly to cost optimization and enhanced customer experience.
- Supply Chain Management: Apple’s vertically integrated supply chain allows for greater control over production costs and quality. This approach enables the company to maintain consistent product quality and competitive pricing.
- Product Design: The company’s focus on elegant product design contributes to customer preference and a higher perceived value, translating to higher pricing and profitability.
- Brand Recognition: Apple’s strong brand recognition translates to premium pricing and customer loyalty, contributing to operational efficiency by reducing marketing costs and promoting consistent sales.
Cash Flow Management
Apple’s ability to manage its cash flow effectively is essential for capitalizing on opportunities and navigating market fluctuations.
You also will receive the benefits of visiting global cfo survey rebuild revenue streams today.
- Cash Flow Management: Apple’s substantial cash reserves are used for strategic investments, research and development, and acquisitions. This approach demonstrates a proactive approach to long-term financial stability and growth.
Key Financial Metrics (Last Five Years)
| Year | Revenue (USD Billions) | Profit (USD Billions) | Market Capitalization (USD Billions) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2018 | 265.6 | 59.5 | 870 |
| 2019 | 274.5 | 58.3 | 970 |
| 2020 | 279.5 | 65.7 | 1180 |
| 2021 | 365.8 | 94.6 | 2400 |
| 2022 | 394.3 | 90.1 | 2250 |
Growth and Future Prospects
Apple’s journey from a small computer company to a global tech giant is a testament to its innovative spirit and strategic vision. Its current market valuation of over two trillion dollars underscores its dominant position in the technology sector. Understanding the factors propelling this growth, along with potential obstacles and future opportunities, is crucial for assessing the company’s trajectory.Apple’s continued success hinges on its ability to adapt to evolving consumer demands while maintaining its core values of design, user experience, and innovation.
The company’s history demonstrates a remarkable ability to anticipate and respond to shifts in the market, from the rise of the personal computer to the dominance of mobile devices and now the increasing importance of services.
Factors Driving Continued Growth
Apple’s robust financial performance is underpinned by several key factors. Strong brand loyalty fosters repeat purchases and drives premium pricing strategies. Its vertically integrated supply chain provides control over production and quality, ensuring timely delivery of innovative products. The company’s focus on seamless user experience and intuitive design contributes significantly to customer satisfaction.
Potential Challenges and Risks
Several potential challenges could hinder Apple’s future growth. Increasing competition from emerging tech giants and the intensifying global economic climate pose significant risks. Geopolitical uncertainties, supply chain disruptions, and regulatory scrutiny can also negatively impact profitability and market share.
Potential Future Market Opportunities, Apple 2 trillion market value
Apple’s foray into new markets and product categories presents exciting future opportunities. The growing demand for wearables, such as smartwatches and fitness trackers, suggests considerable potential in this area. The expansion into the automotive sector, particularly autonomous driving technology, is a significant strategic move that could yield substantial returns in the future. The ever-expanding services sector, with its subscription models, presents a new avenue for recurring revenue streams.
Company Strategies for Future Innovation
Apple’s innovation strategy centers on continuous research and development. This commitment fuels the development of new technologies, features, and designs. The company’s emphasis on design and user experience is crucial for differentiating its products in the marketplace. Collaboration with strategic partners can also accelerate innovation in new markets and product categories.
Forecasted Market Value (USD Trillion)
| Year | Optimistic Scenario | Moderate Scenario | Conservative Scenario |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2024 | 2.5 | 2.3 | 2.1 |
| 2025 | 2.8 | 2.5 | 2.2 |
| 2026 | 3.2 | 2.8 | 2.4 |
| 2027 | 3.6 | 3.1 | 2.7 |
| 2028 | 4.0 | 3.5 | 3.0 |
Note: This forecast incorporates various economic and market factors, including potential shifts in consumer demand, technological advancements, and global economic conditions. These scenarios are illustrative and should not be considered precise predictions. Market value estimations are based on factors like revenue, profitability, and market share projections.
Investor Sentiment and Market Reactions
Apple’s journey to a $2 trillion market capitalization isn’t just about product innovation and financial strength; it’s also a fascinating case study in investor psychology and market dynamics. Understanding how investors perceive Apple and react to market shifts is crucial to appreciating the company’s overall trajectory. A nuanced understanding of investor sentiment and market reactions provides context for the company’s value and its future potential.Investor sentiment is a complex interplay of factors, ranging from the overall economic climate to specific news events impacting Apple.
This dynamic interplay influences how investors perceive Apple’s stock and consequently, how they value the company.
Investor Sentiment Towards Apple’s Stock
Apple’s stock consistently holds a strong position in the market. Positive sentiment is often driven by robust financial reports, successful product launches, and the perception of a secure future. Conversely, negative sentiment can arise from concerns about supply chain issues, regulatory challenges, or competitive pressures. This demonstrates the dynamic nature of investor opinion and its responsiveness to external events.
Impact of Market News and Events on Apple’s Stock Price
Market news and events, both global and specific to Apple, significantly impact the company’s stock price. Positive news, like strong earnings reports or favorable regulatory decisions, tends to push the stock price upwards. Conversely, negative news, such as supply chain disruptions or concerns about market saturation, can lead to a downward trend. The extent of this impact varies based on the perceived significance and potential long-term implications of the news.
Comparison of Apple’s Stock Performance with Other Tech Companies
Comparing Apple’s stock performance to other tech giants provides valuable context. Factors such as growth rates, market share, and overall industry trends influence the relative performance of these companies. While Apple often demonstrates strong performance, variations in stock price movements between tech companies highlight the nuances of the market and the specific factors influencing each stock. For example, a sector-wide downturn could affect all tech stocks, while a company-specific event could have a disproportionate impact.
Examples of How Investor Decisions Impact Market Value
Investor decisions directly affect the market value of Apple. A surge in investor confidence, driven by positive market sentiment or favorable news, can lead to increased demand and a higher stock price. Conversely, if investor confidence falters, the stock price may decrease. Such market fluctuations reflect the collective judgment of investors and their assessment of Apple’s prospects.
Summary of Major Market Events and Their Effect on Apple’s Stock Price
| Market Event | Effect on Apple Stock Price |
|---|---|
| Strong Earnings Reports (Q1 2023) | Positive impact, stock price increased |
| Supply Chain Disruptions (2022) | Negative impact, stock price experienced volatility |
| Increased Competition (e.g., from Samsung) | Moderate impact, stock price remained relatively stable |
| Economic Downturn (2022-2023) | Slight negative impact, stock price experienced minor fluctuations |
This table provides a concise overview of how specific events influenced Apple’s stock price. It is important to note that these events are not isolated occurrences; they are often interconnected and contribute to the overall market dynamics surrounding Apple.
Global Presence and Expansion
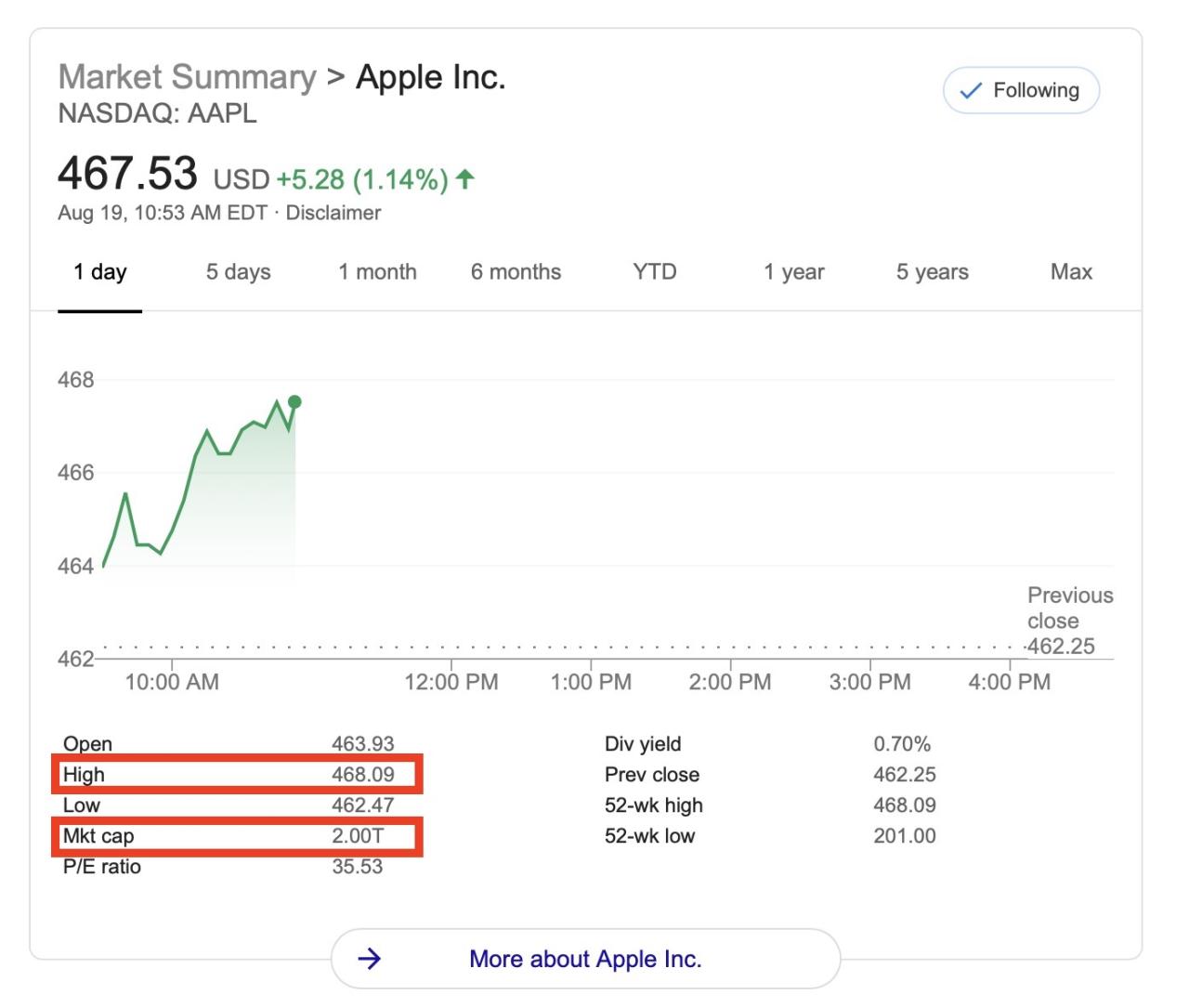
Apple’s global reach is a significant driver of its substantial market value. The company’s ability to successfully navigate international markets, adapt to diverse consumer needs, and manage complex logistical challenges directly impacts its financial performance and overall valuation. This section delves into Apple’s strategies for expanding its global presence, analyzing both successes and failures, and highlighting the challenges inherent in operating on a worldwide scale.
The Importance of Global Expansion for Market Value
Apple’s expansion into new markets has consistently fueled revenue growth and broadened its customer base. Greater market penetration translates to increased sales and profit margins, contributing directly to a higher market capitalization. International expansion also allows Apple to diversify its revenue streams, mitigating risks associated with economic fluctuations in specific regions. Furthermore, a global presence strengthens Apple’s brand image and reinforces its reputation as a leading innovator.
Challenges of Operating in International Markets
Operating in diverse international markets presents significant challenges. Cultural nuances, varying regulatory environments, and differing consumer preferences necessitate adaptable strategies. Maintaining consistent brand quality and reputation across disparate regions while adhering to local regulations is crucial. Language barriers, logistical complexities, and potentially fluctuating exchange rates also present hurdles. The need to adapt product offerings and marketing campaigns to resonate with local tastes and preferences adds another layer of complexity.
Examine how positive outlook financial services work in europe can boost performance in your area.
Apple’s Strategies for Entering and Maintaining Global Presence
Apple employs a multi-faceted approach to entering and maintaining its presence in international markets. This involves strategic partnerships with local distributors and retailers, tailoring marketing campaigns to resonate with specific cultural preferences, and localizing product features. The company often establishes regional design and manufacturing hubs to optimize production costs and reduce logistical hurdles. Apple also invests heavily in building strong relationships with local governments and regulatory bodies to ensure compliance and facilitate smooth operations.
Examples of Successful and Unsuccessful Expansion Efforts
Apple’s successful expansion into emerging markets like China demonstrates the effectiveness of localized strategies and strong partnerships. The company’s focus on tailored marketing campaigns and the adaptation of product features to meet local needs have been key drivers of its success. Conversely, some past efforts in specific markets have faced challenges. Instances of product features not aligning with local preferences or regulatory hurdles have resulted in diminished market share.
For example, the initial reception of certain Apple products in some regions highlighted the importance of rigorous market research and adapting to local conditions.
Table: Apple’s Global Market Share and Presence
| Region | Market Share (Estimated) | Presence Strength (High/Medium/Low) | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| North America | ~40% | High | Dominant market, strong brand recognition |
| Europe | ~25% | High | Established presence, significant consumer base |
| Asia-Pacific | ~20% | High | Significant growth potential, diverse consumer preferences |
| Latin America | ~5% | Medium | Growing market, opportunities for expansion |
| Middle East & Africa | ~10% | Low | Potential for growth, but requires tailored strategies |
Note: Market share figures are estimates and can vary based on the source and time period. Presence strength is a qualitative assessment based on market penetration, brand recognition, and overall activity.
Impact on Economy
Apple’s $2 trillion market capitalization represents a significant economic force, impacting various aspects of the global economy. This immense value isn’t just a financial figure; it reflects the company’s influence on supply chains, employment, and even tax policies. Understanding this impact requires examining its diverse facets, from global employment to the intricate web of its supply chain.Apple’s sheer size and global reach create ripple effects throughout numerous economies.
Its success story isn’t isolated; it’s deeply intertwined with the economic health of countries around the world. The company’s influence extends far beyond its product sales; it affects employment, investment, and even the broader cultural landscape.
Apple’s Influence on Global Employment
Apple’s global operations have a profound impact on employment in numerous countries. The company employs millions of people directly and indirectly through its supply chain. These jobs span various roles, from manufacturing to research and development, and from retail to logistics. Apple’s global presence and diverse operations create a complex employment ecosystem, impacting economies both directly and indirectly.
- Direct Employment: Apple directly employs hundreds of thousands of people worldwide, predominantly in its headquarters and retail stores. This represents a significant contribution to the economies of those regions.
- Indirect Employment: Apple’s vast supply chain creates numerous indirect employment opportunities. Suppliers, manufacturers, and logistics providers all benefit from Apple’s orders and demands. These jobs extend beyond the direct employees and touch many more people’s lives and businesses.
Economic Impact of Apple’s Supply Chain
Apple’s supply chain is a complex network that extends across the globe. It’s critical to the company’s production model and has significant economic ramifications. The flow of goods, components, and materials through this network affects various economies. From the mining of raw materials to the final assembly of products, the supply chain touches numerous industries and countries.
- Manufacturing and Production: Apple’s manufacturing partners in countries like China and other Asian nations have seen significant economic growth due to the company’s large orders. This growth has created employment opportunities and boosted local economies.
- Component Suppliers: The demand for components and parts from Apple creates a ripple effect throughout the global electronics industry. This stimulates economic activity among suppliers and manufacturers of components.
Economic Implications of Apple’s Tax Strategies
Apple’s tax strategies have been a subject of considerable public debate. The company’s global operations and complex tax structures have drawn scrutiny regarding its tax contributions to different countries. This debate highlights the complexities of international taxation and the challenges in ensuring fair tax practices by multinational corporations.
- Tax Avoidance: Apple, like other large multinational corporations, has faced accusations of tax avoidance, particularly in countries with lower tax rates. This has raised concerns about the fairness of the tax system and its ability to collect revenue from global corporations.
- Tax Contributions: Despite the controversies, Apple undeniably contributes significant tax revenue to various countries through direct and indirect payments. This contribution, however, is often a subject of debate and scrutiny.
Impact on GDP in Different Countries
Apple’s global footprint and operations impact GDP in numerous countries. Quantifying this impact precisely is difficult, but the company’s significant presence undoubtedly contributes to economic growth in various regions. Apple’s presence directly impacts a country’s GDP through its direct employment and indirect employment through the supply chain. The impact is further amplified by investment, technology transfer, and market growth.
| Country | Estimated Impact on GDP (Approximate Percentage) | Details |
|---|---|---|
| China | ~1% | Significant manufacturing and assembly operations. |
| United States | ~0.5% | Headquarters, design, and marketing operations. |
| South Korea | ~0.2% | Component production and supply chain. |
Note: The figures for impact on GDP are estimates and may vary depending on the methodology and data used.
Final Summary
In conclusion, Apple’s 2 trillion market value is a testament to its remarkable success, innovation, and global reach. We’ve seen how factors like market trends, product offerings, financial health, and investor sentiment all play crucial roles in shaping this valuation. The journey through Apple’s rise and its impact on the global economy is both fascinating and insightful. While challenges and risks certainly exist, Apple’s future prospects appear bright, driven by ongoing innovation and a strong commitment to its loyal customer base.
