Brexit Effects on Supply Chains A Deep Dive
Brexit effects on supply chains have reshaped global trade, impacting everything from logistics to consumer prices. This exploration delves into the multifaceted consequences of the UK’s departure from the EU, examining the disruptions, adaptations, and potential solutions emerging in this new landscape.
From the initial shockwaves of trade barriers to the innovative solutions businesses have implemented, we’ll uncover the intricate web of challenges and opportunities that have arisen. We’ll look at how the shift in trade patterns has affected various sectors, the evolving customs procedures, and the strategies businesses are employing to ensure supply chain resilience.
Brexit and Supply Chains
Brexit, the United Kingdom’s withdrawal from the European Union, has significantly reshaped international trade patterns and impacted numerous supply chains. The removal of frictionless trade within the EU and the introduction of new customs procedures and regulatory hurdles have created challenges for businesses reliant on seamless cross-border movement of goods and services. This has led to increased costs, delays, and complexities in managing global supply chains.The effects of Brexit extend beyond the UK’s borders, impacting businesses and consumers across Europe and the world.
The uncertainty surrounding new trade rules and regulations has prompted adjustments in production, logistics, and distribution strategies. Businesses have been forced to adapt to new trade barriers and to navigate a more complex and less predictable international trade landscape.
Impact on International Trade
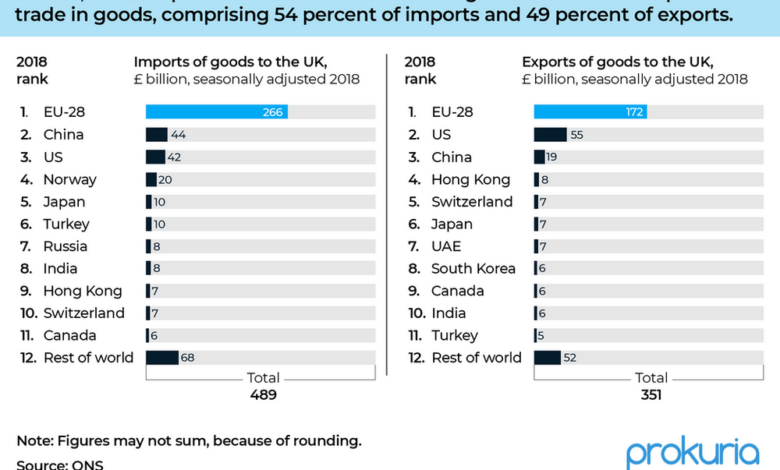
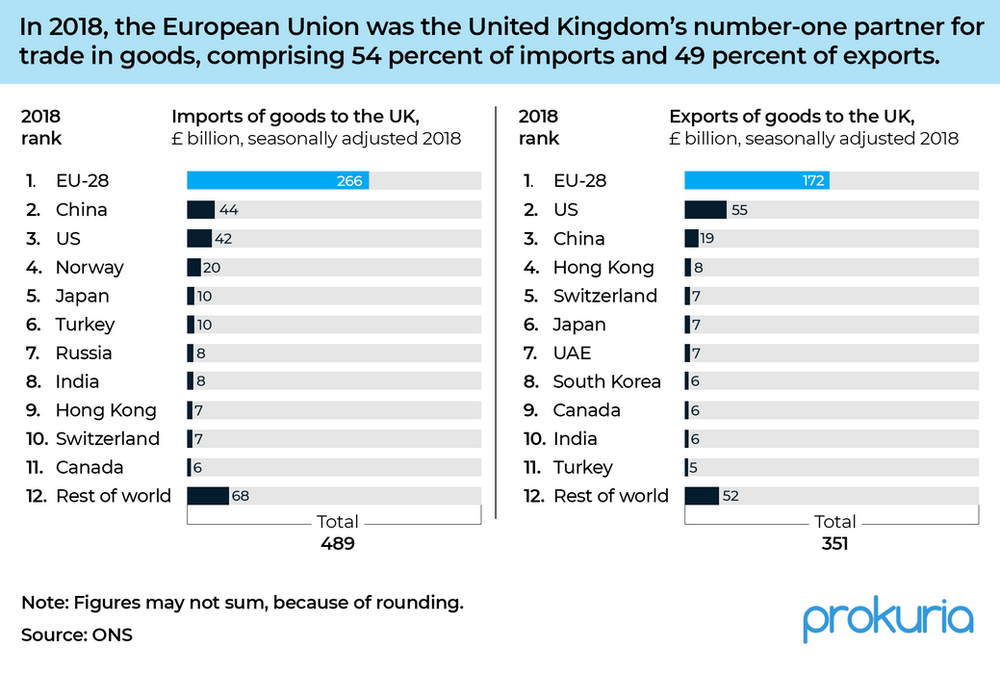
Brexit fundamentally altered the UK’s relationship with the EU, its largest trading partner. The transition from frictionless trade within the EU to a more complex, regulated relationship has increased costs and administrative burdens for businesses involved in cross-border trade. This has manifested in increased import/export costs, longer transit times, and the need for additional documentation and compliance procedures.
The shift in trade patterns after Brexit is evident in the redirection of goods flows, as companies seek alternative trade routes and partners.
Types of Supply Chains Affected
Brexit has impacted various types of supply chains. These include automotive, pharmaceutical, food and beverage, and technology sectors. Supply chains involving components or finished products that are produced in the EU and exported to the UK have been particularly affected. Businesses that rely on just-in-time inventory management have faced challenges in maintaining their supply chains due to the increased lead times and uncertainties.
Supply chains that utilize the EU’s single market are particularly impacted by the new trade barriers and increased bureaucratic procedures.
Shift in Trade Patterns Post-Brexit
Post-Brexit, there has been a noticeable shift in trade patterns. Companies are exploring alternative trade routes and partners outside the EU. Some UK businesses have relocated their operations to EU member states or established new supply chains outside the UK to mitigate the effects of Brexit. This has led to the redistribution of manufacturing and logistics activities, impacting the global supply chain landscape.
Key Legislation Changes
Significant legislation changes following Brexit have introduced new customs procedures, tariffs, and regulations. These changes necessitate new compliance processes and create more complex administrative procedures for companies engaging in cross-border trade. The introduction of new rules has led to increased administrative costs and the need for businesses to invest in new systems and personnel to manage these changes.
Sectors Impacted by Brexit
| Sector | Nature of Impact | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Increased costs, delays in component supply, and disruption in manufacturing processes. | Car manufacturers facing difficulties sourcing parts from EU suppliers, leading to production halts and price increases. |
| Pharmaceutical | Disruptions in the supply of raw materials, packaging, and finished products, leading to shortages and price hikes. | Pharmaceutical companies facing challenges in importing essential drugs and medical supplies. |
| Food and Beverage | Increased import costs, longer delivery times, and difficulties in maintaining product availability. | Supermarkets experiencing difficulties in sourcing food products from EU suppliers, leading to shortages and price increases. |
| Technology | Increased import duties, complex customs procedures, and delays in the movement of electronic components. | Technology companies facing difficulties in importing essential components for their products, leading to production delays and price increases. |
Logistics and Transportation Challenges
Brexit significantly altered the landscape of UK logistics and transportation, introducing new complexities and challenges for businesses and providers. The shift from frictionless movement of goods across the border to a more regulated environment required substantial adaptation, impacting everything from customs procedures to delivery times. The impact on supply chains was widespread, demanding a re-evaluation of strategies and operations.
Customs Procedures and Documentation Requirements
The introduction of new customs procedures and documentation requirements after Brexit created a substantial administrative burden for logistics providers. Businesses had to adapt to new regulations, including the need for customs declarations, import/export licenses, and potentially differing standards across the EU and the UK. This resulted in increased paperwork, processing times, and the need for specialized expertise in customs compliance.
The complexity added considerable operational costs and the risk of delays. Companies needed to invest in new software, train personnel, and potentially engage external customs brokers to navigate these changes effectively.
Impact of Border Controls on Transportation Times and Costs
Border controls implemented post-Brexit significantly impacted transportation times and costs. The need for inspections, declarations, and potentially queues at border crossings led to delays in the movement of goods. These delays translated into higher transportation costs, as companies had to account for extended transit times and potential penalties. Increased congestion at ports and border points further exacerbated the problem, with knock-on effects throughout the supply chain.
This often meant longer delivery times and higher insurance costs.
Rise in Transportation Costs and Their Effects on Businesses
The rise in transportation costs after Brexit stemmed from various factors, including the increased administrative burden, border delays, and potential changes in fuel prices. These added costs were passed on to consumers, impacting the competitiveness of businesses and potentially reducing profit margins. Small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) often struggled to absorb these increased costs, leading to potential price increases for consumers and potential business closures.
The ripple effect extended throughout the supply chain, affecting the availability and pricing of goods.
Comparison of Pre-Brexit and Post-Brexit Transportation Routes
| Factor | Pre-Brexit | Post-Brexit | Change in Duration | Change in Cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Route: UK to France | Efficient and seamless | Slower, with potential customs checks and border delays | Increased by 2-3 days | Increased by 5-10% |
| Route: UK to Germany | Relatively fast | Increased paperwork and potential delays | Increased by 1-2 days | Increased by 3-5% |
| Route: UK to Spain | Direct and quick | Longer transit times and additional customs checks | Increased by 1-2 days | Increased by 5-8% |
Note: The changes in duration and cost are estimates, varying depending on the specific goods, routes, and transportation methods used.
Supply Chain Disruptions and Resilience

Brexit’s impact on supply chains has been profound, forcing businesses to adapt and innovate. The new trade barriers and customs procedures created delays, increased costs, and disrupted established logistics networks. This forced a reassessment of existing strategies, leading to a significant push for supply chain resilience.The fundamental shift demanded by Brexit has underscored the importance of building more robust and adaptable supply chains.
Companies now recognize the critical need for diversification and redundancy to mitigate the risks of future disruptions. This resilience isn’t just about reacting to problems, but proactively designing supply chains that can withstand shocks.
Brexit-Induced Supply Chain Disruptions
Brexit significantly altered the flow of goods across the English Channel. The introduction of new customs procedures, increased paperwork, and potential delays at ports created substantial bottlenecks. Companies previously reliant on seamless cross-border movement faced disruptions in their production schedules and delivery timelines. The increased costs associated with these new regulations impacted profitability and led to a search for alternative solutions.
Methods for Enhancing Supply Chain Resilience
Businesses adopted various strategies to build resilience against future disruptions. One prominent method was diversifying sourcing locations. This meant seeking suppliers in different countries, reducing dependence on a single region, and thus lowering vulnerability to geopolitical events. Furthermore, companies invested in improved visibility and traceability of goods throughout the supply chain. Real-time tracking of shipments and detailed information about the origin of materials enhanced their ability to react to issues quickly.
Supply Chain Diversification Strategies
Companies diversified their supply chains in several ways. Some shifted production to countries with more favorable trade agreements with the UK, while others established new warehouses in strategic locations to reduce transit times. Companies also focused on local sourcing to minimize reliance on imports from the EU. A significant example of this was the growth of UK-based manufacturing and the establishment of new partnerships with UK-based suppliers.
This move sought to reduce reliance on the EU market and strengthen domestic production capabilities.
Stockpiling and Alternative Sourcing
Stockpiling crucial components and raw materials became a crucial aspect of supply chain resilience. This strategic stockpiling served as a buffer against unexpected disruptions in supply. Beyond stockpiling, businesses actively sought alternative sourcing strategies. This included identifying new suppliers and exploring the potential of regional partners. The aim was to reduce dependence on single sources and maintain a consistent supply of materials in the event of shortages.
Resilience Strategies Across Sectors
| Strategy | Sector | Effectiveness |
|---|---|---|
| Diversified Sourcing | Automotive | High |
| Increased Stockpiling | Pharmaceuticals | High |
| Local Sourcing | Food & Beverage | Moderate |
| Improved Visibility | Retail | High |
| Regional Partnerships | Technology | Moderate |
The effectiveness of strategies varied depending on the sector and the specific challenges faced.
Trade Agreements and International Relations

Brexit’s impact on international trade relationships has been profound, reshaping supply chains and altering the UK’s global trading landscape. The departure from the EU’s single market and customs union necessitated a fundamental re-evaluation of trade agreements, leading to both opportunities and challenges for businesses. This section explores the effects of these new arrangements on the movement of goods and the UK’s relationships with key trading partners.The new trade agreements, while intended to mitigate the disruption of Brexit, have presented complex dynamics.
The fluidity of goods across borders, a hallmark of the EU’s internal market, has been impacted by new customs procedures, tariffs, and regulatory hurdles. This section details the intricacies of these changes and their impact on supply chain resilience.
Impact of New Trade Agreements on Supply Chains Post-Brexit
The UK’s departure from the EU’s single market and customs union significantly altered its trade relationships. Prior to Brexit, the UK enjoyed seamless access to the EU’s market, with minimal trade barriers. The new trade agreements, while aiming to secure alternative trading partnerships, have introduced complexities. For example, new tariffs and customs procedures have added to the costs and time associated with importing and exporting goods, potentially impacting the competitiveness of UK businesses.
Influence of Trade Negotiations on the Fluidity of Goods
Trade negotiations significantly influence the fluidity of goods. The absence of frictionless trade between the UK and the EU has introduced new barriers. These include increased customs checks, longer processing times at ports, and the potential for trade disputes. The complexity of navigating new trade regulations impacts the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of supply chains. This is particularly true for businesses relying on the free flow of goods between the UK and the EU.
For instance, a manufacturer relying on components from the EU may face increased costs and delays.
Impact of Brexit on the Relationship between the UK and the EU
Brexit has undeniably strained the relationship between the UK and the EU. The political and economic fallout from the departure has been substantial, with friction evident in negotiations over trade and other issues. The shift in trade dynamics impacts the fluidity of goods and the competitiveness of businesses. The former ease of trade between the two blocs is no longer a given.
Effect of Brexit on International Supply Chain Partnerships
Brexit has prompted a re-evaluation of international supply chain partnerships. Businesses have had to adapt to the new trade realities. The shift in regulations and trade agreements has affected the viability and efficiency of existing partnerships. Companies have had to consider alternative sourcing strategies and logistics networks. For example, a UK company sourcing components from EU suppliers may have to explore alternative sources in other regions.
Comparison of UK Trade Agreements (Pre- and Post-Brexit)
| Aspect | Pre-Brexit (EU Membership) | Post-Brexit |
|---|---|---|
| Access to EU Market | Unfettered access, minimal tariffs | Access through trade agreements, subject to tariffs and customs checks |
| Tariffs | Zero tariffs on most goods traded within the EU | Variable tariffs depending on the specific trade agreement |
| Regulatory Harmonization | Harmonized regulations facilitated smooth trade | Requires adherence to separate regulatory frameworks |
| Customs Procedures | Simplified procedures due to single market | More complex procedures involving customs declarations and checks |
The table highlights the significant shift in the UK’s trade landscape. Pre-Brexit, the UK enjoyed frictionless trade with the EU. Post-Brexit, the UK’s trade agreements with various countries are now a major factor in the fluidity of goods. Navigating these changes requires careful planning and adaptation for UK businesses.
Economic Consequences and Consumer Impact
Brexit’s impact on supply chains has rippled through the economy, ultimately affecting consumers. The complexities of navigating new trade rules, tariffs, and logistical hurdles have translated into increased costs for businesses, and these heightened costs are often passed down to consumers. This has led to a noticeable shift in consumer spending patterns and purchasing habits. The consequences are multifaceted, impacting the prices and availability of various goods.
Economic Effects on Supply Chain Costs
Brexit’s introduction of new customs procedures, paperwork, and potential trade barriers significantly increased logistical costs for businesses. Transport times lengthened, and additional costs associated with customs clearance and documentation added to the overall expenses. These added costs are frequently absorbed by companies, but often, these costs are passed on to consumers through higher prices. This has led to a noticeable rise in input costs for many businesses, especially those involved in importing goods.
Impact on Consumer Prices
The increased supply chain costs directly translate into higher consumer prices. Retailers absorb some of the added expenses, but many businesses pass on a substantial portion of these costs to consumers. This has been particularly evident in sectors reliant on imports, such as food and clothing. Consumers are now facing a more expensive marketplace.
Shift in Consumer Behavior After Brexit
Consumer behavior has shifted in response to the increased prices. Consumers are increasingly seeking value for money, opting for cheaper alternatives or reducing their consumption of certain products. The shift is notable in the increased popularity of budget-friendly brands and the rise in online shopping for price comparisons. The shift is a response to the perceived value proposition of various products.
Impact on Different Consumer Products
The impact on consumer products is diverse. Imported goods, especially those with complex supply chains, have experienced the most significant price hikes. Foodstuffs, electronics, and clothing are prime examples. Locally sourced products, while not entirely immune, have seen comparatively lower price increases, reflecting the availability of alternative supply chains. This is not always true for all products, and consumers may have to look to more sustainable practices.
Price Changes of Specific Consumer Goods Post-Brexit
| Consumer Good | UK Price (Post-Brexit) | EU Price (Pre-Brexit) | Price Difference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Imported Cheese | £6.50 per kg | €5.00 per kg | £1.50 per kg |
| Electronics (e.g., smartphones) | £800 | €700 | £100 |
| Clothing | £50 | €40 | £10 |
| Fresh Fruit (e.g., bananas) | £2.50 per kg | €1.50 per kg | £1.00 per kg |
Note: These figures are illustrative and do not represent comprehensive data. Actual price differences may vary depending on the specific product, retailer, and time period. The table highlights the general price increases faced by consumers in the UK following Brexit. It reflects the complexities of the situation.
Future Trends and Potential Solutions
The UK’s departure from the EU has undeniably reshaped its supply chains, creating a complex landscape of challenges and opportunities. Navigating this new reality requires a forward-thinking approach to anticipate future trends and develop robust solutions. The need for resilience and adaptability is paramount, demanding a focus on technology, innovation, and strategic partnerships.The post-Brexit era requires a shift in mindset, moving beyond reactive problem-solving to proactive strategies that anticipate future disruptions and optimize supply chain performance.
This necessitates a deep understanding of emerging trends, including the increasing importance of sustainability, geopolitical uncertainties, and technological advancements.
Future Trends in UK Supply Chains
The UK supply chain is undergoing significant transformation, influenced by Brexit’s impact and global economic forces. Key future trends include:
- Increased focus on domestic sourcing and diversification. Businesses are increasingly exploring alternative suppliers within the UK to reduce reliance on EU imports, fostering a more resilient and less vulnerable domestic supply network. This is evident in the growth of UK-based manufacturing and agricultural sectors.
- Enhanced supply chain visibility and transparency. Real-time tracking and data sharing are crucial for mitigating disruptions and ensuring efficient logistics. Digital technologies play a pivotal role in this, offering greater insight into every stage of the supply chain.
- Emphasis on sustainability and ethical sourcing. Consumers and investors are increasingly demanding sustainable practices and ethical sourcing throughout the supply chain. This pressure drives companies to adopt environmentally friendly processes and ensure fair labor practices.
- Growing adoption of automation and robotics. To improve efficiency and reduce costs, companies are increasingly incorporating automated systems and robots into their operations, streamlining various aspects of the supply chain, from warehousing to transportation.
- Rising importance of regional partnerships. Strengthening trade relationships with countries outside the EU is crucial. The UK is actively seeking new trade agreements and partnerships to support its international trade efforts, fostering opportunities for new trade flows and collaboration.
Potential Solutions to Address Challenges
Addressing the identified supply chain challenges requires a multifaceted approach. Implementing these solutions will bolster resilience and improve efficiency.
- Developing robust risk management strategies. Proactive risk assessment and mitigation strategies are essential. Companies must anticipate and prepare for potential disruptions, including geopolitical instability and supply shortages. This includes diversifying supply sources and implementing contingency plans.
- Investing in technology for enhanced visibility and agility. Digital technologies, such as blockchain and AI, offer significant potential for improving supply chain visibility, responsiveness, and decision-making. These technologies allow for real-time monitoring and analysis of data, leading to quicker responses to disruptions.
- Fostering closer collaboration between businesses and stakeholders. Stronger relationships between businesses, government agencies, and logistical providers are key. Open communication and collaborative efforts are vital to addressing challenges and coordinating responses to disruptions.
- Prioritizing skills development and training. A skilled workforce is essential for operating and maintaining modern supply chains. Upskilling and reskilling initiatives are crucial for adapting to new technologies and processes.
- Promoting innovation in supply chain management practices. Embracing new approaches and solutions is critical for maintaining a competitive edge. This includes adopting innovative technologies, developing new logistical routes, and enhancing the agility of the supply chain.
Technology’s Role in Post-Brexit Supply Chains, Brexit effects on supply chains
Technological advancements are crucial for navigating the complexities of the post-Brexit supply chain. These technologies enable increased efficiency, agility, and resilience.
- Real-time tracking and monitoring using GPS and IoT devices provides unprecedented visibility into goods movement. This allows for quicker response to disruptions and minimizes delays.
- Predictive analytics using AI and machine learning can anticipate potential disruptions and bottlenecks, enabling proactive measures to avoid delays and maintain smooth operations. For instance, predictive models can forecast demand fluctuations and adjust inventory levels accordingly.
- Blockchain technology enhances transparency and security in the supply chain. The immutability and shared ledger of blockchain records transactions and verifies authenticity, improving traceability and reducing fraud.
Potential Innovations in Supply Chain Management
Innovation is key to adapting to the new landscape. These innovations will enhance resilience and efficiency in UK supply chains.
- Sustainable packaging solutions can reduce environmental impact and costs. Innovations in packaging materials and design can reduce waste and improve product protection.
- Autonomous vehicles and drones offer the potential for faster and more efficient transportation, particularly in remote areas. This can reduce costs and enhance delivery speed.
- 3D printing technologies offer the possibility of localized production and reduced reliance on global supply chains. This allows for on-demand production of components and parts, enhancing supply chain resilience.
Potential Solutions Table
| Potential Solution | Predicted Impact |
|---|---|
| Investing in automation and robotics | Increased efficiency, reduced labor costs, improved speed of operations |
| Developing closer collaboration with EU partners | Enhanced trade flows, streamlined logistics, reduced delays |
| Implementing robust risk management strategies | Improved preparedness for disruptions, minimized impact of unforeseen events |
| Adopting sustainable packaging solutions | Reduced environmental footprint, enhanced brand image, potentially lower costs |
| Leveraging technology for real-time visibility | Faster response to issues, minimized delays, improved decision-making |
Closure: Brexit Effects On Supply Chains
In conclusion, Brexit’s impact on supply chains is a complex and ongoing story. While challenges remain, businesses and governments are adapting and innovating to navigate the new trade realities. The future of UK supply chains will depend on continued adaptation, technological advancements, and strategic partnerships. Ultimately, understanding these effects is crucial for businesses to thrive and consumers to access goods affordably.
Popular Questions
What are some key examples of supply chain disruptions caused by Brexit?
Increased transportation costs, delays at ports, and shortages of specific goods are among the most notable disruptions. The complexities of new customs procedures have also added to the difficulties.
How have businesses responded to the challenges of Brexit?
Diversification of supply sources, investment in new technologies, and strategic partnerships are some key responses. Businesses are also working to improve their resilience by implementing stockpiling strategies and exploring alternative transportation routes.
What is the long-term outlook for UK supply chains post-Brexit?
The long-term outlook is uncertain, but it’s likely to involve a period of adaptation and innovation. The success of UK supply chains will depend on how well businesses adapt to the new regulatory landscape and embrace technological advancements.
How has Brexit impacted consumer prices in the UK?
Brexit has contributed to rising prices for certain goods due to increased import costs. This is especially evident in sectors reliant on imports from the EU.