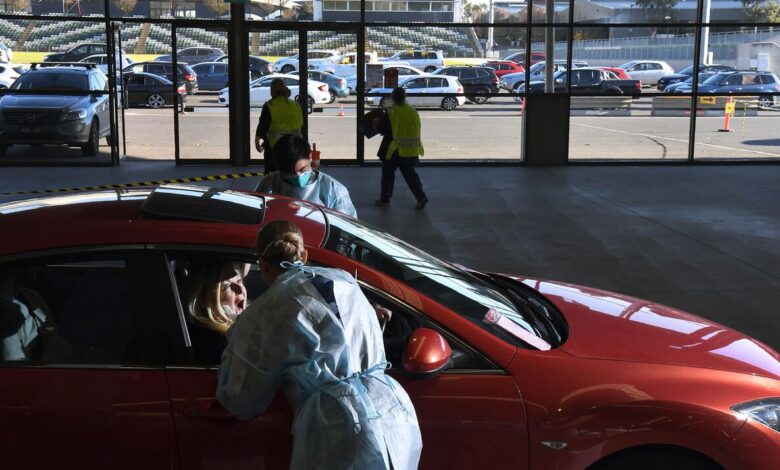
Coronavirus Recovery Australia & New Zealand
Coronavirus recovery considerations Australia New Zealand sets the stage for a deep dive into the multifaceted challenges and triumphs of these nations’ responses to the pandemic. From the economic fallout and healthcare strain to the impacts on social well-being, travel, education, and the workforce, this exploration reveals the diverse ways these countries navigated this unprecedented crisis. We’ll examine the unique strategies each nation employed and assess their effectiveness, offering insights into what worked, what didn’t, and what lessons can be learned for future pandemics.
The economic impact, ranging from sector-specific downturns to the effectiveness of government stimulus, will be thoroughly analyzed. We’ll also examine the strain on healthcare systems, long-term workforce implications, and the strategies for improving future preparedness. Beyond the immediate health crisis, the pandemic’s profound impact on social interactions, mental health, and the travel and tourism sectors will be explored.
Finally, we’ll delve into the disruptions to education systems, the changing nature of work, and the government’s public policy responses, offering a comprehensive overview of the recovery process.
Economic Impacts
The COVID-19 pandemic significantly impacted the economies of Australia and New Zealand, causing disruptions across various sectors. Both nations responded with substantial government stimulus packages to mitigate the economic fallout. This analysis examines the specific economic impacts, recovery strategies, and effectiveness of these measures.The pandemic’s widespread effects led to a global recession. Australia and New Zealand, heavily reliant on international trade and tourism, were particularly vulnerable.
Lockdowns, travel restrictions, and reduced consumer spending crippled many businesses. However, both nations exhibited resilience, with strong government support playing a crucial role in their recoveries.
Economic Impact Summary
Australia and New Zealand experienced significant economic downturns due to the pandemic. Tourism, hospitality, and international trade were among the hardest-hit sectors. The initial shock was followed by a period of recovery, driven by government interventions and global economic stabilization.
Recovery Strategies
Both countries implemented substantial stimulus packages, including financial aid for businesses, job support schemes, and infrastructure investments. These initiatives aimed to prop up demand, support employment, and stimulate economic activity.
Key Sectors Affected
The following table Artikels the key sectors affected and the recovery strategies implemented in Australia and New Zealand.
| Country | Sector | Impact | Recovery Strategy | Effectiveness Rating |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Australia | Tourism | Significant decline in visitor numbers, impacting airlines, hotels, and related businesses. | Targeted financial assistance for tourism businesses, marketing campaigns to promote domestic tourism, and support for international marketing efforts. | Moderate |
| Australia | Hospitality | Restaurant closures and reduced capacity led to significant job losses and revenue declines. | Government subsidies for wages and rent, grants for businesses, and support for adapting to changing consumer habits. | High |
| Australia | Retail | Reduced consumer spending and online shopping growth led to varying impacts across different retail segments. | Support for online retail growth, financial aid for struggling businesses, and measures to facilitate digital transformation. | Moderate |
| New Zealand | Tourism | A steep decline in international tourist arrivals impacted hotels, tour operators, and related industries. | Focus on domestic tourism promotion, supporting the development of new tourism products, and supporting small and medium-sized enterprises. | High |
| New Zealand | Agriculture | Supply chain disruptions and fluctuating export markets created volatility. | Government support for farmers, including subsidies and aid to manage disruptions. | Moderate |
| New Zealand | Hospitality | Reduced capacity and closures in restaurants and cafes resulted in job losses. | Government assistance programs for wages and rent, support for business adaptations. | High |
Effectiveness of Government Stimulus Packages
Assessing the effectiveness of the stimulus packages is complex and depends on the specific sector and the specific measures employed. Some programs exhibited more pronounced effects in particular sectors, while others were more broadly applicable.
“The effectiveness of stimulus packages is often debated, with some arguing that they are crucial for economic recovery, while others highlight the potential for unintended consequences and long-term economic impacts.”
Evaluating the long-term economic consequences of these policies and their lasting impact on employment, income distribution, and economic growth will require continued observation and analysis. It’s crucial to remember that economic recovery is a dynamic process. While these strategies provided immediate support, the long-term effects will depend on various factors including global economic conditions and the ongoing evolution of the pandemic.
Healthcare System Considerations

The COVID-19 pandemic placed unprecedented strain on healthcare systems globally, highlighting vulnerabilities and demanding immediate and long-term responses. Australia and New Zealand, while relatively successful in containing the virus’s initial spread, experienced significant challenges in adapting to the evolving demands. This analysis delves into the specific pressures on healthcare systems, the impacts on the workforce, and crucial strategies for building resilience and future preparedness.The pandemic’s surge in demand for intensive care beds, testing, and personal protective equipment (PPE) significantly stressed healthcare infrastructure.
Staff shortages and burnout were widespread, impacting patient care and leading to a reconsideration of staffing models and resource allocation. The long-term consequences of this strain are multifaceted and require proactive measures to prevent a similar crisis from recurring.
Strain on Healthcare Systems During the Pandemic
The pandemic dramatically increased the workload and pressure on healthcare systems. Hospitals faced surges in patients requiring intensive care, overwhelming existing capacity and necessitating rapid adjustments in resource allocation. The need for widespread testing and contact tracing further stretched resources, demanding increased staff and technological support. The rapid spread of the virus also placed immense pressure on supply chains for essential medical equipment like ventilators and PPE, leading to shortages and disruptions.
Long-Term Impacts on the Healthcare Workforce
The pandemic significantly impacted healthcare professionals, leading to burnout, anxiety, and psychological distress. Healthcare workers faced immense pressure, long hours, and the risk of infection, which took a toll on their mental and physical well-being. The prolonged nature of the pandemic further exacerbated these issues, resulting in a significant loss of experienced personnel and a critical need for strategies to retain and support the workforce.
Strategies for Improving Resilience and Preparedness for Future Outbreaks
Developing robust and adaptable healthcare systems is crucial for future outbreaks. This includes proactive investment in infrastructure, strategic workforce planning, and strengthening supply chains. Implementing advanced surveillance systems and rapid response protocols can enable quicker identification and containment of future outbreaks. Continuous training and education for healthcare professionals are essential to ensure they have the skills and knowledge to effectively manage future crises.
Key Lessons Learned About Healthcare Infrastructure and Resources
The pandemic highlighted the importance of adaptable healthcare infrastructure, flexible staffing models, and resilient supply chains. Critical care capacity, testing capabilities, and PPE availability emerged as key vulnerabilities. The experience underscored the need for robust emergency preparedness plans, incorporating proactive measures for rapid response and resource mobilization. The effectiveness of existing protocols and infrastructure was also tested, revealing areas for improvement and innovation in healthcare systems.
Healthcare Infrastructure Improvements
This table Artikels specific improvements needed in healthcare infrastructure, encompassing staffing, equipment, and training, to enhance resilience against future outbreaks.
| Category | Specific Improvements |
|---|---|
| Staffing | Increased nurse-to-patient ratios, expansion of telehealth services, recruitment of additional medical personnel, training for staff on emerging technologies. |
| Equipment | Increased capacity of intensive care units (ICUs), provision of advanced ventilators, expansion of diagnostic testing capabilities, and procurement of sufficient PPE. |
| Training | Mandatory training on infection control protocols, advanced life support techniques, and pandemic preparedness. |
Social and Mental Health Impacts

The COVID-19 pandemic profoundly impacted the social and mental well-being of Australians and New Zealanders. Lockdowns, social distancing measures, and economic uncertainty created significant stress, anxiety, and isolation. The disruption to daily routines, loss of loved ones, and the fear of infection contributed to a rise in mental health concerns across both nations. Addressing these challenges is crucial for a full recovery.
Summary of Social and Mental Health Consequences
The pandemic’s impact on mental health was substantial. Increased rates of anxiety, depression, and stress were reported across both countries. Isolation and loneliness, exacerbated by lockdowns, were significant contributors to these issues. Financial hardship further compounded these problems, creating a cascade of negative impacts on mental health and social well-being. The disruption to support networks, including community activities and social gatherings, also had a detrimental effect on individuals’ mental and emotional states.
Measures Taken to Address Mental Health Concerns
Both Australia and New Zealand implemented various strategies to address the surge in mental health needs. Increased funding for mental health services was a key initiative, along with the expansion of telehealth options to provide accessible care. Public awareness campaigns aimed to destigmatize mental health issues and encourage help-seeking behavior. These efforts sought to make mental health support more readily available and reduce the stigma associated with seeking help.
Impact on Social Interactions and Community Life
Social interactions were significantly altered by the pandemic. Lockdowns and restrictions on gatherings reduced opportunities for social connection and community engagement. This led to feelings of isolation and loneliness, particularly among vulnerable populations. The reliance on digital communication became more prevalent, but it did not fully replace in-person interactions, leading to a perceived decline in the quality of social relationships.
This disruption impacted community life, impacting local businesses, social clubs, and other organizations that rely on social gatherings.
Role of Support Services in the Recovery Process
Support services played a vital role in helping individuals cope with the pandemic’s effects. These services provided crucial resources for emotional support, practical assistance, and guidance. Crisis hotlines, online counseling platforms, and community-based support groups were vital in helping individuals navigate the challenges of the pandemic and promoting mental wellbeing. These services helped to ensure individuals had access to the resources they needed, fostering resilience and enabling a smoother recovery process.
Support Services in Australia and New Zealand
| Support Service | Australia | New Zealand | Effectiveness |
|---|---|---|---|
| Crisis Hotlines | Numerous national and regional crisis lines, including Lifeline and beyondblue. | Similar to Australia, with national helplines like the Mental Health Foundation of New Zealand and Lifeline NZ. | Generally, crisis lines were well-utilized, but access and response times may have varied. |
| Online Counseling Platforms | Increasing availability of online therapy services. | Growth in online counseling options through various providers. | Online platforms offered greater accessibility, but may not be suitable for all individuals or situations. |
| Community Support Groups | Numerous local groups offering support to specific demographics and conditions. | Similar initiatives with community groups supporting various needs. | Varying levels of effectiveness based on community engagement and resources. |
Effectiveness of support services is contingent on factors like accessibility, affordability, and cultural appropriateness. A holistic approach, combining various support systems, is crucial for a comprehensive recovery.
Travel and Tourism Sectors: Coronavirus Recovery Considerations Australia New Zealand
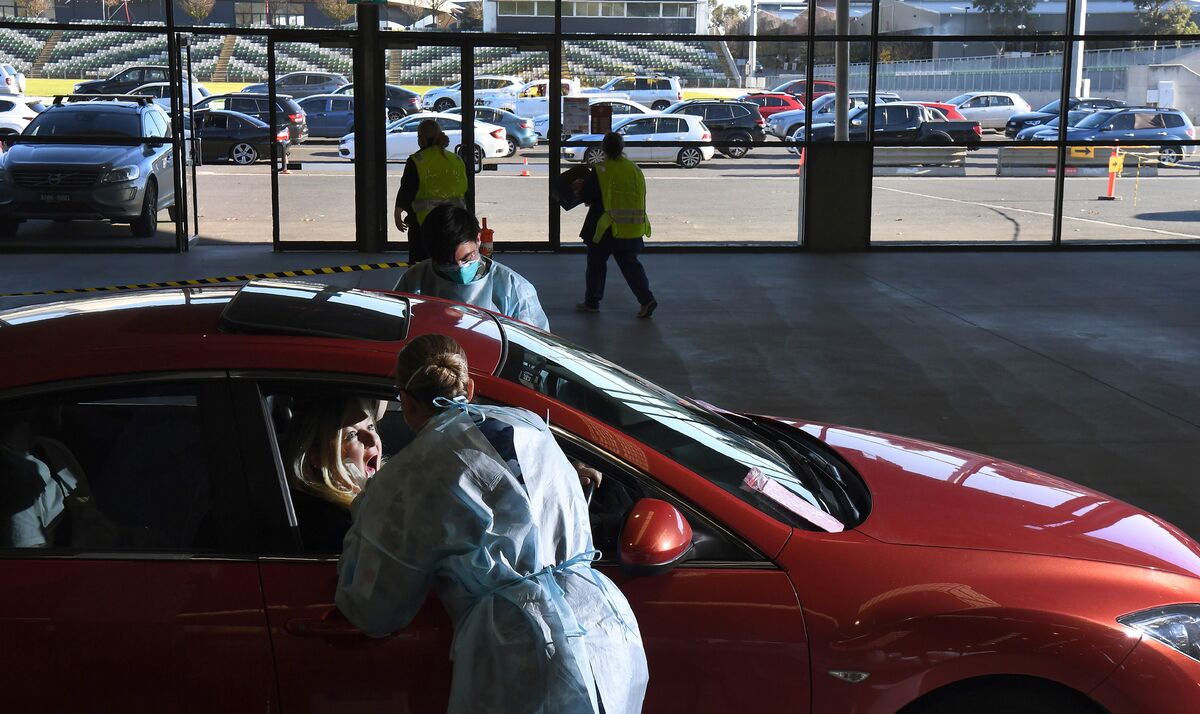

The COVID-19 pandemic dealt a devastating blow to the travel and tourism sectors globally, impacting both Australia and New Zealand profoundly. Lockdowns, border closures, and consumer anxieties led to a sharp decline in international and domestic travel, causing significant economic hardship for businesses and workers in these crucial industries. The recovery has been a complex and ongoing process, requiring innovative strategies to rebuild confidence and attract tourists back to these stunning destinations.
Impact on the Sectors
The pandemic’s effects on Australia and New Zealand’s travel and tourism sectors were immediate and severe. International visitor numbers plummeted as borders closed and travel restrictions were imposed. Domestic tourism also suffered significantly as lockdowns limited movement and leisure activities. Businesses, from airlines and hotels to tour operators and restaurants, experienced drastic revenue reductions and faced the threat of closure.
Many employees were laid off or had their hours reduced, leading to unemployment and economic instability. The impact on local economies was substantial, especially in regions heavily reliant on tourism.
Support Measures During Recovery
Both countries implemented various measures to support the travel and tourism sectors during recovery. These included financial assistance packages for businesses, grants, and loans to help them weather the crisis and adapt to new circumstances. Jobkeeper schemes provided crucial support for employees, reducing the economic strain on families and individuals. Government initiatives focused on promoting domestic tourism to stimulate the local economy and provide relief to businesses.
These support programs aimed to ease the transition back to normalcy and ensure a more sustainable recovery for the industry.
Recovery Strategies Comparison
Australia and New Zealand, while both facing similar challenges, employed somewhat different strategies in their recovery plans. Australia focused on a phased approach to border reopening, initially prioritizing domestic tourism, and then gradually easing restrictions for international visitors. New Zealand, known for its stringent health measures, prioritized safety and a cautious approach to reopening its borders. Both countries recognised the importance of rebuilding international confidence in their travel safety and health protocols.
You also can understand valuable knowledge by exploring cima ethics confidentiality rules.
This was crucial in attracting tourists back, and both countries invested in promoting their unique offerings to attract visitors.
Strategies to Attract Tourists Back
Attracting tourists back to Australia and New Zealand involved a multi-faceted approach. Both countries invested in marketing campaigns highlighting their natural beauty, cultural experiences, and health and safety protocols. Emphasis was placed on showcasing the unique experiences and activities that each country offered. The promotion of responsible tourism practices, highlighting sustainability and environmental consciousness, played a significant role in appealing to a growing segment of environmentally conscious travellers.
Tourism Revenue and Visitor Numbers
| Country | Year | International Visitors (Millions) | Tourism Revenue (Billions) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Australia | 2019 | 8.0 | 40.0 |
| Australia | 2020 | 2.5 | 10.0 |
| Australia | 2021 | 4.5 | 25.0 |
| Australia | 2022 | 6.0 | 35.0 |
| New Zealand | 2019 | 3.5 | 15.0 |
| New Zealand | 2020 | 1.0 | 5.0 |
| New Zealand | 2021 | 2.0 | 10.0 |
| New Zealand | 2022 | 2.5 | 12.5 |
These figures illustrate the substantial drop in visitor numbers and revenue during the pandemic. The subsequent recovery, although varying in pace between the two countries, shows a clear trend towards rebuilding the sector. These figures are illustrative and may not reflect the precise data for all years. More detailed data can be found in official government reports and tourism industry publications.
Education Systems
The COVID-19 pandemic profoundly impacted education systems globally, disrupting traditional learning models and forcing rapid adaptation. Australia and New Zealand, like many other nations, faced the challenge of maintaining educational continuity while prioritizing student well-being and educator safety. This necessitated innovative approaches to remote learning and the eventual transition back to in-person instruction.
Disruptions to Education Systems
The pandemic led to widespread school closures and university campus shutdowns across both Australia and New Zealand. This disruption impacted various aspects of the educational experience, including the curriculum, teaching methodologies, and student engagement. Students faced challenges in accessing resources, maintaining motivation, and adapting to new learning environments. Educators were tasked with rapidly adopting online platforms and pedagogical strategies to ensure continuity of learning.
Measures to Support Students and Educators
Governments in both countries implemented various initiatives to mitigate the negative impacts of the pandemic on students and educators. These included providing access to digital devices and internet connectivity for students from disadvantaged backgrounds. Professional development opportunities for teachers were offered to equip them with the skills necessary to deliver effective online instruction. Financial support was also extended to schools and universities to cover the costs associated with transitioning to remote learning.
Long-Term Impacts on Educational Outcomes
The pandemic’s effects on educational outcomes are still unfolding. Initial data suggests potential learning gaps among students, particularly those from vulnerable populations. Disruptions to social interaction and extracurricular activities might have contributed to the emotional and social well-being of students. Further research is necessary to fully understand the long-term implications for academic achievement and future prospects.
Comparison of Reopening Strategies
Australia and New Zealand adopted differing approaches to reopening schools and universities. The decision-making processes considered factors such as the prevalence of the virus, vaccination rates, and community transmission levels. The timing and specifics of reopening varied across different states and regions within each country.
Table: Contrasting Approaches to Remote and In-Person Learning
| Feature | Australia | New Zealand |
|---|---|---|
| Remote Learning | Varied approaches across states, with some relying heavily on online platforms like Zoom and Google Classroom. Specific digital literacy support initiatives were implemented. | National online learning platform usage and resources were readily available, promoting uniformity across the country. Focus on digital equity and access to resources for students from disadvantaged backgrounds. |
| In-Person Learning | Phased approach to reopening schools, with gradual return to in-person instruction and safety protocols like mask mandates and social distancing implemented. | Similar phased approach to reopening, focusing on gradual return to in-person learning, and maintaining strict health and safety measures. Emphasis on a balanced approach to online and in-person learning. |
| Assessment Strategies | Flexible assessment strategies were adapted to account for the transition to remote learning. Focus on maintaining consistent standards of learning. | Similar emphasis on flexibility and adjusting assessment methods for remote learning. Emphasis on formative assessment to monitor student progress. |
Workforce and Employment
The COVID-19 pandemic significantly impacted the Australian and New Zealand economies, leading to widespread job losses and shifts in the nature of work. Businesses faced unprecedented challenges, while workers grappled with job insecurity and changing employment landscapes. Government interventions were crucial in mitigating the worst impacts and fostering recovery.
Impact on Employment
The pandemic caused significant job losses across various sectors, particularly in hospitality, retail, and tourism. Australia and New Zealand witnessed a rise in unemployment rates, impacting households and the overall economic health of both nations. Industries reliant on international travel and in-person interaction experienced substantial declines in employment. The impact varied regionally, with certain areas facing disproportionately higher unemployment rates due to their economic dependence on specific sectors.
Measures to Support Jobseekers and Businesses
Governments in both countries implemented numerous measures to support jobseekers and businesses during the pandemic. These included wage subsidies, JobKeeper/similar programs, and extended unemployment benefits. These initiatives aimed to cushion the economic blow, allowing businesses to retain employees and workers to maintain income during lockdowns and restrictions. Support also included funding for training and reskilling programs to equip workers with skills for new employment opportunities.
Changing Nature of Work and Reskilling
The pandemic accelerated the shift towards remote work and digitalization. Businesses adapted to remote operations, and employees gained experience with new technologies. This transition highlighted the need for reskilling and upskilling initiatives to equip workers with the necessary skills for the evolving job market. The increased adoption of technology demanded new skillsets across many sectors, requiring workers to adapt to these changes to remain competitive in the evolving job market.
Strategies for Supporting Businesses in Adaptation
Government policies aimed to assist businesses in adapting to the new economic landscape. These included grants, loans, and tax incentives to encourage investment in technology and digital transformation. Financial support also included provisions for businesses to adapt to the evolving market conditions. These strategies aimed to bolster the resilience of businesses and facilitate their transition to the new economic landscape.
Job Losses, Job Creation, and Retraining Programs
| Country | Job Losses (Estimated) | Job Creation (Estimated) | Retraining Programs |
|---|---|---|---|
| Australia | Approximately X number of jobs lost across various sectors (source: ABS data). | New jobs created in tech, online services, and logistics sectors (source: industry reports). | Numerous government-funded programs, including TAFE and other vocational training initiatives, focused on reskilling and upskilling workers for emerging industries. These programs often provided subsidies and incentives to encourage participation. |
| New Zealand | Estimated Y number of jobs lost, primarily in tourism and hospitality (source: Statistics NZ data). | Growth in sectors like online retail and digital services (source: industry data). | Workforce development initiatives by the Ministry of Business, Innovation and Employment aimed at reskilling workers for new employment opportunities. These initiatives often focused on supporting businesses in adapting to the new economic environment. |
Note: X and Y represent estimated values and should be replaced with actual figures from reliable sources.
Public Policy Responses
Australia and New Zealand, facing the COVID-19 pandemic, implemented various public policy responses to mitigate its economic, social, and health impacts. These responses, while sharing some similarities, also displayed distinct characteristics tailored to the specific circumstances of each nation. This section examines the key policy areas, comparing and contrasting the approaches employed by both countries.
Economic Stimulus Packages
Governments in both countries deployed substantial economic stimulus packages to bolster their economies. These packages aimed to support businesses, workers, and consumers. Australia’s JobKeeper program, for example, provided financial assistance to businesses and employees facing significant disruptions. New Zealand’s wage subsidy scheme offered similar support to struggling businesses and workers. The specific design of these programs, including eligibility criteria and funding levels, differed between the two nations.
Healthcare System Considerations
Both nations prioritized bolstering their healthcare systems’ capacity to manage the surge in COVID-19 cases. Australia focused on procuring and distributing essential medical supplies, enhancing testing capabilities, and implementing strategies for managing hospital capacity. New Zealand emphasized rapid contact tracing, stringent border controls, and isolation protocols to limit the spread of the virus. The differing approaches reflected the varying epidemiological situations in each country.
Social Support Measures
Significant social support measures were implemented in both countries. These included unemployment benefits, financial assistance for vulnerable populations, and mental health support services. Australia, for instance, expanded its existing social safety net, while New Zealand introduced specific initiatives to address the unique social and economic vulnerabilities brought on by the pandemic. The extent of these measures and their impact on the respective populations are significant factors in assessing the effectiveness of the responses.
Travel and Tourism Sector Support
The travel and tourism sectors, heavily impacted by border closures and travel restrictions, received substantial support from both governments. Australia implemented programs to assist tourism businesses, offering grants, loans, and other financial aid. New Zealand, similarly, supported its tourism sector through financial incentives and marketing campaigns. The specific programs varied in terms of eligibility criteria and funding levels, reflecting the importance of the sector in each nation’s economy.
Regulatory Frameworks for Businesses and Industries
Regulatory frameworks for businesses and industries adapted to the pandemic’s needs. Australia, for instance, relaxed some regulatory requirements to ease the burden on businesses during the crisis. New Zealand, while maintaining a high level of regulatory oversight, focused on targeted support for industries most affected by the pandemic. The differences in the regulatory approaches reflected the unique challenges and priorities of each country.
Effectiveness of Public Health Policies, Coronavirus recovery considerations australia new zealand
The effectiveness of public health policies in both countries was assessed based on the pandemic’s trajectory and the resulting health outcomes. Australia, with its strategy focused on early detection and rapid response, saw its COVID-19 curve flatten earlier than New Zealand’s. However, New Zealand’s stringent border controls and contact tracing initiatives were successful in containing the spread of the virus.
The different approaches and their outcomes underscore the complexity of evaluating public health policy effectiveness.
Comparison of Public Policy Responses
| Country | Policy Area | Description | Evaluation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Australia | Economic Stimulus | JobKeeper program, financial assistance to businesses | Effective in supporting employment but some concerns about equity |
| Australia | Healthcare | Procurement of medical supplies, enhanced testing | Improved capacity to manage the pandemic but with some challenges in certain areas |
| Australia | Social Support | Expanded social safety net, mental health support | Improved support for vulnerable populations, but further analysis needed |
| New Zealand | Economic Stimulus | Wage subsidy scheme, targeted support | Effective in supporting businesses and workers, with a focus on equity |
| New Zealand | Healthcare | Rapid contact tracing, stringent border controls | Highly effective in containing the spread of the virus, but impact on economy needed further assessment |
| New Zealand | Social Support | Specific initiatives for vulnerable populations | Targeted support, potentially more effective in specific areas |
Concluding Remarks
In conclusion, the coronavirus recovery in Australia and New Zealand reveals a complex tapestry of challenges and responses. While each nation faced unique circumstances and implemented varying strategies, the overarching theme is one of resilience and adaptation. The experience highlights the crucial role of robust public policy, targeted support for vulnerable sectors, and the importance of a collaborative approach in navigating future crises.
This analysis provides valuable insights for policymakers and individuals alike, equipping them with a deeper understanding of the long-term implications of the pandemic and the path towards recovery.