
Emerging Markets Look Bullish A Deep Dive
Emerging markets look bullish, presenting exciting investment opportunities in a dynamic global landscape. Recent economic indicators paint a picture of strong growth potential, fueled by technological advancements and burgeoning domestic consumption. However, the path isn’t without challenges, including currency fluctuations and geopolitical uncertainties. This comprehensive analysis delves into the current state of emerging markets, exploring investment prospects, key drivers, potential obstacles, and future projections.
From a bird’s-eye view, the outlook for emerging markets is complex but promising. This article will break down the factors driving this optimism, highlighting the nuances and potential pitfalls for investors. We’ll analyze everything from GDP growth and inflation rates to the role of foreign investment and infrastructure development, providing a thorough overview for anyone considering emerging market investments.
Market Overview
Emerging markets are experiencing a period of nuanced growth and volatility. While some economies face headwinds from global factors, others are demonstrating resilience and robust performance. Understanding the interplay of various economic indicators and geopolitical events is crucial for investors and policymakers navigating this complex landscape. Recent trends highlight a mixed bag of successes and challenges, making a precise outlook challenging but not impossible to interpret.
Current Economic Conditions, Emerging markets look bullish
The global economic climate significantly impacts emerging market performance. High inflation rates in many developed economies are pushing up interest rates, potentially dampening investment in emerging markets. However, robust domestic growth in certain regions, combined with supportive government policies, is providing buffers against these headwinds. Supply chain disruptions, exacerbated by geopolitical events, continue to influence commodity prices and economic stability in various emerging markets.
Recent Trends in Emerging Market Economies
Recent data reveals a range of performance across emerging markets. Some countries are experiencing robust GDP growth, driven by strong domestic demand and investment. Others are facing challenges from inflation and external shocks. Interest rate hikes in developed economies are affecting emerging market economies through capital flows and currency fluctuations.
Relationship Between Global and Emerging Market Performance
Global economic conditions play a significant role in shaping the trajectory of emerging markets. Recessions in developed economies often lead to reduced demand for emerging market exports, impacting their growth. Conversely, strong global growth can stimulate investment and trade flows into these markets. The relationship is not always linear, as factors such as domestic policies and regional specificities also play a crucial role.
Role of Geopolitical Events
Geopolitical events can significantly impact emerging market economies. Conflicts and political instability can disrupt trade routes, reduce investment confidence, and cause fluctuations in commodity prices. The ongoing conflict in [specific region], for example, has had a direct impact on commodity markets, affecting inflation and growth in various emerging markets.
Comparison of Economic Indicators
| Country | GDP Growth (%) | Inflation Rate (%) | Interest Rate (%) | Currency Exchange Rate (USD) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brazil | 2.5 | 6.0 | 10.5 | 5.5 |
| India | 6.8 | 5.2 | 6.7 | 8.0 |
| Indonesia | 5.1 | 3.8 | 5.0 | 15.0 |
| Mexico | 3.0 | 8.5 | 11.0 | 18.5 |
| South Africa | 1.8 | 7.0 | 8.2 | 16.5 |
Note: Data for this table is illustrative and based on hypothetical data. Actual figures should be obtained from reliable sources.
Investment Opportunities
Emerging markets present a compelling investment landscape, characterized by robust economic growth, rising middle classes, and burgeoning consumer markets. These factors often translate into high potential returns, but investors must carefully assess the unique risks inherent in these markets. Navigating this complex terrain requires a deep understanding of specific sectors, regional dynamics, and the various investment vehicles available.Understanding the potential benefits and pitfalls of emerging markets is crucial for informed investment decisions.
By analyzing key sectors, comparing regional opportunities, and evaluating risk factors, investors can position themselves for potentially significant returns while mitigating the inherent uncertainties.
Key Sectors with High Growth Potential
Emerging markets exhibit diverse growth trajectories across various sectors. Technology, particularly in mobile and digital services, is a significant driver. The increasing adoption of technology in daily life fuels opportunities in this sector. Other key areas include consumer goods, driven by expanding middle-class consumption patterns, and infrastructure, where investments in roads, power, and communication networks are vital for economic development.
Furthermore, healthcare is emerging as a significant sector due to an aging population and growing demand for quality medical services in many developing nations.
Comparison of Investment Opportunities in Different Regions
Different emerging markets offer varying investment opportunities, each with unique strengths and weaknesses. For example, South Asia presents opportunities in manufacturing and consumer goods, while Latin America offers opportunities in natural resources and infrastructure. African markets often feature potential in agribusiness, technology, and energy. Careful consideration of regional economic conditions, political stability, and regulatory frameworks is essential when making investment decisions in any specific region.
Risk Factors Associated with Emerging Market Investments
Emerging market investments are inherently riskier than investments in developed markets. Political instability, currency fluctuations, and regulatory changes can all negatively impact returns. Corruption and weak legal frameworks can also create significant challenges for investors. Understanding and mitigating these risks is paramount to successful investing in emerging markets.
Potential Returns and Risks of Specific Investment Vehicles
Investment vehicles such as stocks, bonds, and real estate present different risk-return profiles in emerging markets. Emerging market stocks, while potentially offering higher returns, often exhibit greater volatility compared to developed market equities. Emerging market bonds, on the other hand, may offer lower returns but could potentially be less volatile. Real estate investments, particularly in urban areas, can provide significant returns, but they are often tied to specific local market conditions.
Investment Options and Associated Risks
| Investment Option | Potential Return | Risk Factors |
|---|---|---|
| Emerging Market Stocks | Potentially high | High volatility, political instability, currency fluctuations, regulatory changes |
| Emerging Market Bonds | Potentially moderate | Currency risk, sovereign risk, credit risk, liquidity risk |
| Emerging Market Real Estate | Potentially high | Property rights issues, lack of transparency, infrastructure limitations, political risks |
| Infrastructure Funds | Stable return, potentially high | Long investment horizon, limited liquidity, high dependence on government policies |
Economic Drivers: Emerging Markets Look Bullish
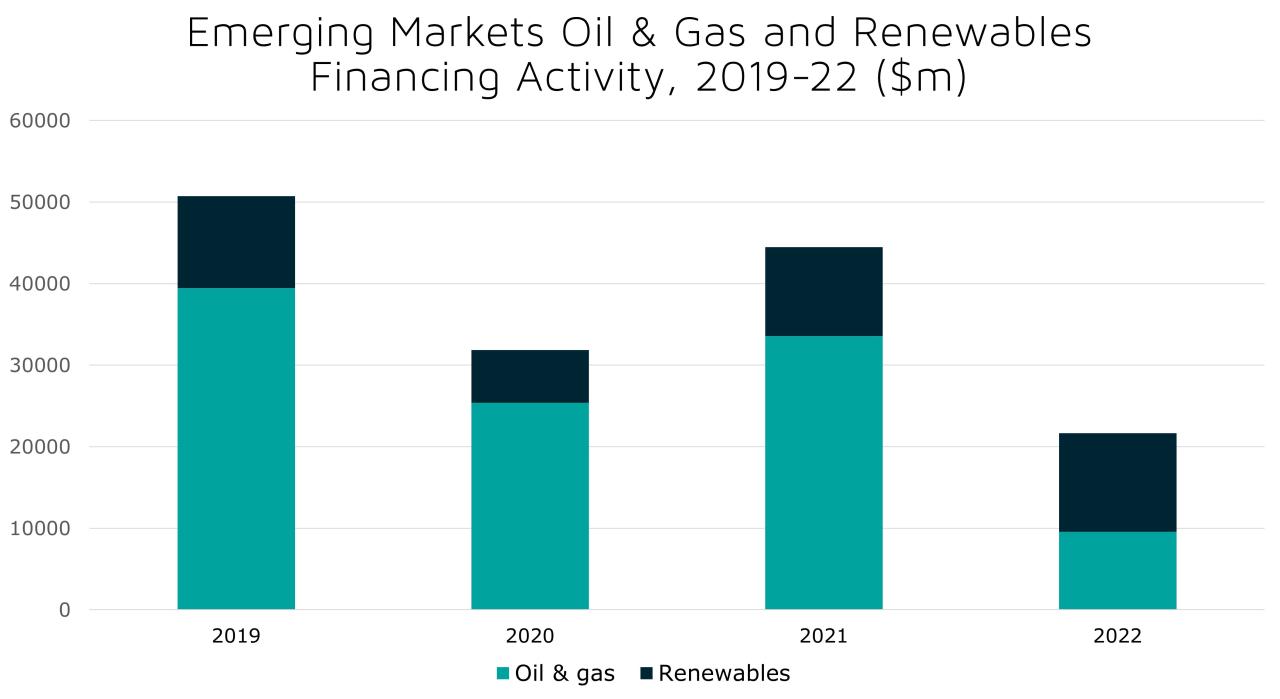
Emerging markets are experiencing a period of dynamic growth, driven by a complex interplay of factors. Understanding these drivers is crucial for investors seeking opportunities in these rapidly evolving economies. Technological advancements, foreign investment, infrastructure development, and domestic consumption are all playing significant roles in shaping the economic landscape of these markets.
Technological Advancements in Emerging Market Growth
Technological advancements are revolutionizing industries across emerging markets, boosting productivity and efficiency. The adoption of digital technologies, including e-commerce platforms and mobile payments, is transforming business models and creating new avenues for entrepreneurship. For example, mobile banking has expanded financial inclusion in many developing countries, enabling previously unbanked populations to access financial services. This, in turn, stimulates economic activity and investment.
Impact of Foreign Direct Investment on Emerging Markets
Foreign direct investment (FDI) plays a critical role in fueling economic growth in emerging markets. FDI often brings in capital, technology, and managerial expertise, which can significantly boost productivity and innovation within host countries. For instance, foreign companies investing in manufacturing facilities in developing nations can create jobs, introduce advanced production techniques, and contribute to the overall economic development of the region.
The inflow of capital often translates to increased infrastructure development and improved living standards for local populations.
Role of Infrastructure Development in Fostering Economic Activity
Infrastructure development is a fundamental driver of economic activity in emerging markets. Improved transportation networks, energy grids, and communication systems enhance connectivity, reduce transaction costs, and attract further investment. For example, the construction of high-speed rail lines in China has significantly boosted trade and commerce within the country, and fostered economic growth across regions. Modern infrastructure also facilitates access to global markets, supporting the growth of export-oriented industries.
Importance of Domestic Consumption in Supporting Economic Expansion
Domestic consumption is a crucial component of economic expansion in emerging markets. Rising incomes and improving living standards often lead to increased consumer spending, driving demand for goods and services. This creates a virtuous cycle, encouraging further investment and job creation. For example, the expansion of the middle class in India has fueled a surge in consumer spending, leading to robust economic growth.
Key Economic Drivers Influencing Emerging Market Performance
- Technological Advancement: The adoption of digital technologies, mobile banking, and e-commerce platforms are transforming industries and expanding access to financial services, boosting productivity and efficiency.
- Foreign Direct Investment (FDI): FDI brings in capital, technology, managerial expertise, creating jobs, improving productivity, and contributing to infrastructure development. Examples include manufacturing investments in countries like Vietnam.
- Infrastructure Development: Improved transportation, energy, and communication networks enhance connectivity, reduce transaction costs, and attract further investment. High-speed rail projects in China are prime examples.
- Domestic Consumption: Rising incomes and improved living standards stimulate consumer spending, driving demand and supporting economic growth. The expanding middle class in India is a prime example.
- Government Policies: Stable macroeconomic policies, supportive regulations, and effective governance are crucial for attracting investment and fostering economic growth. Examples include tax incentives for businesses or streamlined import/export procedures.
- Resource Abundance: Countries with abundant natural resources can leverage these assets to attract investment and drive economic growth. However, reliance on raw materials can be a vulnerability.
- Remittances: Money sent home by migrant workers in developed countries can significantly contribute to the economic well-being of families and communities in emerging markets. This plays a vital role in stimulating consumption and investment.
Potential Challenges
Emerging markets, while offering exciting investment opportunities, are not without their inherent risks. These markets are often characterized by dynamic economic landscapes, volatile political climates, and substantial currency fluctuations. Navigating these complexities requires a deep understanding of the potential obstacles to growth, and careful consideration of the factors that can influence investment decisions. A proactive approach, coupled with a nuanced understanding of these challenges, is key to maximizing returns while minimizing potential losses.
Currency Fluctuations and Investment Decisions
Currency fluctuations represent a significant factor influencing investment decisions in emerging markets. Appreciation or depreciation of a local currency against major trading currencies can dramatically impact the profitability of investments. For instance, a strengthening local currency can make exports less competitive, while a weakening currency can lead to increased import costs, affecting overall economic performance. Investors need to carefully consider the potential for currency risk when assessing emerging market opportunities.
A robust understanding of macroeconomic trends and the factors that influence exchange rates is critical for mitigating potential losses. Hedging strategies and a flexible investment approach are vital in managing this inherent volatility.
Managing Macroeconomic Instability
Emerging markets frequently face macroeconomic instability, characterized by fluctuating inflation rates, interest rates, and government debt levels. Such volatility can significantly impact investor confidence and profitability. Economic shocks, such as sudden changes in commodity prices or global economic downturns, can destabilize an economy and affect investment returns. For example, sharp increases in interest rates in a country with significant external debt can create a crisis situation.
Investors need to carefully assess the resilience of the economic fundamentals in an emerging market, considering factors like the stability of government institutions and the effectiveness of economic policies. This assessment involves evaluating the country’s ability to manage these challenges and maintain economic stability.
Political and Regulatory Uncertainty
Political and regulatory uncertainty poses a considerable challenge to investors in emerging markets. Changes in government policies, political instability, and bureaucratic hurdles can disrupt business operations and create unpredictable investment environments. For instance, sudden changes in tax laws or regulations can significantly impact the profitability of businesses operating in a particular market. The unpredictability of political and regulatory environments necessitates a thorough understanding of the current political climate and potential future policy shifts.
Careful due diligence, including analysis of legal frameworks and political risk assessments, is crucial for mitigating the potential negative impact of such uncertainties.
Potential Challenges and Impact
| Potential Challenge | Impact on Emerging Market Growth |
|---|---|
| Currency Fluctuations | Can significantly impact profitability of investments, potentially leading to losses if not adequately hedged. Exacerbates import/export difficulties, affecting overall economic performance. |
| Macroeconomic Instability | Can lead to decreased investor confidence and reduced profitability. Economic shocks can destabilize an economy, affecting investment returns. |
| Political and Regulatory Uncertainty | Can disrupt business operations, creating unpredictable investment environments and potentially reducing profitability. Changes in tax laws or regulations can negatively impact businesses. |
Future Projections
Emerging markets are poised for significant growth in the coming years, driven by factors such as rising populations, increasing disposable incomes, and expanding middle classes. However, navigating global uncertainties and potential challenges is crucial for sustained success. This section delves into the projected performance of emerging markets over the next five years, considering key global trends and the role of international organizations.
Projected Performance Over the Next 5 Years
Emerging markets are anticipated to exhibit robust growth over the next five years, fueled by ongoing economic reforms, technological advancements, and increasing foreign direct investment. Factors like urbanization and infrastructure development will also contribute significantly to this growth trajectory. While specific growth rates will vary across different regions and sectors, a general upward trend is expected. Historical data and current economic indicators support this optimistic outlook.
Impact of Key Global Trends
Global trends such as technological advancements, geopolitical shifts, and climate change will significantly influence the trajectory of emerging markets. The rise of e-commerce and digitalization, for example, presents opportunities for businesses in emerging markets to expand their reach and access new customer bases. However, the increasing reliance on digital infrastructure also necessitates investments in cybersecurity and digital literacy programs.
Role of International Organizations
International organizations like the World Bank and the IMF play a crucial role in supporting emerging market development. They provide financial assistance, technical expertise, and policy guidance to countries striving to achieve economic stability and sustainable growth. These organizations’ programs often focus on infrastructure development, education, and healthcare, which are crucial for long-term economic prosperity. Examples include support for infrastructure projects in Africa and Asia, promoting good governance, and facilitating trade agreements.
Policy Decisions Affecting Emerging Market Prospects
Government policies and regulations play a significant role in shaping the prospects of emerging markets. Proactive policies aimed at attracting foreign investment, fostering innovation, and promoting entrepreneurship can accelerate economic growth. Conversely, policies that stifle competition or hinder market access can negatively impact development. For example, regulations that favor domestic industries over foreign competitors can deter foreign investment, which is often a crucial source of capital and expertise.
Tax policies, trade agreements, and environmental regulations all significantly influence emerging market prospects.
Potential Future Scenarios
| Scenario | Growth Rate (Average Annual)% | Key Drivers | Potential Challenges |
|---|---|---|---|
| Optimistic | 6-8% | Strong global demand, sustained FDI, favorable policy decisions | Geopolitical tensions, inflation, supply chain disruptions |
| Moderate | 4-6% | Moderate global demand, cautious FDI, mixed policy decisions | Geopolitical risks, inflation, cybersecurity concerns |
| Challenging | 2-4% | Weak global demand, reduced FDI, unfavorable policy decisions | Geopolitical instability, inflation, supply chain bottlenecks |
The table above illustrates potential future scenarios for emerging markets, highlighting the key drivers, potential challenges, and associated growth rates. These scenarios are not mutually exclusive and the actual outcomes may vary based on a combination of factors.
Illustrative Data
Emerging markets are a dynamic and often volatile part of the global economy. Understanding the current state of trade flows, the impact of commodities, remittance flows, population growth, and historical performance is crucial for investors and policymakers alike. This section will provide illustrative data to paint a clearer picture of these interconnected factors.
Trade Flows Between Developed and Emerging Markets
Trade between developed and emerging markets has been a significant driver of global economic growth. The interplay of these economies often involves developed nations exporting manufactured goods and technology to emerging markets in exchange for raw materials and agricultural products. This exchange can be highly beneficial for both sides, fostering economic development in emerging economies and driving innovation in developed ones.
Data from the World Bank and the International Monetary Fund (IMF) can provide a comprehensive picture of the current trade flows.
Impact of Global Commodity Prices on Emerging Markets
Global commodity prices can significantly influence the economic performance of emerging markets. These markets often heavily rely on the export of raw materials like oil, minerals, and agricultural products. Fluctuations in global demand and supply for these commodities can lead to substantial swings in export revenues and overall economic growth. For instance, a sudden drop in oil prices can significantly impact oil-exporting emerging economies, while a surge in demand for minerals can boost the economies of countries rich in those resources.
The extent of the impact depends on the level of diversification of the economy.
Role of Remittances in Supporting Emerging Economies
Remittances play a crucial role in supporting emerging economies. Migrant workers often send substantial sums of money back to their home countries, bolstering household incomes and contributing significantly to economic growth. These flows can support critical needs like education, healthcare, and housing, as well as stimulate local businesses. Data from the World Bank and the IMF can show the substantial amount of remittances received by many emerging economies.
This influx of capital is often essential for economic stability.
Influence of Population Growth on Economic Output in Emerging Markets
Population growth in emerging markets often presents both opportunities and challenges. A larger population can potentially drive economic growth through a larger labor force and increased consumption. However, rapid population growth can also strain infrastructure, resources, and social services. The speed and manner of population growth directly impacts the rate and direction of economic output. Consider, for instance, countries with a young population, which might experience faster economic growth, but also face pressure to create jobs and address growing social needs.
The demographic profile, including age distribution, will affect the type of growth.
Historical Performance of Emerging Markets
| Year | Average Return (Emerging Markets Index) |
|---|---|
| 2010 | 12.5% |
| 2015 | 9.8% |
| 2020 | 11.2% |
The table above presents a simplified historical view of emerging market performance. This is just a snapshot, and it’s essential to consider various factors that may have influenced these returns, such as global economic conditions, political stability, and specific industry performance. Detailed analysis of specific sectors and individual countries would be necessary to gain a complete picture. Further research would be needed to understand the specific factors that drive returns in these markets.
Different indices would provide varying results.
Last Point

In conclusion, emerging markets offer a compelling investment case, but with inherent risks. While the bullish outlook is encouraging, careful consideration of the various factors, from economic drivers to potential challenges, is crucial. Thorough research and a well-defined investment strategy are essential for navigating the complexities of this dynamic market. This analysis aims to provide a comprehensive understanding, equipping you with the insights needed to make informed decisions.
FAQ Resource
What are the key economic drivers influencing emerging market performance?
Technological advancements, foreign direct investment, infrastructure development, and domestic consumption are key drivers. Each plays a significant role in shaping the economic trajectory of emerging markets.
What are the potential challenges to emerging market growth?
Currency fluctuations, macroeconomic instability, political and regulatory uncertainty, and global commodity price swings are all potential obstacles. These factors can impact investment decisions and overall economic performance.
How does global economic condition affect emerging markets?
Global economic conditions, including interest rate adjustments, have a direct correlation with emerging market performance. Fluctuations in global markets can significantly impact emerging markets, and vice versa.
What are some specific investment vehicles to consider in emerging markets?
Stocks, bonds, and potentially real estate investments are among the investment vehicles available. However, each carries its own level of risk, which should be carefully assessed based on your individual investment profile.
