Financial Reporting Update Revenue Recognition IR
Financial reporting update revenue recognition IR unveils the intricacies of how companies report their financial performance, focusing on revenue recognition principles and investor relations strategies. This comprehensive overview details the key elements of these updates, from the foundational principles of revenue recognition to the crucial role of investor relations in communicating these changes to the market. Understanding this process is vital for investors, analysts, and anyone interested in comprehending a company’s financial health and future prospects.
The update process involves a careful analysis of various factors impacting revenue recognition, such as industry specifics, regulatory changes, and the potential for errors. We’ll explore the methods used to accurately reflect these changes on financial statements, and discuss the significance of effective communication strategies for stakeholders.
Overview of Financial Reporting Update
Financial reporting updates are crucial for companies to transparently communicate their financial performance and position to stakeholders. These updates provide a snapshot of the company’s health, enabling investors, creditors, and analysts to make informed decisions. Accurate and timely reporting is essential for maintaining investor confidence and ensuring the company’s long-term viability.Financial reporting updates are not just about presenting numbers; they’re about conveying a story.
They highlight key trends, explain significant events, and offer context to the financial data. By presenting this narrative, companies can effectively communicate their financial health and strategic direction.
Purpose and Importance of Financial Reporting Updates
Financial reporting updates, whether quarterly or annually, are essential for maintaining investor confidence and demonstrating the company’s ability to achieve its financial goals. These updates provide a crucial platform for companies to communicate their financial performance, allowing stakeholders to assess the company’s health and make informed decisions. Transparency and accuracy are paramount in maintaining trust and building a strong reputation.
Components of a Financial Reporting Update
A typical financial reporting update includes several key components. Revenue recognition is a critical element, as it reflects the company’s ability to generate income from its operations. Other significant components include a summary of financial performance (e.g., revenue, expenses, and profit/loss), a discussion of key financial trends, and a review of the company’s overall financial position. Management’s discussion and analysis (MD&A) often accompanies these updates, providing context and insights into the reported data.
Revenue Recognition in Financial Reporting Updates
Revenue recognition is a crucial element in financial reporting updates. It Artikels how a company records revenue, typically following accounting principles like recognizing revenue when goods or services are delivered and earned. Specific methodologies vary depending on the industry and nature of the transactions. A well-defined revenue recognition policy enhances the reliability and comparability of financial statements across different periods.
Examples of Financial Reporting Updates, Financial reporting update revenue recognition ir
Different types of financial reporting updates exist, each with specific characteristics. Quarterly reports typically focus on recent performance and provide an insight into the company’s progress during the quarter. Annual reports offer a comprehensive overview of the company’s performance throughout the year, providing context and analysis. Interim reports, such as those released mid-year, present an overview of performance up to that point, often highlighting key achievements or challenges.
Timeline of a Typical Financial Reporting Update Cycle
| Phase | Duration | Key Activities |
|---|---|---|
| Planning | 1-2 weeks | Defining the scope, gathering data, and preparing the report |
| Data Collection & Analysis | 2-4 weeks | Gathering and verifying financial data, analyzing key trends, and identifying significant events. |
| Drafting & Review | 1-2 weeks | Preparing the draft report, reviewing the accuracy and completeness of the data, and seeking approvals from relevant stakeholders. |
| Dissemination | 1 day | Publishing the report to investors and stakeholders. |
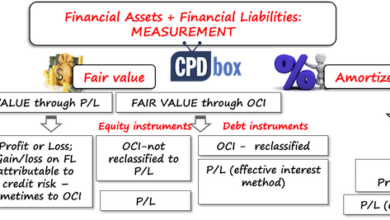
Revenue Recognition in Financial Reporting
Revenue recognition is a crucial aspect of financial reporting, dictating how and when companies record revenue. Accurate revenue recognition ensures that financial statements reflect a company’s true financial performance, enabling investors, creditors, and other stakeholders to make informed decisions. The principles governing revenue recognition are complex and have evolved over time to address evolving business models and economic realities.
Fundamental Principles of Revenue Recognition
Revenue recognition principles are designed to ensure consistency and transparency in financial reporting. These principles focus on recognizing revenue when it is earned and realizable. Earned means that the performance obligations to the customer have been fulfilled. Realizable means that there’s a reasonable expectation that the company will collect the revenue. Crucially, revenue recognition isn’t tied to cash receipt but rather to the transfer of promised goods or services.
Key Factors Influencing Revenue Recognition Decisions
Several key factors influence revenue recognition decisions, including the nature of the transaction, the terms of the contract, the risks and rewards associated with the transaction, and the business model. For example, in software sales, if the customer can access and use the software immediately, revenue might be recognized upon delivery. However, if the customer needs to be trained, revenue might be recognized over time.
The specific circumstances of each contract are carefully considered.
Different Revenue Recognition Methods
Various revenue recognition methods exist, each suitable for specific types of transactions. One common method is recognizing revenue over time, applicable when the customer receives the benefit of the goods or services as they are being provided. Another approach is recognizing revenue upon completion of the transaction, often used in construction or manufacturing. Understanding the characteristics of each method is essential for proper application.
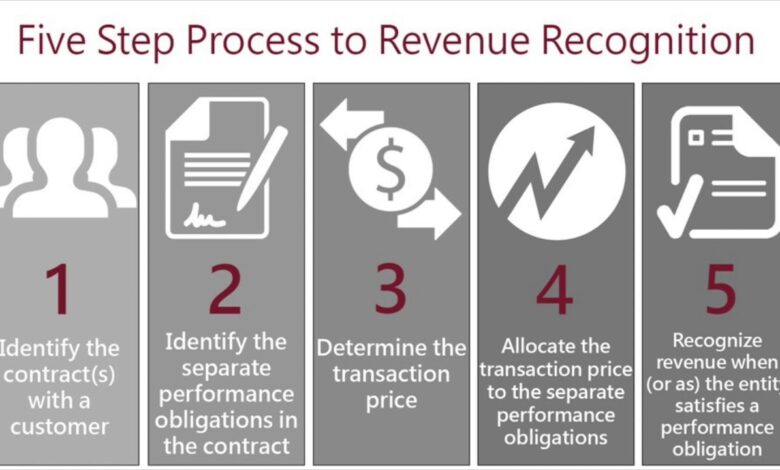
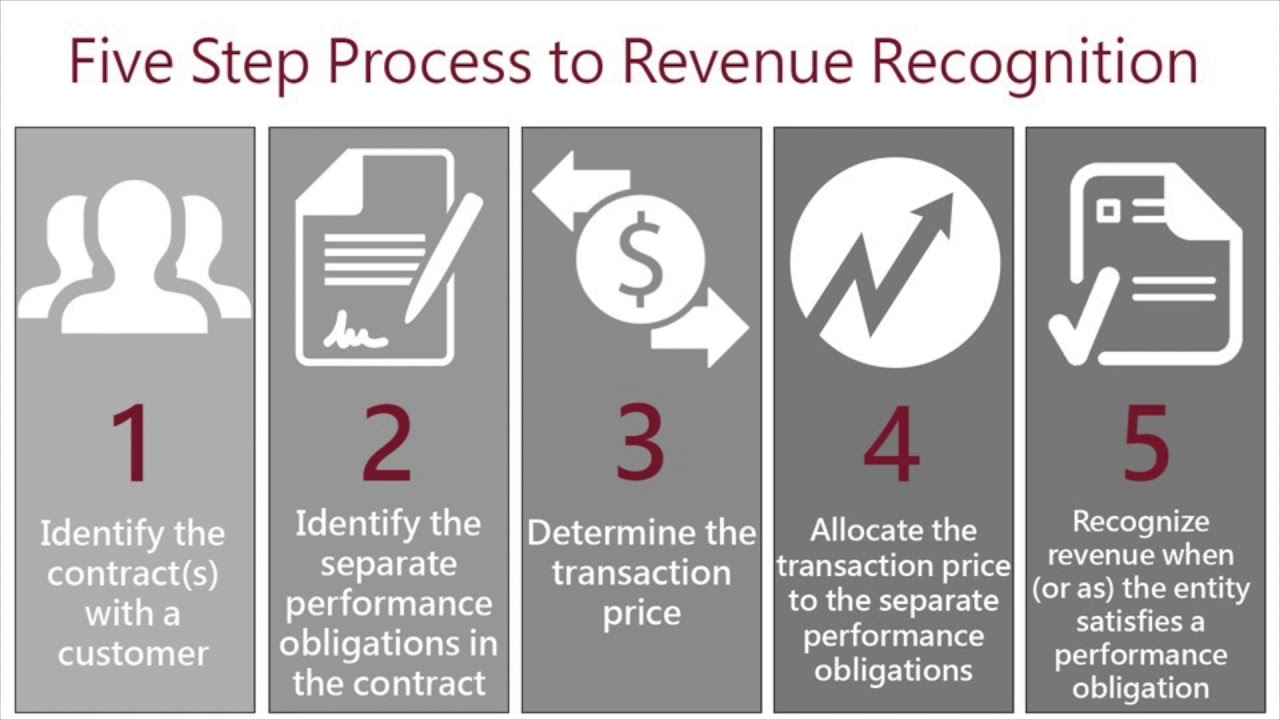
Steps Involved in Applying a Specific Revenue Recognition Standard
The steps involved in applying a revenue recognition standard, like the one issued by the International Accounting Standards Board (IASB) or the Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB), generally follow a structured process. This is crucial for consistency and comparability in financial reporting.
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| 1. Identify the contract with a customer | This involves determining whether a contract exists between the company and the customer. |
| 2. Identify the performance obligations in the contract | This involves identifying the distinct promises to transfer goods or services to a customer. |
| 3. Determine the transaction price | This involves determining the amount of consideration the company expects to receive from the customer. |
| 4. Allocate the transaction price to the performance obligations | This involves dividing the transaction price among the distinct performance obligations. |
| 5. Recognize revenue when (or as) the company satisfies a performance obligation. | Revenue is recognized when control of the goods or services is transferred to the customer. |
Importance of IR (Investor Relations) in Reporting Updates

Investor relations (IR) plays a crucial role in effectively communicating financial reporting updates to the investment community. A well-executed IR strategy can significantly impact investor confidence and market perception, ultimately affecting a company’s stock price and overall success. This crucial link between the company’s financial performance and investor sentiment is often overlooked, but it’s a vital aspect of any successful reporting update.Investor relations acts as a bridge between a company’s financial performance and the market’s perception of that performance.
The role extends beyond simply disseminating information; it involves crafting a narrative that resonates with investors, addressing concerns, and fostering transparency. This active engagement builds trust and ultimately impacts investor decisions.
Disseminating Financial Reporting Updates
Effective dissemination of financial reporting updates is paramount to maintaining investor confidence. IR professionals utilize various channels to ensure timely and comprehensive communication. These channels range from press releases and investor presentations to conference calls and interactive investor websites. By leveraging a multi-faceted approach, companies can ensure the broadest possible audience receives critical information.
- Press Releases: Concise, factual announcements disseminated to media outlets and financial news services. These releases typically summarize key highlights of the financial report, ensuring rapid distribution of the information.
- Investor Presentations: Detailed presentations often accompanied by Q&A sessions. These provide an in-depth look at the financial data and the company’s outlook.
- Conference Calls: A live audio/video broadcast where management teams discuss the financial results and address investor questions. This is a vital forum for direct engagement and explanation.
- Investor Websites: Dedicated sections on investor websites, often featuring interactive dashboards, presentations, and detailed financial statements. This allows investors to access information at their convenience and engage with the company in a more interactive way.
Impact on Investor Confidence and Market Perception
Investor relations activities significantly impact investor confidence and the overall market perception of a company. Positive communication strategies build trust, which can translate to increased investor confidence and a more favorable market response. Conversely, poor communication can damage investor confidence and negatively impact the stock price.
- Transparency and Clarity: A clear and transparent approach to financial reporting builds trust. Investors appreciate the ability to understand the company’s performance and its future prospects. The more transparent a company is, the more investors are inclined to view the company positively.
- Proactive Communication: Proactive communication, anticipating investor questions and concerns, can address issues before they escalate. This proactive approach demonstrates a company’s commitment to transparency and builds investor trust.
- Addressing Concerns: Addressing investor concerns promptly and thoroughly can alleviate anxieties and prevent negative market reactions. This approach ensures a positive impact on market perception and investor confidence.
Strategies for Effective Investor Communication
Companies employ various strategies to effectively communicate with investors. These strategies often involve tailoring messages to specific investor segments and utilizing multiple channels to reach a broad audience. Regular communication and engagement are key to building and maintaining investor trust.
- Tailoring Messages: Tailoring communication to the specific needs and interests of different investor segments is crucial. For instance, institutional investors may require detailed financial analysis, while individual investors might appreciate more concise summaries.
- Utilizing Multiple Channels: Using a diverse array of communication channels—from investor presentations to social media—allows companies to reach a wider audience and cater to different investor preferences.
- Building Relationships: Developing relationships with key investors and analysts can foster understanding and trust. Direct engagement builds a more positive image of the company.
Examples of Communication Channels
Different communication channels play vital roles in conveying financial reporting updates. The choice of channel depends on the specific information being disseminated and the target audience.
| Communication Channel | Description | Target Audience |
|---|---|---|
| Press Release | Short, factual announcement about key financial results. | Broad investor base, media outlets. |
| Investor Presentation | Detailed presentation outlining financial performance and outlook. | Institutional investors, analysts. |
| Conference Call | Live discussion with management team, addressing investor questions. | Institutional investors, analysts, individual investors. |
| Investor Website | Dedicated section with interactive tools, financial statements, and presentations. | All investor segments. |
Analyzing Revenue Recognition Practices
Revenue recognition, a cornerstone of financial reporting, dictates when a company records revenue from a transaction. Understanding its intricacies is crucial for investors, analysts, and stakeholders alike. This section delves into the diverse application of revenue recognition across industries, highlighting potential pitfalls and consequences of misapplication.Revenue recognition principles are not universally applied, and their practical application often requires careful consideration of the specific circumstances of each transaction.
Different industries face unique challenges in implementing these standards, leading to variations in revenue recognition practices.
Comparing Revenue Recognition Practices Across Industries
Various industries have distinct revenue streams and transaction structures. This variation often necessitates adjustments to the application of revenue recognition standards. For instance, software companies frequently recognize revenue over time as customers utilize their products, while construction companies often recognize revenue based on the completion of specific stages of a project. The diverse approaches illustrate the necessity for a nuanced understanding of industry-specific practices.
Potential Challenges in Accurate Revenue Recognition
Accurate application of revenue recognition standards is challenging for several reasons. Contract complexity, particularly in long-term agreements, can often lead to ambiguities about the timing and measurement of revenue. Furthermore, the interpretation of accounting standards can differ among entities, potentially resulting in inconsistencies in reported revenue.
Common Pitfalls in Revenue Recognition
Several common pitfalls can lead to inaccurate revenue recognition. One pitfall is failing to appropriately account for contract terms, such as contingencies or penalties. For example, a company might recognize revenue prematurely if it overlooks a clause requiring the customer to return the product under specific circumstances. Another pitfall is misclassifying revenue streams, which can distort the true financial picture of a company.
For example, if a company mistakenly treats a one-time service fee as recurring revenue, it may inflate its reported earnings.
Potential Consequences of Inaccurate Revenue Recognition
Inaccurate revenue recognition can have significant consequences. It can mislead investors, analysts, and other stakeholders, potentially affecting investment decisions and market perceptions. Incorrect revenue recognition can also lead to legal and regulatory issues, including penalties and fines. Ultimately, the financial health and reputation of the company are at risk.
Impact of Updates on Financial Statements

Financial reporting updates, particularly those concerning revenue recognition, significantly impact the presentation of a company’s financial performance. These changes ripple through the core financial statements, demanding careful analysis to understand the implications for investors and stakeholders. The impact isn’t merely cosmetic; it directly affects the perceived profitability, liquidity, and overall health of the organization.Understanding how these updates affect key financial statements is crucial for investors and analysts to make informed decisions.
These changes require a shift in perspective, demanding a more nuanced approach to interpreting the figures presented. The impact is not uniform across all companies; it depends heavily on the nature of the company’s operations and the specifics of the revenue recognition policies in place.
Impact on the Income Statement
Changes in revenue recognition directly influence the income statement, impacting the timing and amount of revenue reported in specific periods. This can affect the overall reported earnings and profit margins. For example, if a company delays recognizing revenue until a later period due to a change in policy, the current period’s income will be lower than it would have been under the previous method.
Conversely, accelerating the recognition of revenue could inflate current-period earnings.
Impact on the Balance Sheet
The balance sheet is also affected by revenue recognition updates, primarily through changes in accounts receivable and deferred revenue. As revenue recognition criteria shift, the timing of when revenue is recorded and when related assets and liabilities are recognized also changes. For instance, a new policy might require a company to record a portion of the revenue as deferred revenue, leading to an increase in liabilities on the balance sheet.
Impact on Key Financial Metrics
Changes in revenue recognition policies can significantly impact various financial metrics used to assess a company’s performance. Analyzing the specific impact on these metrics provides valuable insight into the long-term implications of the update.
| Financial Statement Metric | Impact of Change in Revenue Recognition | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Revenue | Increased/Decreased depending on the timing of recognition | A company shifting from recognizing revenue upon delivery to recognizing revenue over time will likely show lower revenue in the period of delivery and higher revenue over the period of service. |
| Gross Profit | Potentially increased or decreased due to timing of expense recognition | Recognizing revenue sooner might show higher gross profit in the current period if the associated expenses are recognized later. |
| Net Income | Increased/Decreased due to the impact on revenue and expenses | A change in revenue recognition might lead to a lower net income in the current period but potentially higher net income over the long term. |
| Accounts Receivable | Increased/Decreased depending on the timing of recognition | Companies recognizing revenue over time instead of upon delivery will see an increase in accounts receivable as they track the revenue earned over a period. |
| Deferred Revenue | Increased/Decreased depending on the timing of recognition | A company that recognizes revenue over a service period will likely see an increase in deferred revenue on the balance sheet. |
Reflecting Changes in Financial Statements
The changes in revenue recognition policies are reflected in the financial statements through adjusting entries, which are journal entries made to update the accounts for the effects of a change. These adjustments are made in the period of the change, and the prior periods are not restated. Comprehensive disclosure is crucial to enable users to understand the nature and impact of these changes.
Changes in accounting policies should be disclosed in the notes to the financial statements, explaining the rationale for the change and the impact on the financial statements.
Communicating Financial Reporting Updates to Stakeholders
Keeping stakeholders informed is crucial for any financial reporting update. Transparency builds trust and allows for informed decision-making. This section dives into the various methods and strategies used to effectively communicate these updates to different groups, from investors to the media.Effective communication is paramount during financial reporting updates. It fosters understanding and reduces uncertainty, crucial elements in maintaining stakeholder confidence.
The methods chosen should align with each stakeholder’s specific needs and information preferences, maximizing the impact of the message.
Methods for Communicating Updates
Different methods are employed to deliver financial reporting updates, each catering to the specific needs and preferences of various stakeholders. Direct communication channels, such as investor calls and presentations, allow for real-time engagement and Q&A sessions. News releases, press conferences, and investor relations websites act as readily accessible sources of information for a broader audience. Furthermore, tailored reports and presentations are distributed to specific stakeholders, ensuring the message is delivered precisely.
Communication Strategies for Different Stakeholders
The strategy for communication must be tailored to the specific stakeholder group. For example, investors and analysts require in-depth financial data and analysis, while the media seeks concise, newsworthy summaries.
Investor Communication
Investor relations teams often host conference calls and webcasts with financial analysts and investors to discuss the update. Detailed presentations highlighting key financial metrics and performance indicators are frequently shared. These communications are usually accompanied by a comprehensive investor relations website that provides easy access to financial statements, presentations, and past communications.
Analyst Communication
Analysts, driven by research and financial modeling, require thorough data and insights. Tailored presentations, frequently updated investor relations websites, and detailed financial statements are provided to support their research and modeling efforts. Analysts often receive invitations to exclusive investor conferences and meetings to gain further insights and discuss their analysis.
Media Communication
The media seeks concise and newsworthy summaries of the financial update. Press releases, often with key highlights and quotes from leadership, are distributed to news outlets. Media conferences and interviews are scheduled to address questions and provide a platform for disseminating the update.
Key Messages and Target Audiences
| Communication Channel | Key Messages | Target Audience |
|---|---|---|
| Investor Calls/Webinars | Key financial metrics, operational updates, future outlook, Q&A session | Investors, analysts |
| Press Releases | Summary of key findings, impact on the business, executive quotes | Media, general public |
| Investor Relations Website | Comprehensive financial information, presentations, past releases, contact information | Investors, analysts, media, general public |
| Tailored Reports | Specific data, detailed analysis, personalized insights | Investors, analysts, select stakeholders |
Examples of Effective Communication Strategies
A company that experienced a surge in revenue due to a successful product launch communicated this update by hosting an investor call with analysts and investors. This call included detailed analysis of the product’s performance and its implications for future revenue projections. Simultaneously, a concise press release highlighting the key figures and positive outlook was disseminated to the media.
The company’s investor relations website was updated with the detailed financial statements and the call recording. This integrated approach ensured all stakeholders received the relevant information.
Illustrative Examples of Reporting Updates
Financial reporting updates are crucial for maintaining transparency and investor confidence. These updates often reflect changes in accounting standards, operational shifts, or new business initiatives. Analyzing real-world examples provides valuable insights into the process, challenges, and outcomes of these updates.
Netflix’s 2011 Revenue Recognition Change
Netflix’s 2011 change in revenue recognition exemplifies a significant reporting update. Previously, Netflix recognized revenue upon subscription commencement. The 2011 update shifted to recognizing revenue over the subscription period, reflecting a more accurate depiction of the streaming service’s revenue stream.
Challenges Faced
The transition required a complete overhaul of their accounting systems and processes. The biggest challenge was the need to accurately estimate the revenue over the subscription period. The company had to adjust its forecasting models and potentially reconcile past financial statements.
Strategies Employed
Netflix employed several strategies to navigate this change. These included meticulous system upgrades, robust revenue recognition software, and comprehensive training for accounting staff. Furthermore, they likely established clear guidelines and procedures to ensure consistent application of the new standard across the organization.
Impact on Financial Performance and Market Valuation
The update led to a more realistic portrayal of Netflix’s revenue and profitability. Initially, the change might have caused some fluctuations in quarterly reports as the company adjusted to the new method. However, in the long run, the update provided a clearer picture of their revenue stream, positively impacting market perception and potentially attracting more investors.
Communication to Stakeholders
Netflix likely communicated the update to investors through detailed disclosures in their annual reports, investor presentations, and conference calls. They likely highlighted the rationale behind the change, Artikeld the impact on financial statements, and provided forecasts for future performance under the new method. This transparent communication was essential to manage investor expectations and maintain confidence.
Salesforce’s Adoption of ASC 606
Salesforce’s adoption of the new revenue recognition standard (ASC 606) was another noteworthy example. The standard requires a more detailed approach to recognizing revenue from contracts with customers, emphasizing the allocation of consideration to different performance obligations.
Challenges Faced
The complexity of ASC 606 presented a considerable challenge. Many contracts involved multiple services or products with varying performance obligations. Salesforce needed to analyze these complex contracts and appropriately allocate revenue to each element.
Strategies Employed
Salesforce likely implemented robust software solutions and processes to comply with ASC 606. They also needed to establish a clear methodology for identifying, measuring, and recognizing revenue. This required significant training and knowledge transfer across the organization.
Impact on Financial Performance and Market Valuation
Salesforce’s transition to ASC 606 could have impacted reported revenue figures and potentially influenced market valuation. The revised reporting standards would provide a more precise representation of their revenue streams.
Communication to Stakeholders
Salesforce, like Netflix, likely provided thorough explanations of the change in their investor reports and communications. These explanations would include the rationale behind adopting the new standard, the expected impact on future earnings, and a discussion of the methodology employed. This communication helped manage stakeholder expectations and maintain transparency.
Trends and Future of Financial Reporting
The landscape of financial reporting is constantly evolving, driven by technological advancements, changing business models, and evolving regulatory frameworks. Understanding these trends is crucial for businesses to adapt and ensure their financial statements accurately reflect their performance and position. This section explores emerging trends in financial reporting and revenue recognition, their potential impact on future reporting updates, and potential regulatory changes.
Emerging Trends in Financial Reporting
Several emerging trends are reshaping financial reporting. Increased reliance on technology, particularly cloud-based accounting systems and AI-powered analytics, is streamlining processes and enhancing data accuracy. The rise of subscription-based models and other complex revenue streams is challenging traditional revenue recognition methods. Sustainability reporting, driven by investor and stakeholder demand for environmental, social, and governance (ESG) data, is gaining prominence.
Influence of Trends on Future Reporting Updates
These trends are likely to influence future reporting updates in several ways. Updates will likely incorporate more robust disclosures related to technology adoption, subscription revenue models, and sustainability metrics. Furthermore, the increasing sophistication of accounting software might lead to changes in the required level of detail in financial statements. The complexity of new business models necessitates more detailed explanations of accounting policies and methods.
Potential Future Regulatory Changes in Revenue Recognition Standards
Regulatory bodies are continuously assessing the effectiveness of existing revenue recognition standards. Future changes might focus on enhancing clarity and consistency in applying the standards to new and evolving business models, including subscription services, software licensing, and digital products. There could be a push for more comprehensive disclosures regarding the risks and uncertainties associated with revenue recognition. An example is the evolving use of cloud-based accounting systems; regulators might require more detailed information about the systems used and their impact on financial reporting.
Impact of Changes on Business Practices and Financial Statements
The impact of potential changes will be multifaceted. Businesses will need to adapt their internal processes to comply with new standards and disclosures. This may require investments in new software, training for staff, and adjustments to internal control procedures. Financial statements will likely reflect more nuanced disclosures about revenue recognition, including breakdowns of different revenue streams and associated risks.
For example, companies with substantial subscription revenue may need to provide more granular details about contract terms, customer churn rates, and estimated future revenue.
Predicting the Impact of Changes on Financial Statements
Predicting the precise impact on financial statements is challenging. However, companies with significant exposure to emerging business models (such as subscription-based services) should expect more scrutiny from investors and analysts. For example, a company transitioning from traditional sales to a subscription model might experience a change in revenue recognition patterns, potentially impacting reported revenue and earnings over time.
Moreover, companies failing to adapt to the evolving landscape of financial reporting may face increased scrutiny and potential regulatory actions.
Concluding Remarks: Financial Reporting Update Revenue Recognition Ir
In conclusion, financial reporting updates, especially those concerning revenue recognition, are critical for both internal decision-making and external market perception. By understanding the components, impacts, and communication strategies, investors and stakeholders can better assess a company’s financial health and future potential. The insights provided in this discussion equip readers with a better understanding of the dynamics surrounding these updates, allowing them to make informed decisions.
Commonly Asked Questions
What are the typical components of a financial reporting update?
Typical components include an overview of the update, details on revenue recognition methods, an explanation of the impact on financial statements, and communication strategies for stakeholders.
How do revenue recognition methods differ across industries?
Revenue recognition practices vary based on the specifics of each industry. Factors like the nature of products or services, contract terms, and the timing of customer payments influence the chosen method.
What are the potential consequences of inaccurate revenue recognition?
Inaccurate revenue recognition can lead to misrepresentation of a company’s financial health, impacting investor confidence and potentially resulting in regulatory penalties or legal actions.
What are some emerging trends in financial reporting?
Emerging trends include greater transparency in financial disclosures, an increased emphasis on sustainability reporting, and the potential for increased use of data analytics in the reporting process.