FRC Proposes UK/Ireland Accounting Standards Amendments
Frc proposes uk ireland accounting standards amendments – FRC proposes UK/Ireland accounting standards amendments, signaling potential shifts in how businesses in the UK and Ireland report their financial performance. This initiative is a response to evolving economic landscapes and regulatory pressures. The proposed changes aim to update existing standards, ensuring they remain relevant and aligned with best practices. A deep dive into the proposal reveals a comprehensive review, touching upon historical context, specific amendments, and potential impacts across different sectors.
The framework governing accounting practices in the UK and Ireland has been under scrutiny for some time. Significant economic and regulatory changes have prompted the need for adjustments. This proposal from the FRC Artikels specific changes to accounting standards, addressing existing issues and aiming to improve financial reporting transparency and consistency. The proposal encompasses a thorough impact assessment, considering the potential benefits and drawbacks for various stakeholders, including small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) and large corporations.
Background of the Proposal
The Financial Reporting Council (FRC) in the UK and the Irish Accounting Standards Board (IASB) have a long history of shaping accounting standards in their respective jurisdictions. This proposal for amendments reflects a continuous evolution in response to changing economic landscapes and regulatory pressures. The fundamental aim is to ensure financial reporting remains reliable, comparable, and relevant to the needs of investors and stakeholders.
History of UK and Irish Accounting Standards
The UK’s accounting standards have evolved significantly since the adoption of the Companies Act of 1985. Initially, the standards were largely based on the principles-based approach, evolving toward more detailed and prescriptive standards. The UK’s journey has included periods of convergence with International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS). Similarly, Irish accounting standards have mirrored this evolution, often aligning with or adopting IFRS.
This historical progression has been crucial in maintaining consistency and comparability across different jurisdictions, a key aspect of international trade and investment.
You also can understand valuable knowledge by exploring global cfo survey rebuild revenue streams.
Current Framework Governing Accounting Practices
Currently, the UK follows IFRS, while Ireland also predominantly uses IFRS. The framework involves a complex interplay of legislation, regulations, and guidance issued by the FRC and the IASB. This framework is designed to provide a consistent structure for companies to report their financial performance and position. Crucially, it aims to ensure transparency and comparability of financial statements, allowing investors to make informed decisions.
Context for Proposed Amendments
These proposed amendments arise from a variety of factors, including evolving economic circumstances, new regulations, and feedback from various stakeholders. For example, the rise of new technologies and business models might necessitate adjustments to accounting standards to reflect these emerging trends. Amendments could also be in response to significant economic shifts, such as financial crises or major regulatory reforms.
Key Bodies Involved in the Proposal, Frc proposes uk ireland accounting standards amendments
The Financial Reporting Council (FRC) is the primary driver for the proposed amendments in the UK, while the Irish Accounting Standards Board (IASB) likely plays a pivotal role in developing and influencing the direction of the amendments. Collaboration with other regulatory bodies and industry stakeholders is essential for the success of the proposals. Governmental bodies, such as the UK Treasury and the Department of Finance in Ireland, also play an important oversight role.
Comparison of Existing Accounting Standards in the UK and Ireland
| Feature | UK | Ireland |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Accounting Framework | IFRS | IFRS |
| Governing Body | Financial Reporting Council (FRC) | Irish Accounting Standards Board (IASB) |
| Specific Legislation | Companies Act 2006 | Relevant Irish legislation |
| Enforcement Mechanisms | FRC enforcement procedures | IASB and relevant Irish regulatory oversight |
| Degree of Convergence with International Standards | High | High |
The table above highlights the key similarities and differences in the accounting standards frameworks of the UK and Ireland. Despite the convergence, minor differences in application or interpretation of IFRS may still exist, thus necessitating the amendment proposal. Maintaining a high level of alignment is essential to ensure consistency and facilitate cross-border financial transactions.
Proposed Amendments

The FRC’s proposed amendments to UK and Ireland accounting standards aim to enhance the reliability and comparability of financial reporting. These revisions are a crucial step in maintaining the integrity of the financial markets and fostering investor confidence. These adjustments are designed to address identified shortcomings and provide a more robust framework for financial reporting, particularly in light of evolving economic conditions and business practices.
Specific Changes Proposed
The proposed amendments span several key areas of accounting standards, focusing on improving transparency and accuracy. Significant changes target areas where existing standards lacked clarity or where practical application posed challenges for businesses. This comprehensive review ensures that standards remain relevant and adaptable to the changing landscape of financial reporting.
Key Areas of Amended Standards
The FRC has identified several key areas requiring amendments. These include, but are not limited to, revenue recognition, lease accounting, and financial instrument classification. These revisions aim to clarify and standardize the application of these principles across various business models, promoting consistency and accuracy in financial reporting.
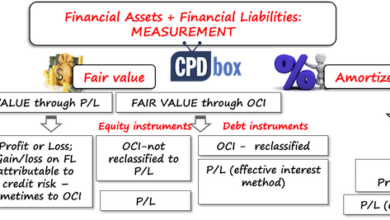
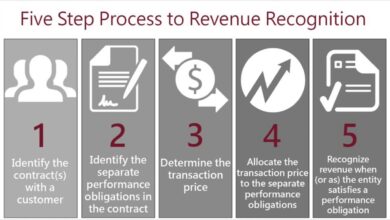
Revenue Recognition Amendments
The amendments to revenue recognition address the complexities surrounding contract arrangements. The proposed changes aim to provide more detailed guidance on recognizing revenue when contracts involve multiple deliverables or are subject to significant uncertainties. The updated framework offers a clearer and more consistent method for revenue recognition in complex transactions, ensuring that revenue is recognized when it is earned and measurable.
This will enhance the accuracy and reliability of reported revenue streams.
Lease Accounting Revisions
Significant changes are proposed for lease accounting. The updated standards aim to improve transparency by requiring all leases to be recognized on the balance sheet, irrespective of their term. This aligns the treatment of leases with the accounting for finance leases, improving comparability and providing a more complete picture of a company’s financial obligations. The revisions enhance the accuracy of reported liabilities and assets, reflecting the economic substance of leasing arrangements.
Financial Instrument Classification Refinements
The FRC proposes amendments to financial instrument classification, aiming to enhance the consistency and comparability of reporting across various financial instruments. These changes aim to clarify the criteria for classifying financial instruments as held-for-trading, held-to-maturity, or available-for-sale. This detailed guidance will assist businesses in accurately classifying their financial instruments, leading to more consistent and transparent reporting.
Detailed Table of Proposed Changes
| Current Provision | New Provision | Reasoning |
|---|---|---|
| Revenue recognized upon completion of the contract | Revenue recognized at various stages of the contract based on performance | Improved recognition of revenue streams during the contract lifecycle |
| Lease accounting based on the nature of the lease | All leases recognized on the balance sheet | Increased transparency in lease obligations, aligning with the economic substance of leasing |
| Vague criteria for classifying financial instruments | Clearer and more consistent criteria for classifying financial instruments | Improved comparability of financial instrument reporting across businesses |
Impact Assessment: Frc Proposes Uk Ireland Accounting Standards Amendments

The proposed amendments to UK and Ireland accounting standards represent a significant shift in how businesses report their financial performance. Understanding the potential impact on various stakeholders, from small businesses to multinational corporations, is crucial for effective adaptation and informed decision-making. This assessment explores the potential benefits and drawbacks, focusing on different sectors and the implications for financial reporting processes.
Potential Impact on Businesses
The amendments are likely to affect businesses in a variety of ways. Some changes might streamline reporting procedures, reducing administrative burden and costs. Conversely, new complexities could arise, demanding significant investment in training and technology upgrades. The magnitude of this impact will depend heavily on the specific nature of the amendment and the size and structure of the business.
For instance, smaller enterprises might face a steeper learning curve compared to large corporations with dedicated accounting teams.
Benefits of the Proposed Changes
Several potential benefits are anticipated. Improved comparability of financial statements across businesses and industries is a key advantage. This enhancement can facilitate better investment decisions and market analysis. Furthermore, enhanced transparency in financial reporting can build investor confidence and attract capital. The amendments might also encourage a more robust corporate governance framework.
Drawbacks of the Proposed Changes
However, potential drawbacks must also be acknowledged. Implementation costs for businesses, especially SMEs, could be substantial. Training staff on new accounting standards and adjusting existing systems will require time and resources. Furthermore, the amendments could lead to increased complexity in financial reporting, potentially impacting the accessibility and understandability of financial information.
Impact on Different Sectors
The impact on different sectors will vary. SMEs, with their often limited resources, might find the implementation more challenging. Large corporations, with their established accounting departments and technological infrastructure, might be better equipped to handle the changes. The impact will likely be more pronounced in sectors with complex business models or significant international operations.
Impact on Stakeholders
| Stakeholder | Potential Benefits | Potential Drawbacks |
|---|---|---|
| Investors | Improved comparability, enhanced transparency, potentially increased investor confidence | Increased complexity, potential delays in receiving accurate financial information, increased implementation costs |
| Businesses (SMEs) | Potential benefits of improved comparability, enhanced transparency | Higher implementation costs, potentially greater challenges in adapting to new standards |
| Businesses (Large Corporations) | Potential benefits of improved comparability, enhanced transparency | Higher costs of training, potential for increased complexity in financial reporting, increased demands on IT infrastructure |
| Regulators | Enhanced financial reporting, improved market stability | Potential increase in regulatory oversight, need for robust monitoring and enforcement |
Model Illustrating the Impact on Financial Reporting Processes
The proposed amendments might lead to a shift in the financial reporting cycle. For example, the inclusion of new disclosure requirements could necessitate the collection and analysis of additional data. The new standards could necessitate the use of specialized software and tools.
Example: A company previously reporting revenue on a cash basis might need to switch to an accrual basis, requiring the development of more sophisticated accounting systems and training for staff.
This transition might also involve the restructuring of internal teams and the reallocation of resources. Overall, the implementation of the amendments is likely to require a thorough review of current financial reporting procedures and potential adjustments to internal controls.
Public Consultation and Feedback
Transparency and stakeholder engagement are crucial in any standard-setting process. This section details the public consultation process for the proposed UK and Ireland accounting standards amendments, outlining the mechanisms for feedback, the timeline, and how the received input influenced the final proposals.
Public Consultation Process Summary
The consultation was a multi-faceted process designed to gather diverse perspectives. It employed various channels to ensure broad participation from stakeholders, including businesses, investors, and professional bodies. This approach aimed to capture a comprehensive range of viewpoints and experiences relevant to the proposed amendments.
Feedback Mechanisms
Stakeholders could submit feedback via a dedicated online portal, participate in webinars and Q&A sessions, or provide written submissions. These channels facilitated direct communication and engagement with the standard-setting bodies. The online portal offered a secure and accessible platform for submissions, while webinars and Q&A sessions allowed for real-time discussion and clarification of the proposals.
Consultation Timeline
The consultation period spanned 8 weeks, beginning on [Start Date] and concluding on [End Date]. This timeframe allowed ample opportunity for stakeholders to review the proposals, consider their implications, and provide their feedback. A detailed schedule outlining specific deadlines for different submission types was available on the consultation portal.
Remember to click how to clearly communicate feedback and expectations to understand more comprehensive aspects of the how to clearly communicate feedback and expectations topic.
Key Stakeholder Concerns
| Category of Concern | Specific Concerns |
|---|---|
| Complexity of Amendments | Several stakeholders expressed concerns about the complexity of the proposed amendments, particularly regarding the impact on small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). They highlighted the potential for increased compliance costs and the need for simplified guidance. |
| Practical Application | Concerns were raised about the practical application of certain amendments in diverse business contexts. Specific issues included difficulties in accurately measuring certain metrics and the lack of clarity on transitional arrangements. |
| Impact on Financial Reporting | Some stakeholders questioned the impact of the amendments on the overall quality and comparability of financial reporting. They also voiced concerns about the potential for increased complexity and inconsistencies in financial statements. |
| Implementation Challenges | Specific challenges related to implementation, including the need for training and capacity building for accountants, were highlighted. Stakeholders emphasized the importance of practical support during the transition period. |
Incorporation of Feedback
The feedback received during the consultation period was carefully analyzed by the standard-setting body. The proposals were reviewed to address the concerns raised by stakeholders. The degree of incorporation varied depending on the specific issue. Some amendments were adjusted directly based on feedback, while others were addressed through clarifications or supplementary guidance. A comprehensive report detailing the responses to the feedback is available on the [website address].
International Considerations

The proposed amendments to UK and Ireland accounting standards are not isolated events. Understanding their impact requires examining the global landscape of accounting practices. This section delves into the international implications, comparing the proposed changes to similar standards worldwide and exploring potential harmonization efforts.The proposed amendments seek to improve financial reporting transparency and comparability within the UK and Ireland.
However, a global perspective is crucial to assess the potential for these changes to contribute to a broader, more uniform approach to accounting standards internationally. This is vital for multinational corporations and investors seeking to understand financial statements across different jurisdictions.
International Comparisons of Accounting Standards
A key aspect of assessing the proposed amendments is comparing them to similar accounting standards globally. The International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) are the most widely adopted set of accounting standards globally, and it is essential to analyze how the proposed changes relate to them.
You also can understand valuable knowledge by exploring cima ethics confidentiality rules.
Alignment and Divergence from International Best Practices
The proposed changes might align with or diverge from international best practices. Analyzing the proposed amendments against established international standards is crucial to understand their global implications. For example, if the proposed changes enhance comparability with IFRS, they would contribute to a more unified global financial reporting environment. Conversely, significant divergence could create challenges for international investors and businesses operating in multiple jurisdictions.
Similarities and Differences with Other Jurisdictions
The following table highlights key similarities and differences between the proposed UK/Ireland amendments and those in other jurisdictions, specifically focusing on IFRS.
| Characteristic | UK/Ireland Proposed Amendments | IFRS | Other Jurisdictions (e.g., US GAAP) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Recognition of Revenue | Proposed changes align with IFRS in most cases, emphasizing the core principles of control and performance obligation fulfillment. | Revenue recognition is governed by IFRS 15, emphasizing the five-step model for recognizing revenue. | US GAAP has specific revenue recognition rules, often differing in detail from IFRS. |
| Leasing Standards | Likely alignment with IFRS 16 on lease accounting, moving towards a more comprehensive treatment of lease obligations. | IFRS 16 mandates the recognition of all leases as assets and liabilities on the balance sheet. | US GAAP has separate guidance on leasing that sometimes aligns with IFRS 16, but also has unique aspects. |
| Financial Instruments | Potential for alignment with IFRS 9 on financial instruments, which focuses on the fair value measurement and impairment of financial assets and liabilities. | IFRS 9 dictates how financial instruments should be classified, measured, and recognized. | US GAAP’s treatment of financial instruments often shares similarities with IFRS 9, though specific criteria can differ. |
This table demonstrates that there is a degree of overlap between the proposed UK/Ireland changes and current international standards, especially IFRS. However, there may be subtle differences that need further analysis.
Potential for Harmonization
The potential for harmonizing accounting standards across the UK, Ireland, and internationally is significant. Increased convergence would lead to greater transparency and comparability of financial statements. The proposed amendments can contribute to this harmonization effort. If these amendments are well-aligned with international standards, they could encourage a more unified approach, reducing the complexity of financial reporting for multinational corporations.
However, successful harmonization requires consistent efforts from various jurisdictions to align their accounting frameworks.
Potential Future Implications
The proposed amendments to UK and Ireland accounting standards represent a significant step forward, but their impact extends far beyond the present. Anticipating future developments is crucial for businesses and stakeholders to adapt and thrive in the evolving landscape. Understanding potential updates to the standards and the regulatory environment will be essential for navigating the changing economic conditions.The accounting world is dynamic.
Market forces, technological advancements, and evolving global regulations will undoubtedly shape the future of these standards. Proactive consideration of potential future implications ensures that businesses remain compliant and can leverage these changes to their advantage.
Potential Updates to Standards in Response to Market Changes
Market fluctuations and emerging technologies will drive future adjustments to the standards. Adapting to the changing needs of businesses and investors is paramount. For instance, the rise of cryptocurrencies and decentralized finance (DeFi) could necessitate modifications to existing accounting frameworks. Similarly, the increasing adoption of artificial intelligence (AI) in financial processes might demand adjustments to ensure the accuracy and reliability of financial reporting.
Consider the emergence of new business models, like subscription-based services or online marketplaces. These innovative structures may necessitate the creation of new accounting standards to reflect their unique characteristics.
Potential Changes to the Regulatory Environment
Changes in the regulatory environment will significantly impact the interpretation and application of accounting standards. International harmonization efforts and the introduction of new legislation will undoubtedly influence future amendments. For example, a shift towards greater sustainability reporting requirements, spurred by global initiatives like the UN Sustainable Development Goals, would necessitate revisions to accounting standards to incorporate environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors.
Anticipated Future Amendments and Their Implications
| Anticipated Amendment | Potential Implications ||—|—|| Inclusion of ESG factors in financial reporting | Increased transparency and accountability, potentially altering valuation models, investment decisions, and regulatory scrutiny. || Adaptation to new technologies (e.g., blockchain) | Potential development of new accounting principles for cryptocurrencies and decentralized finance, requiring updated standards to ensure accuracy and comparability. || Enhancement of financial reporting disclosures | Increased investor confidence, improved transparency in financial statements, and potentially more stringent reporting requirements for certain sectors.
|| Greater emphasis on sustainability | Enhanced disclosure requirements for environmental and social performance, potentially leading to new accounting standards and metrics for measuring and reporting sustainability impacts. |
Visual Representation of Potential Long-Term Impact on Financial Reporting
Imagine a dynamic, interconnected web representing the current accounting standards. New technologies and evolving market forces are depicted as external forces pulling and pushing on the web. The web itself is constantly being updated with new principles and regulations to ensure it remains relevant and effective in reflecting the complexities of modern financial reporting. This visualization demonstrates the continuous evolution of the accounting standards framework in response to the dynamic environment in which they operate.
The web’s nodes represent various accounting standards and regulations, and the connections between them represent their interdependencies and the flow of information within the financial reporting process. The external forces symbolize factors like market changes, new technologies, and evolving regulatory environments. The continuous adjustments to the web represent the adaptation of accounting standards to these dynamic factors, ensuring that financial reporting remains accurate, reliable, and relevant.
Final Summary
In conclusion, the FRC’s proposed amendments to UK/Ireland accounting standards represent a significant step toward aligning financial reporting with current economic realities and best practices. The consultation process is crucial for gathering feedback and ensuring the amendments are effective and beneficial for all stakeholders. This initiative demonstrates a commitment to adapting accounting standards to the changing landscape, and the potential long-term implications are significant.
The proposed changes, if implemented, will affect how businesses operate, and the accounting profession will need to adapt to the new regulations.