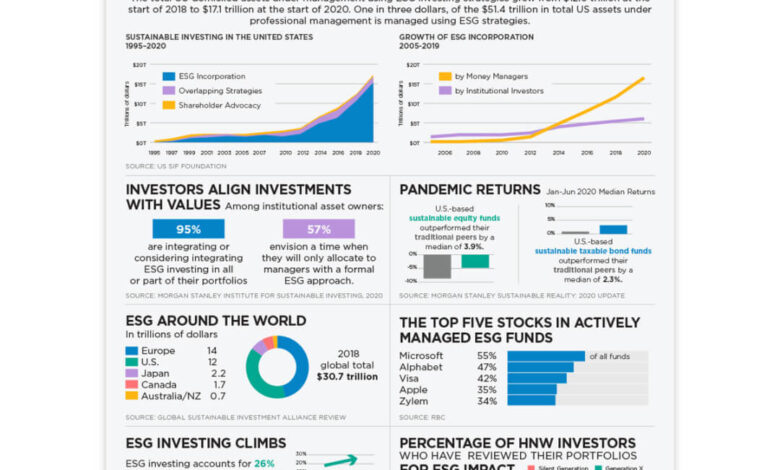
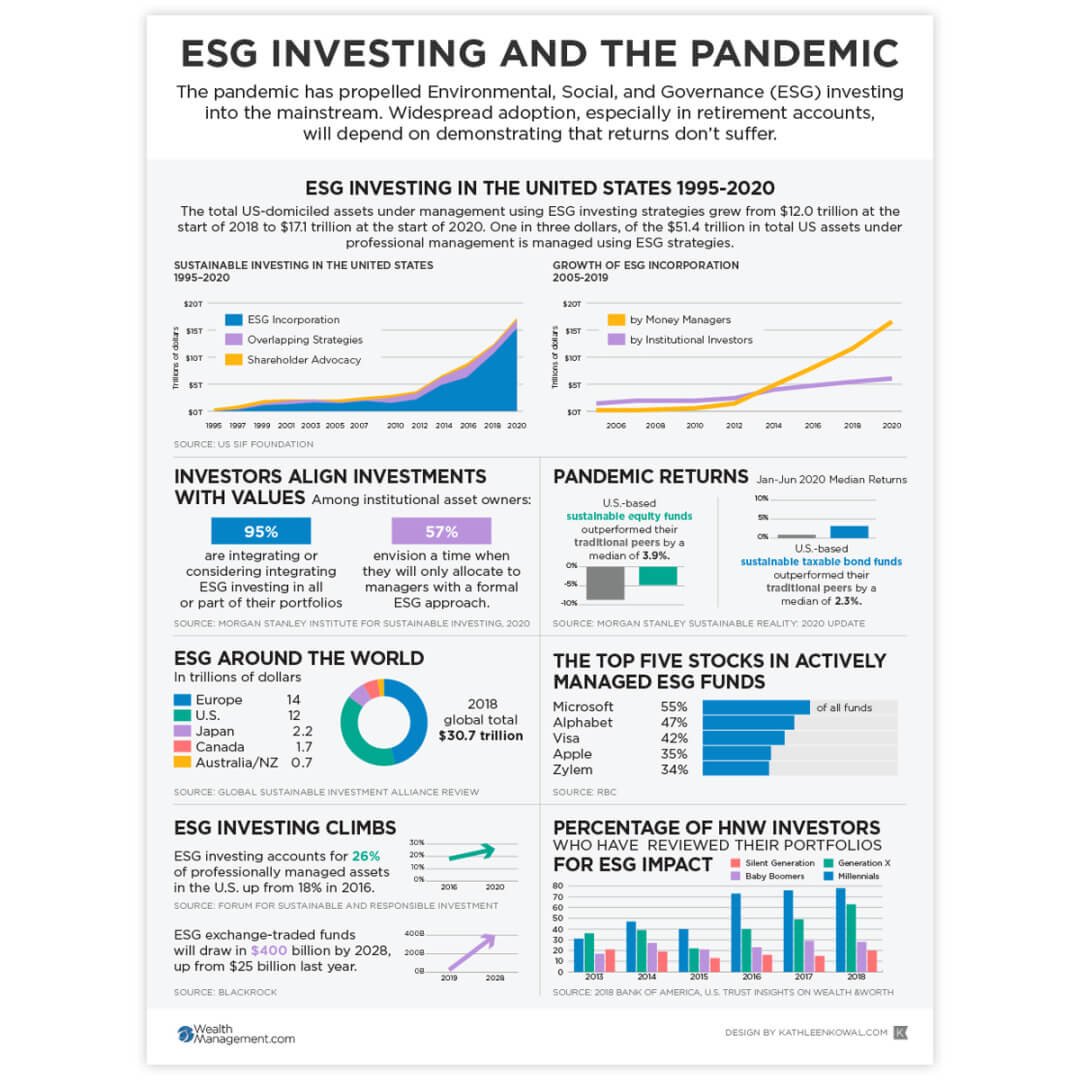
Investors Say Coronavirus Pushed ESG to Forefront
Investors say coronavirus pushed ESG to forefront, signaling a significant shift in investment priorities. The pandemic highlighted the interconnectedness of economic, social, and environmental factors, prompting investors to consider the long-term impact of their decisions beyond just financial returns. This newfound focus on Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) factors is driving a re-evaluation of traditional investment strategies, prompting crucial questions about how to integrate these considerations into portfolios and potentially enhance long-term performance.
From scrutinizing supply chains to assessing corporate governance, the landscape of investment is evolving, and the pandemic is a major catalyst in this transformation.
This shift is evident in how investors are now actively incorporating ESG factors into their investment decisions, moving beyond simply profit maximization. The article explores the key drivers behind this trend, the evolving ESG factors gaining prominence, and how investors are measuring and evaluating these factors to understand their impact on financial performance. Further, the piece investigates the challenges and opportunities associated with ESG integration, examining the evolution of ESG reporting and disclosure, and its impact across different asset classes.
Ultimately, this transformation signifies a broader societal shift towards more sustainable and responsible investment practices.
Impact on Investment Strategies
The coronavirus pandemic acted as a catalyst, accelerating the already-growing trend of incorporating Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) factors into investment decisions. Investors are increasingly recognizing the interconnectedness of financial performance and societal impact, leading to a fundamental shift in how portfolios are constructed and managed. This shift reflects a growing awareness of long-term risks and opportunities, and a desire to align investments with broader societal values.Investors are now actively seeking out companies demonstrating strong ESG practices, recognizing that these factors can significantly influence long-term financial performance.
This proactive approach contrasts with the previous paradigm, where ESG considerations were often relegated to a secondary role. The pandemic highlighted vulnerabilities in supply chains and exposed systemic inequalities, further emphasizing the importance of ESG integration.
Shift in Investment Priorities
The pandemic underscored the importance of resilient and sustainable businesses. Investors realized that companies with robust ESG profiles were better positioned to navigate crises and emerge stronger in the long run. Companies with strong environmental practices, ethical labor standards, and transparent governance structures were seen as more dependable partners. This realization prompted a significant shift in investment priorities, with ESG factors moving from a peripheral concern to a central pillar of investment strategy.
Examples of ESG Integration
Investors are now incorporating ESG factors into their investment decisions in various ways. Actively managed funds are increasingly screening for companies with strong ESG profiles. Passive investment strategies are also adapting, with ESG-focused indexes and exchange-traded funds (ETFs) gaining popularity. Furthermore, investors are engaging directly with companies to encourage positive ESG changes. This engagement can take the form of shareholder resolutions or direct dialogue with management.
For example, investors might encourage a company to reduce its carbon footprint or improve its labor practices.
Types of ESG Factors Gaining Prominence
Several ESG factors are gaining significant traction in investment strategies. Environmental factors, such as carbon emissions and resource management, are particularly important. Social factors, such as diversity, equity, and inclusion, are also crucial for ensuring ethical and fair labor practices. Governance factors, including board structure and executive compensation, are seen as indicators of long-term corporate responsibility and accountability.
These factors are no longer viewed as peripheral concerns but as vital components of comprehensive risk assessment and portfolio construction.
Comparison of Pre- and Post-Pandemic Strategies
Pre-pandemic investment strategies often prioritized short-term returns over long-term sustainability. Companies with strong ESG profiles were sometimes overlooked in favor of those with higher short-term growth potential. Post-pandemic, this paradigm has shifted. Investors are now more acutely aware of the long-term value of ESG factors, recognizing their ability to mitigate risk and enhance resilience.
Key Drivers Behind Increased Focus on ESG
Several key drivers are behind the increased focus on ESG. Investors are increasingly recognizing the financial risks associated with environmental and social issues. The growing awareness of climate change, supply chain disruptions, and social inequalities is pushing investors towards more sustainable and ethical investment choices. Furthermore, regulatory pressure and investor activism are also driving the integration of ESG factors.
Investment Strategies Table
| Pre-Pandemic Strategy | Pandemic-Influenced Strategy | ESG Integration Methods |
|---|---|---|
| Focus on short-term returns, potentially neglecting long-term sustainability. | Prioritizing long-term sustainability and resilience in addition to short-term returns. | Limited or no ESG screening; passive investment with little consideration for ESG factors. |
| Traditional financial metrics are prioritized over ESG factors. | ESG factors are integrated into financial models, allowing for a comprehensive risk assessment. | Active screening for companies with strong ESG profiles; direct engagement with management; investment in ESG-focused indexes and ETFs. |
| Supply chain disruptions are viewed as temporary and manageable. | Recognizing the vulnerability of supply chains, leading to a focus on resilience and diversity. | Emphasis on diverse and resilient supply chains; supplier assessments for ethical and environmental practices. |
ESG Factors and Financial Performance: Investors Say Coronavirus Pushed Esg To Forefront
The coronavirus pandemic accelerated the integration of Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) factors into investment strategies. Investors are increasingly recognizing the interconnectedness of sustainability and financial performance. This shift reflects a growing understanding that companies with strong ESG profiles often exhibit better long-term resilience and profitability.ESG factors are no longer just a “nice-to-have” but a crucial component of a comprehensive investment analysis.
Find out about how how to clearly communicate feedback and expectations can deliver the best answers for your issues.
The link between ESG performance and financial returns is becoming more apparent, prompting a reassessment of traditional investment approaches. Investors are seeking opportunities that align with their values while also generating attractive returns.
Correlation Between ESG Performance and Financial Returns
A positive correlation between strong ESG performance and financial returns is emerging. Studies suggest that companies with robust environmental, social, and governance practices tend to exhibit better operational efficiency, reduced risks, and enhanced brand reputation. This, in turn, can lead to higher profitability and shareholder value over the long term.
Do not overlook explore the latest data about positive outlook financial services work in europe.
Potential Risks and Rewards of ESG Investing
ESG investing presents both opportunities and challenges. The rewards include access to companies with strong growth potential and the potential for higher returns. However, challenges include the complexity of evaluating ESG factors and the potential for misalignment between ESG criteria and financial performance.
Long-Term Impacts of ESG Integration on Financial Performance
The long-term impacts of ESG integration on financial performance are expected to be profound. Companies with strong ESG profiles are anticipated to experience greater resilience during economic downturns and periods of heightened social and environmental risk. Investors are increasingly recognizing that sustainable practices can enhance long-term value creation.
Methods for Measuring and Evaluating ESG Factors
Various methodologies exist for measuring and evaluating ESG factors. These methodologies often involve quantitative and qualitative assessments, drawing on publicly available information, company disclosures, and independent ratings.
Metrics Used to Assess ESG Performance
| Metric Name | Definition | Measurement Method |
|---|---|---|
| Carbon Footprint | The total amount of greenhouse gas emissions generated by a company’s operations and supply chain. | Measured using various standardized methodologies like the Greenhouse Gas Protocol, and verified by independent third-party auditors. |
| Water Usage | The total volume of water consumed by a company’s operations. | Measured through company disclosures and water footprint assessments. |
| Employee Relations | The company’s policies and practices regarding employee safety, compensation, diversity, and inclusion. | Assessed through company disclosures, employee surveys, and independent audits. |
| Supply Chain Management | The company’s practices regarding labor standards, ethical sourcing, and environmental impact throughout its supply chain. | Measured through supply chain audits and assessments, including independent third-party certifications. |
| Corporate Governance | The structure and processes by which a company is governed, including its board of directors, executive compensation, and risk management. | Assessed through company disclosures, corporate governance ratings, and compliance with regulations. |
Investor Motivation and Rationale
The COVID-19 pandemic acted as a catalyst, accelerating the integration of Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) factors into investment strategies. Investors are increasingly recognizing the interconnectedness of financial performance with societal and environmental well-being. This shift signifies a fundamental change in how investors approach risk and opportunity, moving beyond traditional financial metrics to encompass a broader range of considerations.The growing awareness of climate change, social inequalities, and corporate governance issues is driving investors to prioritize ESG factors in their decision-making processes.
This includes a recognition that companies with strong ESG profiles often demonstrate greater resilience and long-term value creation.
Motivations Behind Increased ESG Adoption
Investors are motivated by a multifaceted set of considerations when incorporating ESG factors into their portfolios. These factors extend beyond mere ethical concerns and are increasingly linked to improved financial performance and risk mitigation.
- Improved Risk Management: ESG factors can help identify and mitigate risks associated with environmental hazards, social conflicts, and governance failures. For example, a company with poor environmental records may face increased regulatory scrutiny, reputational damage, and potentially higher operational costs, all of which could negatively impact financial performance.
- Enhanced Long-Term Value Creation: Companies with strong ESG profiles are often better positioned for long-term success. Investors are recognizing that companies committed to sustainable practices are better equipped to adapt to changing market conditions and emerging trends. This can lead to more stable and predictable returns over time.
- Ethical and Societal Concerns: Many investors are motivated by a desire to align their investments with their personal values and contribute to positive societal change. For instance, investors may choose to invest in companies committed to reducing their carbon footprint or promoting diversity and inclusion.
Societal and Environmental Concerns in Investment Decisions
Societal and environmental concerns are playing an increasingly important role in shaping investment decisions. The growing recognition of the interconnectedness of financial performance with broader societal and environmental well-being is transforming the investment landscape.
- Climate Change: The threat of climate change is influencing investor decisions as companies are increasingly assessed on their carbon footprint, energy efficiency, and resilience to climate-related risks. This translates to investors actively seeking out companies that are actively reducing their carbon emissions and implementing sustainable practices.
- Social Inequality: Social inequality is another significant concern impacting investment decisions. Investors are looking at companies’ labor practices, human rights record, and diversity and inclusion policies. This focus extends to evaluating the social impact of a company’s operations and its contributions to broader societal issues.
Ethical and Social Considerations Influencing Investor Choices
Ethical and social considerations are influencing investors’ choices across various sectors. The pressure to align investments with values is growing, leading to a shift in investor preferences and demand for companies that demonstrate strong ethical and social responsibility.
- Labor Practices: Investors are scrutinizing companies’ labor practices, including fair wages, safe working conditions, and worker rights. A growing number of investors are choosing to invest in companies that demonstrate ethical and transparent labor practices, creating a positive impact on workers’ lives.
- Human Rights: Human rights are becoming a key consideration for investors. Companies with poor human rights records may face divestment pressure, as investors seek to avoid supporting businesses with questionable ethical standards. This is particularly important in sectors such as mining, agriculture, and manufacturing.
Regulatory Pressures and Investor Activism, Investors say coronavirus pushed esg to forefront
Regulatory pressures and investor activism are driving greater accountability and transparency in ESG reporting and performance. The growing importance of ESG factors is influencing policy and investor behavior.
- Regulatory Frameworks: Government regulations and reporting standards are increasingly demanding greater disclosure and transparency regarding ESG performance. This is creating a level playing field for companies to demonstrate their commitment to ESG principles and attracting responsible investors.
- Investor Activism: Investor activism, in the form of shareholder resolutions and engagement, is putting pressure on companies to improve their ESG performance. Investors are using their voice and influence to push companies toward more sustainable and responsible practices.
Investor Motivations: A Summary Table
| Motivation | Rationale | Supporting Evidence |
|---|---|---|
| Improved Risk Management | Identifying and mitigating risks associated with ESG factors leads to more stable and predictable returns. | Studies show a correlation between strong ESG performance and lower financial volatility. |
| Enhanced Long-Term Value Creation | Companies committed to sustainable practices are better positioned for long-term success. | Case studies of companies with strong ESG profiles demonstrate outperformance in the long run. |
| Ethical and Societal Concerns | Investors seek to align their investments with their personal values and contribute to positive societal change. | Surveys indicate a growing number of investors prioritize ESG factors in their investment decisions. |
Challenges and Opportunities
The integration of Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) factors into investment strategies presents both exciting opportunities and significant hurdles. While the shift toward ESG investing is undeniable, navigating the complexities of data, measurement, and potential misrepresentation is crucial for responsible and successful implementation. Addressing these challenges head-on will be essential to unlocking the full potential of ESG investing and ensuring its long-term sustainability.The path to truly impactful ESG investing requires a comprehensive understanding of the challenges and opportunities that lie ahead.
A careful examination of data availability, potential misrepresentation, and the development of robust frameworks is critical to realizing the full potential of this burgeoning field. Innovative solutions and a clear comparison of various approaches will be key to overcoming these obstacles.
Challenges Associated with Integrating ESG Factors
Integrating ESG factors into investment decisions presents several challenges. Different companies use various reporting standards, making consistent comparisons difficult. Subjectivity in ESG criteria interpretation can also lead to inconsistencies. Furthermore, the lack of standardized methodologies for ESG data collection and analysis introduces significant challenges in measuring and comparing the ESG performance of different companies. These issues can make it challenging for investors to make informed decisions and compare companies fairly.
Data Availability and Measurement Issues in ESG
Data availability and measurement issues are significant obstacles in ESG investing. Comprehensive and reliable data on ESG factors is often lacking, particularly for smaller or emerging companies. Furthermore, the methodologies for measuring and reporting ESG factors are often not standardized, making comparisons across companies difficult. This lack of consistent data can hinder the ability to accurately assess ESG performance and identify meaningful investment opportunities.
Potential for Misrepresentation and Greenwashing in ESG Reporting
The potential for misrepresentation and greenwashing in ESG reporting is a serious concern. Companies may exaggerate or misrepresent their ESG performance to attract investors or improve their public image. Without robust verification mechanisms and independent audits, investors risk falling victim to misleading information. This issue erodes trust in ESG reporting and can ultimately undermine the integrity of the entire ESG investing landscape.
Investigate the pros of accepting global cfo survey rebuild revenue streams in your business strategies.
Framework for Addressing ESG Investing Challenges
A framework for addressing the challenges and opportunities in ESG investing should prioritize transparency and standardization. Standardized reporting frameworks and methodologies are essential for consistent data collection and analysis. Collaboration between companies, investors, and regulators can help to build trust and promote accurate ESG reporting. Furthermore, independent audits and verification mechanisms are crucial to ensure the authenticity and reliability of ESG data.
Innovative Solutions to Overcome Challenges
Several innovative solutions are emerging to address the challenges in ESG investing. Blockchain technology can be used to create transparent and verifiable ESG data records. Third-party ESG rating agencies are developing more sophisticated and comprehensive methodologies for assessing ESG performance. Investor engagement and dialogue with companies can also help uncover and address ESG issues. These solutions aim to enhance the accuracy and reliability of ESG data.
Comparison of Approaches to Addressing ESG Challenges
Various approaches to addressing ESG challenges exist. Some investors focus on screening out companies with poor ESG performance, while others engage with companies to improve their ESG practices. A blended approach that combines both screening and engagement can be highly effective. Different investors may choose different approaches depending on their specific goals and investment philosophies.
Potential for New Investment Opportunities
The focus on ESG factors creates numerous investment opportunities. Companies with strong ESG performance are often more resilient and sustainable in the long term. Investors can identify and support companies making progress in areas like renewable energy, sustainable agriculture, and responsible resource management. This focus also presents new investment opportunities in companies that provide solutions to environmental and social challenges.
Evolution of ESG Reporting and Disclosure
The COVID-19 pandemic significantly accelerated the push for greater transparency and accountability in corporate ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) practices. Investors, recognizing the interconnectedness of ESG factors and financial performance, demanded more robust reporting mechanisms. This evolution reflects a broader societal shift towards a more sustainable future, with companies increasingly recognizing the need to integrate ESG considerations into their core strategies.ESG reporting has moved beyond voluntary initiatives towards mandatory disclosures, driven by a growing awareness of the risks and opportunities associated with environmental, social, and governance factors.
This transition is a testament to the growing importance of ESG considerations in the investment landscape. The rise of ESG reporting standards and frameworks has created a more standardized approach to measuring and communicating corporate sustainability performance, fostering a more informed and engaged investment community.
ESG Reporting Standards and Frameworks
Various reporting standards and frameworks have emerged to guide companies in disclosing their ESG performance. These frameworks provide a common language and set of metrics, enabling investors to compare companies across different sectors and geographies. Different frameworks offer varying levels of depth and specificity, allowing companies to select the most appropriate framework based on their specific needs and circumstances.
Examples of ESG Reporting Standards
Several prominent ESG reporting standards exist, each with unique features and applications. The Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) is a widely recognized framework, offering a comprehensive set of standards and guidelines for sustainability reporting. The Sustainability Accounting Standards Board (SASB) focuses on materiality, identifying the ESG factors most relevant to a company’s specific industry and financial performance. The Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD) specifically addresses climate-related risks and opportunities, providing a structured approach for companies to disclose their climate-related strategies and impacts.
Increasing Transparency and Disclosure Requirements
Transparency in ESG reporting is rapidly increasing, driven by growing investor demand and regulatory pressures. Investors are demanding more comprehensive and standardized disclosures, seeking a deeper understanding of companies’ ESG performance and its potential impact on financial outcomes. This push for transparency is fostering a more informed and engaged investment community.
Role of Regulatory Bodies in Driving ESG Disclosure
Regulatory bodies are playing an increasingly important role in driving ESG disclosure, through the introduction of mandatory reporting requirements and the development of specific guidelines. This regulatory intervention is critical in creating a level playing field for companies and ensuring greater consistency and comparability in ESG reporting. Specific examples include regulations in the EU and the US regarding sustainability disclosures.
Comparison of ESG Reporting Standards
| Standard Name | Key Features | Reporting Requirements |
|---|---|---|
| GRI | Comprehensive framework, widely recognized, covers a broad range of ESG topics. | Flexible, allows for customization based on company size and industry. Requires disclosure of key performance indicators (KPIs). |
| SASB | Industry-specific standards focusing on materiality, aligning with financial performance. | Companies must identify and disclose ESG factors relevant to their industry and financial performance. |
| TCFD | Focuses specifically on climate-related risks and opportunities. | Requires disclosure of climate-related strategies, risks, opportunities, and targets. |
Impact on Different Asset Classes
The coronavirus pandemic significantly accelerated the integration of ESG factors into investment strategies. This shift has had profound impacts across various asset classes, demanding a nuanced understanding of how ESG considerations are reshaping investment decisions and market dynamics. Investors are increasingly seeking alignment between financial returns and societal and environmental well-being.
ESG Integration Approaches Across Asset Classes
Different asset classes present unique challenges and opportunities for ESG integration. For example, the implementation of ESG factors in the stock market often involves detailed analysis of company policies and practices, while in the bond market, ESG considerations might be incorporated through credit rating methodologies and due diligence. Real estate investments often focus on the sustainability of buildings and the environmental impact of development projects.
Impact on Stock Investments
ESG integration in the stock market often involves analyzing a company’s environmental, social, and governance practices. Companies demonstrating strong ESG performance can attract socially conscious investors, potentially leading to higher valuations and investor confidence. Conversely, companies with poor ESG records may face a decline in valuations and investor support. Examples include divestment from fossil fuel companies and increased investment in renewable energy companies.
Companies with strong ESG profiles, like those in the renewable energy sector, often experience growth as investors increasingly favor sustainability.
Impact on Bond Investments
ESG integration in the bond market is gaining traction, although its implementation varies. Some bond funds specifically screen for environmentally sustainable or socially responsible issuers. Others may use ESG factors to assess creditworthiness and adjust risk assessments. This approach aims to identify potential risks and opportunities related to ESG factors within the bond market.
Impact on Real Estate Investments
ESG factors are increasingly influencing real estate investments. Sustainable building practices, energy efficiency, and responsible land use are gaining prominence. Investors are seeking properties that meet specific sustainability standards, leading to increased demand for green buildings and environmentally conscious developments. This trend is creating a market for sustainable real estate products and driving innovation in the sector.
Impact on Other Asset Classes
ESG considerations are also influencing alternative investments like private equity and infrastructure. Investors are looking for opportunities to align their investments with ESG principles. The specific approaches and metrics vary depending on the asset class.
Impact on Specific Industries
The energy sector is experiencing significant transformation due to ESG concerns. Investors are increasingly shifting away from fossil fuels toward renewable energy sources. The technology sector is also being affected by ESG pressures, as investors scrutinize companies’ environmental impact and social responsibility. Companies in both sectors must adapt to the changing demands of investors.
Emerging Trends in ESG Investing
Emerging trends include the use of standardized ESG metrics and reporting frameworks. This facilitates comparison and consistency across different asset classes. Furthermore, the focus is shifting from simply excluding companies with poor ESG performance to actively investing in companies with strong ESG profiles.
Potential for Diversification in Portfolios
Integrating ESG factors can enhance portfolio diversification. By incorporating companies and assets with strong ESG performance, investors can potentially reduce risk and improve long-term returns. This diversification can also reflect changing consumer preferences and market demands.
Impact on Asset Classes: A Comparative Analysis
| Asset Class | ESG Integration Method | Impact on Performance |
|---|---|---|
| Stocks | Company analysis, screening, engagement | Potentially higher valuations for companies with strong ESG performance, potential decline for those with poor ESG performance. |
| Bonds | Credit rating adjustments, ESG screening | Potential for improved risk assessment and identification of opportunities/risks related to ESG factors. |
| Real Estate | Sustainable building practices, responsible land use | Increased demand for green buildings and environmentally conscious developments. |
| Alternatives (Private Equity, Infrastructure) | Alignment with ESG principles | Opportunities to align investments with ESG principles. |
Closing Summary
In conclusion, the coronavirus pandemic has acted as a catalyst for a significant evolution in investment strategies, pushing ESG factors to the forefront. Investors are increasingly recognizing the importance of integrating environmental, social, and governance considerations into their portfolios, driven by a combination of ethical concerns, societal pressures, and potential financial rewards. While challenges remain in terms of data availability and potential for misrepresentation, the potential for new investment opportunities and long-term performance enhancement is undeniable.
The future of investment appears to be firmly rooted in a more sustainable and responsible approach.