New Finance Opportunities Beyond Lockdown
New finance opportunities beyond coronavirus lockdown present exciting possibilities for navigating the post-pandemic world. This exploration delves into emerging financial models, the rise of digital finance, shifts in consumer behavior, and the impact on small businesses, alongside global implications and investment prospects. The evolving regulatory landscape will also be examined.
From innovative financial products addressing pandemic-era needs to the changing demands of remote work, this discussion unveils a new financial paradigm. The transformation of traditional financial services and the growth of fintech companies are highlighted. Furthermore, the content examines how consumer habits, investment strategies, and small business financing have been altered. This analysis explores the global implications, investment opportunities, and the adaptation of regulatory frameworks in a post-pandemic financial landscape.
Emerging Financial Models
The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated the adoption of innovative financial products and services, prompting a significant shift in how individuals and businesses manage their finances. Traditional financial institutions are responding by incorporating new models to meet the evolving needs of their customers. These emerging models are not simply incremental improvements; they represent fundamental changes in access, cost, and efficiency of financial services.These new financial models address previously unmet needs in the financial landscape.
The pandemic highlighted the limitations of traditional methods, especially regarding accessibility and affordability. This led to a surge in demand for digital solutions, remote services, and flexible payment options. The rise of fintech and the adaptation of existing financial institutions to the digital sphere are reshaping the financial industry.
Examples of Innovative Financial Products and Services
The pandemic spurred the development of several innovative financial products and services. These include digital lending platforms, robo-advisors, peer-to-peer (P2P) lending, and mobile payment systems. These models offer quicker, more accessible, and often cheaper financial solutions compared to traditional methods.
Comparison of Emerging Models with Traditional Financial Offerings
Emerging financial models differ significantly from traditional financial institutions in their approach to service delivery and pricing. Traditional methods often involve extensive paperwork, physical branch visits, and rigid processes. Innovative models, in contrast, rely heavily on technology, leveraging digital platforms for efficiency and often providing personalized financial advice and management. This shift toward digitalization and automation has led to lower transaction costs and increased accessibility for a broader range of customers.
Key Features of Emerging Financial Products, New finance opportunities beyond coronavirus lockdown
| Product | Target Customer Segment | Value Proposition | Key Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| Digital Lending Platforms | Small businesses, entrepreneurs, individuals needing short-term capital | Faster access to funds with streamlined application processes | Online application, quick decision, flexible repayment options, often lower interest rates than traditional loans |
| Robo-advisors | Individuals seeking automated investment management | Low-cost, diversified investment portfolios tailored to individual risk profiles | Automated portfolio rebalancing, low minimum investment requirements, access through mobile apps |
| P2P Lending Platforms | Borrowers seeking alternative financing options | Reduced borrowing costs compared to traditional loans | Direct lending between individuals, often without intermediaries, access to potentially lower interest rates |
| Mobile Payment Systems | Individuals and businesses needing fast and convenient transactions | Enhanced transaction speed and security | Digital wallets, mobile payment apps, QR code payments, international money transfers |
| Neobanks | Young adults, tech-savvy individuals | Simplified financial management with low-cost or no-cost services | Mobile-first banking experience, budgeting tools, account management apps, often with unique features like international money transfer deals |
Evolution of Traditional Financial Services
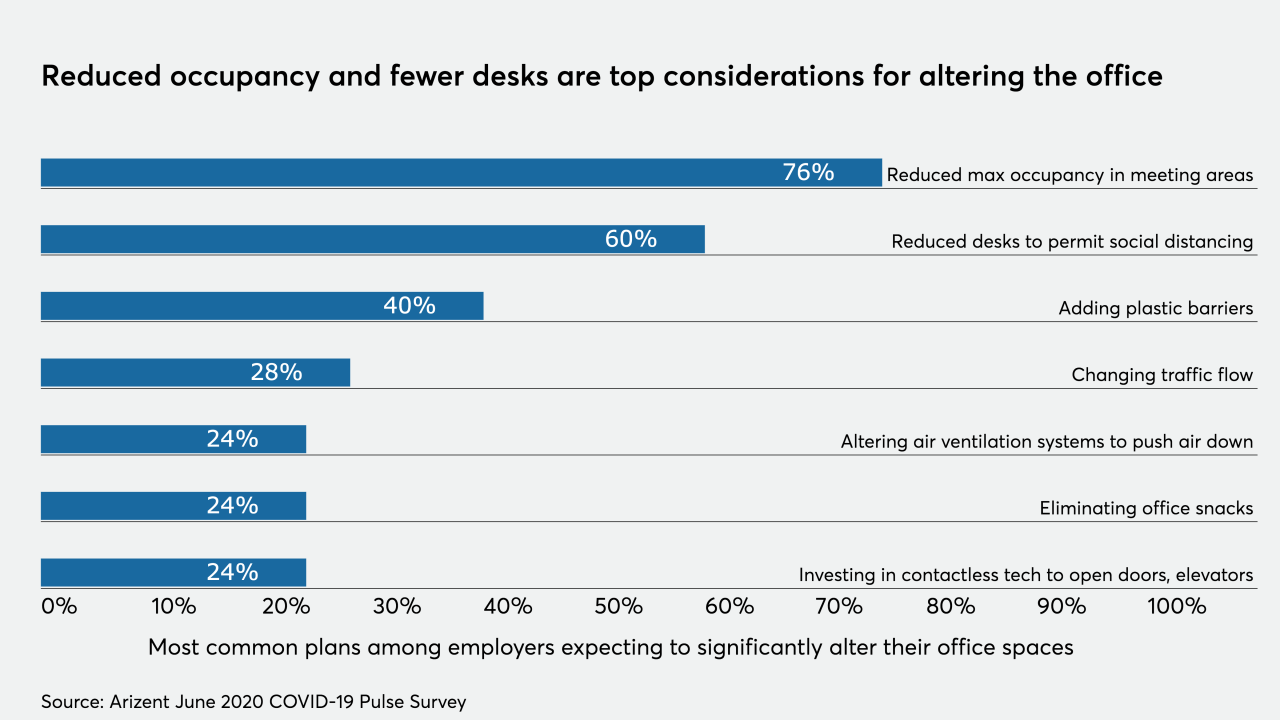
Traditional financial institutions have been adapting to the changing landscape. The pandemic accelerated their digital transformation efforts, leading to the development of online banking platforms, mobile apps, and digital account management tools. This evolution aims to meet customer demands for remote access to services, enhance convenience, and improve efficiency.
| Service | Pre-Pandemic | Post-Pandemic |
|---|---|---|
| Banking | Reliance on physical branches, limited online options | Extensive online banking platforms, mobile apps, enhanced digital security |
| Investment Management | Limited online investment options, high minimum investment requirements | Robo-advisors, fractional share investing, access to global markets |
| Lending | Extensive paperwork, lengthy approval processes | Digital lending platforms, online applications, faster approval times |
| Payment Processing | Limited digital payment options, reliance on cash | Mobile payment apps, contactless payments, digital wallets |
Remote Work and Digital Finance
The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated the shift towards remote work, dramatically increasing the demand for digital financial tools and services. This transition has fundamentally reshaped how people manage their finances, interact with banks, and conduct transactions. The need for secure and convenient online options became paramount, pushing innovation in fintech and reshaping the financial landscape.Remote work has profoundly influenced the demand for digital financial tools and services.
The necessity for remote transactions, coupled with the convenience and speed of digital platforms, fostered a significant growth in online banking, mobile payments, and digital investment platforms. This shift was not just a reaction to the pandemic but also a catalyst for long-term changes in the financial sector.
Impact of Remote Work on Digital Finance
The rise of remote work has directly fueled the need for secure and efficient digital financial services. Employees working from home require tools for managing payroll, sending and receiving funds, and accessing their financial accounts conveniently. This has led to an explosion in the use of digital payment systems and online banking platforms.
Role of Fintech Companies in Facilitating Remote Transactions
Fintech companies play a crucial role in facilitating remote financial transactions. They develop innovative solutions that address the needs of remote workers and streamline financial processes. These companies offer a wide range of services, from mobile payment apps to peer-to-peer (P2P) transfer platforms, and digital investment platforms. Their role is crucial in adapting the financial system to the new realities of remote work.
Security and Regulatory Aspects of Digital Finance
The increased reliance on digital finance necessitates robust security measures. Cybersecurity threats are a significant concern, and companies need to implement strong encryption, multi-factor authentication, and fraud detection systems to protect user data. Regulations are also crucial to ensure transparency and consumer protection in the digital financial space. Governments worldwide are actively working to establish clear guidelines and frameworks to mitigate risks while fostering innovation.
Examples of Popular Digital Payment Systems
Several digital payment systems have gained popularity since the pandemic. These include mobile payment apps like Alipay and WeChat Pay, which have become integral parts of daily transactions in many countries. Other popular options include PayPal, Venmo, and various domestic mobile payment platforms. These systems have proven their value in enabling seamless transactions, reducing the need for physical cash, and facilitating remote payments.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Digital Financial Platforms
| Digital Financial Platform | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Mobile Banking Apps | Convenience, accessibility, real-time account access, mobile payments | Potential security risks, dependence on mobile devices, limited physical interaction |
| P2P Transfer Platforms | Fast and convenient peer-to-peer transactions, reduced reliance on traditional banking channels | Limited fraud protection, potential for scams, lack of comprehensive financial advice |
| Digital Investment Platforms | Easy access to diverse investment options, low transaction costs, potentially higher returns | Complexity of investment options, risk of investment loss, potential for misleading information |
The table above Artikels the key advantages and disadvantages of various digital financial platforms. Each platform caters to specific needs, and users should carefully consider their priorities and risk tolerance when choosing a platform. Consumers should understand the associated risks and benefits before adopting a digital financial platform.
Shift in Consumer Behavior
The COVID-19 pandemic drastically reshaped consumer financial behavior, impacting everything from saving habits to investment strategies. This shift reflects a new awareness of financial fragility and a desire for greater control over personal finances. The pandemic forced many to re-evaluate their spending and prioritize financial security, leading to significant changes in consumer behavior that are likely to persist beyond the immediate recovery phase.The pandemic accelerated the already growing trend toward digital financial services.
Consumers embraced online platforms and apps for managing finances, making transactions, and accessing financial information. This reliance on digital tools has broadened the accessibility of financial services, making them more convenient and potentially more affordable for a wider range of individuals. Simultaneously, the pandemic highlighted the need for financial literacy and the importance of understanding personal finances.
Key Changes in Consumer Financial Behavior Post-Pandemic
Consumers are becoming more cautious with their spending and are actively seeking ways to improve their financial stability. This includes increased focus on emergency funds and contingency planning. A significant shift is also evident in their investment strategies, driven by a desire for diversification and reduced risk exposure.
Impact of the Pandemic on Saving Habits and Investment Strategies
The pandemic dramatically impacted saving habits, with many individuals prioritizing building emergency funds and reducing discretionary spending. This increased focus on savings often translates to a more conservative investment approach, with a preference for lower-risk assets and a higher emphasis on security over potential high returns. This is exemplified by a rise in demand for fixed-income investments like bonds and a decrease in interest in high-growth stocks.
Role of Personal Finance Apps and Online Resources in Shaping Consumer Choices
Personal finance apps and online resources have become indispensable tools for consumers in managing their finances and making informed investment decisions. These platforms provide readily available financial information, budgeting tools, and investment trackers. This readily available information allows for informed decisions and potentially fosters greater financial literacy among users.
How the Pandemic Influenced Consumer Attitudes Towards Risk and Reward in Investments
The pandemic significantly altered consumer attitudes towards risk and reward in investments. Increased uncertainty and economic volatility led to a heightened awareness of risk, prompting many to favor safer investment options with lower potential returns. A shift towards long-term investment strategies is also evident, with consumers focusing on stability and security over short-term gains.
Different Types of Personal Finance Apps
Understanding the diverse needs of different consumer demographics is crucial in the financial services sector. This requires personal finance apps tailored to meet these specific needs.
| App Type | Target Demographic | Key Functionalities |
|---|---|---|
| Budgeting and Expense Tracking Apps | Individuals with limited financial literacy, and those seeking to improve their spending habits. | Detailed expense tracking, budgeting tools, and financial goal setting features. Some apps also offer personalized financial advice or recommendations. |
| Investment Tracking and Portfolio Management Apps | Individuals with existing investment portfolios and those looking to actively manage their investments. | Real-time portfolio tracking, diversified investment options, and investment analysis tools. Some apps may offer robo-advisory services, allowing for automated portfolio management. |
| Student Loan Management Apps | Students and young adults facing student loan debt. | Tools to track loan payments, manage interest rates, and potentially explore loan consolidation options. Some apps may offer resources for financial planning and debt management. |
Impact on Small Businesses
The COVID-19 pandemic significantly impacted small businesses globally, forcing many to adapt to unprecedented challenges. Reduced consumer spending, supply chain disruptions, and government restrictions created a volatile environment, leading to a surge in business closures and financial hardship. This period highlighted the critical need for innovative financial solutions and support systems to help these enterprises navigate the crisis and thrive in the post-pandemic landscape.Small businesses, often the backbone of local economies, are particularly vulnerable to economic downturns.
Their smaller financial buffers and dependence on specific industries or customer bases make them more susceptible to external shocks. The pandemic’s effects exposed existing vulnerabilities and created new ones, emphasizing the importance of resilience and adaptability.
Financial Challenges Faced by Small Businesses During the Pandemic
The pandemic presented a range of financial challenges for small businesses. Reduced revenue, increased operational costs, and difficulty accessing traditional financing sources were common struggles. Many businesses faced disruptions in supply chains, impacting production and delivery, while others experienced a sharp decline in customer demand due to lockdowns and changing consumer habits. This led to a significant decrease in revenue and profitability for many small businesses, putting them in a precarious financial position.
Innovative Financing Options to Support Small Businesses
Several innovative financing options emerged to support small businesses during the pandemic. Government-backed loan programs, grants, and forgivable loans were designed to provide immediate relief and bridge the gap for struggling businesses. These initiatives aimed to stabilize cash flow and prevent further business closures. Furthermore, digital platforms facilitated alternative lending options, enabling businesses to access funding more quickly and efficiently than through traditional channels.
Peer-to-peer lending platforms also gained traction, connecting borrowers with investors directly, reducing reliance on traditional banks.
Changes in Access to Credit and Funding for Small Businesses
Access to credit and funding for small businesses experienced significant shifts during the pandemic. Traditional lending institutions often tightened their lending criteria, making it more difficult for small businesses to secure loans. The increased risk aversion and the stringent requirements for collateral and credit history were major obstacles. This led many small businesses to explore alternative funding sources, highlighting the importance of diversification in funding strategies.
Comparison of Traditional and New Funding Sources for Small Businesses
Traditional funding sources, such as bank loans, often require extensive documentation, stringent eligibility criteria, and a longer approval process. Conversely, new sources like online lending platforms and crowdfunding platforms offer faster access to capital with potentially lower requirements, but may involve higher interest rates or fees. The choice between traditional and new sources depends on the specific needs and circumstances of each small business.
Strategies for Securing Funding Post-Pandemic
Small businesses can implement various strategies to secure funding post-pandemic. Building a strong financial record, demonstrating a clear business plan, and actively seeking funding opportunities are crucial steps. Developing strong relationships with potential investors and showcasing a resilient business model are essential factors in securing funding. Moreover, exploring various funding options, from traditional bank loans to alternative lending platforms, is a wise approach.
Global Financial Implications
The COVID-19 pandemic profoundly reshaped the global financial landscape, triggering a cascade of economic shifts that continue to ripple through international markets. From supply chain disruptions to shifts in consumer behavior, the pandemic’s impact was felt across borders, demanding new approaches to cross-border transactions, investment strategies, and international financial collaboration. Understanding these implications is crucial for navigating the evolving global financial environment.
Global Economic Shifts Triggered by the Pandemic
The pandemic’s impact on global economies manifested in various ways. Supply chains were significantly disrupted, leading to shortages and price increases for essential goods. Lockdowns and restrictions imposed by governments globally led to a sharp contraction in economic activity, with some sectors experiencing a far greater impact than others. Reduced consumer spending and business closures resulted in a substantial decline in employment in many countries.
These economic shifts necessitated substantial government intervention, including stimulus packages and financial support measures.
Influence on Cross-Border Financial Transactions and Investment Strategies
The pandemic significantly influenced cross-border financial transactions. Increased reliance on digital platforms for transactions, and the need for remote work, became prominent. This shift accelerated the digitalization of financial services, impacting traditional methods of money transfer and international trade. Investment strategies were also profoundly affected. Investors re-evaluated risk profiles and diversified their portfolios, seeking opportunities in sectors deemed less vulnerable to the pandemic’s impact.
Implications for International Financial Institutions and Regulations
The pandemic highlighted the need for stronger international cooperation and regulatory frameworks to address global economic challenges. International financial institutions, such as the IMF and World Bank, played a critical role in providing financial assistance and support to countries facing economic hardship. The pandemic underscored the need for greater flexibility and adaptability in international financial regulations to address unforeseen events and facilitate effective responses.
International Financial Collaborations
The pandemic fostered new forms of international financial collaboration. Bilateral and multilateral agreements emerged to facilitate the sharing of knowledge, resources, and best practices in addressing the crisis. For instance, several countries cooperated to develop and distribute COVID-19 vaccines globally. These collaborations demonstrated the importance of international partnerships in addressing global challenges.
Obtain access to cima ethics confidentiality rules to private resources that are additional.
Global Distribution of Funding Sources for Small Businesses Post-Pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic created significant challenges for small businesses worldwide, and this led to shifts in funding sources.
| Region | Government Funding | Private Sector Funding | International Organizations Funding |
|---|---|---|---|
| North America | Significant, focused on targeted relief programs | Venture capital and private equity funds adapted to new needs | Limited but some assistance programs existed |
| Europe | Extensive government aid programs, particularly for SMEs | Significant private equity investment focused on digital transformation | EU-level initiatives and support from IMF/World Bank |
| Asia | Varying degrees of government support, often tailored to specific industries | Growth of fintech platforms and angel investors | ADB and other regional development banks played a key role |
| Latin America | Mixed results, with some countries having robust support programs, while others struggled | Challenges in access to capital and increased competition | Support from multilateral institutions and regional banks was crucial in some cases |
| Africa | Limited resources, with challenges in accessing funding | Limited private investment due to specific market conditions | Increased need for international assistance from institutions like the African Development Bank |
Note: This table provides a generalized overview. Specific funding levels and distribution varied significantly by country and sector.
Investment Opportunities
The post-pandemic landscape presents a unique blend of challenges and opportunities for investors. Shifting consumer habits, evolving work models, and the rise of digital finance have created new avenues for capital deployment. Navigating these changes requires a nuanced understanding of emerging trends and potential risks. Careful diversification and a focus on sustainable practices are crucial for long-term success.
Emerging Investment Sectors
The pandemic accelerated the adoption of digital technologies and remote work, creating opportunities in sectors like cloud computing, e-commerce, and digital payment systems. These industries have demonstrated strong growth potential, driven by increased demand for online services and solutions. Furthermore, the surge in demand for remote work solutions has led to an increase in investment in companies providing remote work tools and platforms.
- Cloud Computing: The growing reliance on cloud-based services has fueled demand for infrastructure providers and software developers. Companies like Amazon Web Services and Microsoft Azure have experienced substantial growth, demonstrating the long-term potential of this sector.
- E-commerce and Logistics: The shift to online shopping has spurred significant investment in e-commerce platforms and logistics companies. Companies facilitating online delivery and fulfillment have seen impressive growth, reflecting the lasting impact of online shopping trends.
- Digital Payments and Fintech: The digitalization of payments has created opportunities for innovative financial technologies. Companies offering digital wallets, peer-to-peer payment systems, and other financial solutions have attracted considerable investment capital.
Sustainable and Responsible Investments
Investors are increasingly recognizing the importance of aligning their portfolios with environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors. Sustainable and responsible investments are not only ethically sound but also often demonstrate strong long-term performance. Companies with robust ESG profiles are likely to be more resilient and adaptable to future challenges, providing investors with potentially better risk-adjusted returns.
- ESG Integration: Incorporating ESG factors into investment strategies involves analyzing a company’s environmental impact, social responsibility, and governance practices. This approach helps investors identify companies with sustainable business models, potentially leading to better long-term performance.
- Impact Investing: Impact investing focuses on generating a measurable social or environmental impact alongside financial returns. This approach is increasingly appealing to investors seeking to make a difference while generating financial returns.
Risk Factors
While new investment opportunities abound, it’s crucial to acknowledge the potential risks. Market volatility, regulatory changes, and unforeseen economic shocks can significantly impact investment returns. Investors should conduct thorough due diligence and develop diversified investment strategies to mitigate potential risks.
- Market Volatility: Unpredictable market conditions can cause significant fluctuations in asset values. Diversification across different asset classes and sectors can help mitigate these risks.
- Regulatory Changes: Government regulations in emerging sectors can evolve rapidly. Staying informed about potential regulatory changes and their impact on specific investments is crucial.
- Economic Uncertainty: Unforeseen economic shocks, such as global events or natural disasters, can disrupt market conditions. Robust risk management strategies are vital in such circumstances.
Innovative Investment Strategies
Diversifying investment portfolios is crucial for mitigating risk. Considering a combination of traditional and alternative investments, such as private equity or real estate, can create a more robust and balanced portfolio.
- Diversification Across Asset Classes: A balanced portfolio includes stocks, bonds, real estate, and alternative investments. This strategy spreads risk and helps to mitigate potential losses in any single asset class.
- Alternative Investments: Consider exploring investments beyond traditional stocks and bonds. Private equity, real estate, and infrastructure investments can provide diversification and potentially higher returns.
- Focus on Growth Sectors: Emerging sectors like renewable energy, biotechnology, and artificial intelligence show strong growth potential. Investors can allocate a portion of their portfolio to these promising sectors.
Regulatory Landscape
The post-pandemic era has ushered in a dynamic shift in financial regulations, driven by the need to adapt to the unprecedented challenges and opportunities presented by the crisis. Governments worldwide are actively re-evaluating existing frameworks and introducing new measures to foster innovation, safeguard consumers, and maintain financial stability. This evolution is particularly critical in the realm of emerging financial models, which often operate outside traditional regulatory structures.The pandemic accelerated the adoption of digital financial services and remote work, placing significant pressure on regulatory bodies to keep pace.
Existing regulations often struggled to address the complexities of these new models, leading to a period of adaptation and clarification. Navigating these evolving landscapes is crucial for both established institutions and new entrants in the financial sector. The regulatory environment has become a critical factor in shaping the future of finance.
Evolving Regulatory Frameworks
Governments globally are responding to the pandemic’s impact by updating and modernizing financial regulations. This includes adapting rules to accommodate remote work, digital financial services, and the changing consumer behavior patterns. Regulations are being amended to address new risks associated with emerging financial models, while simultaneously fostering innovation in areas like fintech and open banking.
Regulatory Adaptation to Pandemic Challenges
The pandemic forced a swift adaptation in regulatory frameworks. Central banks and financial regulators worldwide implemented measures to support economic stability, including interest rate cuts and liquidity injections. These actions were often accompanied by temporary regulatory flexibilities to assist businesses and consumers facing financial hardship. The temporary relief measures are now being gradually withdrawn, but the regulatory landscape is expected to continue to evolve.
Regulatory Hurdles and Considerations for New Financial Services
New financial services often face unique regulatory hurdles. These hurdles stem from the innovative nature of the products and services, the need to ensure consumer protection, and the potential for systemic risk. Navigating the regulatory environment can be challenging, particularly for startups and fintech companies. Regulatory sandboxes are being implemented in some jurisdictions to allow for the testing of new financial products in a controlled environment.
This approach can help to reduce the risk for both regulators and innovators.
Comparative Regulatory Approaches to Emerging Financial Models
Different countries have adopted diverse approaches to regulating emerging financial models. Some jurisdictions have adopted a more cautious approach, emphasizing the need for thorough risk assessments and consumer protection measures. Others have prioritized fostering innovation, introducing regulatory sandboxes, and adopting agile regulatory frameworks. This variation creates challenges for businesses operating in multiple markets, requiring a nuanced understanding of each jurisdiction’s specific requirements.
Table: Regulatory Changes in Key Financial Sectors
| Financial Sector | Pre-Pandemic Regulation | Post-Pandemic Regulation | Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Digital Payments | Traditional payment methods with some regulatory oversight | Increased emphasis on cybersecurity, data privacy, and anti-money laundering (AML) measures for digital payments | Enhanced security and consumer protection for digital transactions |
| Investment Platforms | Traditional investment regulations focused on broker-dealers | Adapting to robo-advisors and other digital investment platforms; greater scrutiny on algorithmic trading | Increased transparency and accountability for investment services |
| Lending | Regulations on traditional lending practices | Increased focus on responsible lending practices, affordability assessments, and digital lending platforms | Protecting consumers from predatory lending practices and promoting financial inclusion |
End of Discussion: New Finance Opportunities Beyond Coronavirus Lockdown

In conclusion, the coronavirus lockdown has sparked a revolution in finance, ushering in a new era of digital transactions, innovative products, and evolving consumer behaviors. The opportunities for investment and the challenges of adapting to the new normal are substantial. This analysis provides insights into the changing financial landscape, highlighting emerging trends and offering a comprehensive overview for readers seeking to understand the post-pandemic financial world.