Internal Audit Technology Risks A Deep Dive
Internal audit technology risks are a growing concern in today’s digital landscape. As organizations rely more heavily on technology, the potential for vulnerabilities and breaches increases, impacting everything from data security to operational efficiency. This exploration examines the multifaceted nature of these risks, from the evolving threats to practical mitigation strategies.
This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of internal audit technology risks, highlighting various types, contributing factors, and the profound impact they can have on an organization. We’ll cover everything from data breaches and software vulnerabilities to the challenges posed by emerging technologies like AI and cloud computing. The discussion also includes real-world case studies and actionable strategies to mitigate these risks, ultimately equipping you with the knowledge to navigate the complexities of the digital age.
Introduction to Internal Audit Technology Risks
Internal audit technology risks are emerging threats that stem from the increasing reliance on technology in modern organizations. These risks can significantly impact an organization’s ability to conduct effective internal audits, potentially leading to financial losses, reputational damage, and regulatory penalties. The nature of these risks is constantly evolving as technology advances and new threats arise. Understanding these risks is critical for organizations to mitigate their impact and maintain robust internal controls.
Defining Internal Audit Technology Risks
Internal audit technology risks encompass a broad spectrum of potential vulnerabilities related to the use of technology in internal audit functions. These risks can manifest in various forms, including vulnerabilities in audit software, reliance on inaccurate data, cyberattacks targeting audit systems, and inadequate training for audit personnel on new technologies. Effectively managing these risks requires a proactive and holistic approach that encompasses all aspects of the internal audit function.
Evolving Nature of Risks in the Digital Landscape
The digital landscape is constantly evolving, creating a dynamic environment for internal audit technology risks. New technologies, such as cloud computing, big data analytics, and artificial intelligence, introduce both opportunities and challenges for internal auditors. These advancements necessitate the adaptation of audit methodologies and procedures to maintain the effectiveness of internal controls. The increasing interconnectedness of systems also amplifies the potential impact of cyberattacks and data breaches.
Potential Impact on Organizations
Internal audit technology risks can have far-reaching consequences for organizations. A breach of security or a failure in audit software could expose sensitive data, disrupt operations, and result in financial losses. Furthermore, the inability to perform effective audits could lead to non-compliance with regulations, reputational damage, and legal repercussions. For instance, a company relying heavily on cloud-based systems for data storage might face significant operational disruptions if a security vulnerability compromises the cloud environment.
Comparison of Traditional and Modern Audit Methods
| Characteristic | Traditional Audit Methods | Modern Technology-Based Methods |
|---|---|---|
| Data Collection | Manual data collection from various sources, often time-consuming and prone to errors. | Automated data extraction from databases and systems, enabling faster and more accurate data collection. |
| Data Analysis | Manual analysis of data using spreadsheets or statistical software. Often limited by the volume and complexity of data. | Advanced analytics and machine learning algorithms to analyze large volumes of data, uncovering hidden patterns and anomalies. |
| Audit Efficiency | Slower and more resource-intensive, potentially limiting the scope of audits. | Enhanced efficiency and effectiveness, allowing for more comprehensive audits and a quicker turnaround time. |
| Risk Identification | Reliance on historical data and expert judgment. May miss emerging risks. | Real-time monitoring of systems and data, enabling proactive identification and mitigation of risks. |
| Cost | Higher cost due to manual processes and personnel. | Potentially lower cost in the long run due to automation and efficiency gains. |
Traditional audit methods are often resource-intensive and can be limited in scope. Modern technology-based methods offer enhanced efficiency and accuracy, allowing for more comprehensive and effective audits. Organizations must adapt their internal audit practices to leverage the advantages of technology while addressing the associated risks.
Types of Internal Audit Technology Risks
Internal audit functions are increasingly reliant on technology to perform their duties effectively. However, this reliance brings a new set of risks that must be proactively addressed. These risks can significantly impact the audit process, the quality of findings, and ultimately, the organization’s ability to mitigate operational and financial vulnerabilities. Understanding these risks is crucial for establishing robust internal controls and mitigating potential damage.
Data Security and Privacy Risks
Data breaches and unauthorized access to sensitive information are significant concerns in today’s digital landscape. Internal audit functions often handle confidential data related to financial transactions, employee information, and business strategies. This data is vulnerable to cyberattacks, phishing attempts, and insider threats. Protecting this data is paramount, and failures to do so can lead to reputational damage, legal ramifications, and financial losses.
Software Vulnerabilities and System Failures
The reliance on software applications for audit tasks creates vulnerabilities. Software bugs, outdated versions, and inadequate security measures can expose the organization to significant risks. Similarly, system failures, whether due to hardware malfunctions, software glitches, or unforeseen circumstances, can disrupt the audit process, leading to delays, missed deadlines, and compromised audit findings. Such disruptions can severely impact the audit’s effectiveness.
Audit Automation and RPA Risks
The implementation of automation tools like robotic process automation (RPA) can streamline internal audit tasks. However, the reliance on these tools introduces new risks. If the automation systems are not properly designed, tested, and maintained, errors can be introduced into the audit process, leading to inaccurate results. Furthermore, the dependence on these systems can create a single point of failure, potentially compromising the audit’s integrity if the system malfunctions.
A critical risk is that audit staff may become over-reliant on automation, losing essential judgment skills.
Third-Party Software and Cloud Computing Risks
Organizations increasingly use third-party software and cloud computing services for various internal audit functions. These external providers may have security vulnerabilities or inadequate controls, exposing sensitive data to potential risks. Moreover, data breaches or service disruptions at the third-party provider can have a cascading effect on the organization’s audit operations. The lack of visibility into the security measures and data handling practices of third-party providers adds complexity to risk assessment and mitigation.
Table of Internal Audit Technology Risks
| Type of Risk | Potential Consequences |
|---|---|
| Data Security and Privacy Breaches | Reputational damage, financial loss, legal penalties, loss of customer trust |
| Software Vulnerabilities/System Failures | Delayed audits, inaccurate findings, loss of audit evidence, operational disruption |
| Audit Automation/RPA Errors | Inaccurate audit results, loss of audit quality, increased audit time |
| Third-Party Software/Cloud Computing Risks | Data breaches, service disruptions, lack of visibility into security measures, increased complexity in risk assessment |
Factors Contributing to Internal Audit Technology Risks

Internal audit functions are increasingly reliant on technology to perform their tasks effectively. However, this reliance introduces a new set of risks that must be carefully considered and mitigated. These risks stem from various factors, ranging from inadequate cybersecurity measures to outdated IT infrastructure. Understanding these contributing factors is crucial for internal audit departments to proactively address potential vulnerabilities and maintain the integrity of their work.
Inadequate Cybersecurity Measures
Robust cybersecurity measures are paramount to protect sensitive audit data and systems from unauthorized access, breaches, and cyberattacks. Weaknesses in these measures create significant risks. A lack of robust firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and regular security updates can expose audit systems to malicious actors, leading to data breaches and the compromise of confidential information. This, in turn, compromises the integrity of audit findings and potentially exposes the organization to financial and reputational damage.
Lack of Employee Training and Awareness
Employee training and awareness programs are critical in fostering a security-conscious culture. A lack of training on cybersecurity best practices, phishing scams, and social engineering techniques leaves employees vulnerable to becoming unwitting victims of attacks. Phishing attempts and malicious software can be successfully deployed through unsuspecting employees, significantly increasing the risk of data breaches. Consequently, internal audit departments must prioritize employee training to minimize this risk.
Outdated or Poorly Maintained IT Systems
Outdated or poorly maintained IT systems pose significant risks to internal audit functions. Legacy systems, often lacking modern security features, are vulnerable to known exploits. The lack of necessary updates and maintenance can create vulnerabilities, making the system susceptible to malware, viruses, and other malicious attacks. Moreover, the incompatibility of these systems with current security protocols can hinder the efficient operation of audit activities and compromise data integrity.
Poor Data Governance Practices
Poor data governance practices significantly contribute to internal audit technology risks. Lack of clear data ownership, access controls, and data validation procedures can lead to data inconsistencies, errors, and breaches. This can impact the quality of audit findings, potentially hindering the identification of material weaknesses and impacting the effectiveness of internal controls. Poor data governance can also result in the inability to retrieve critical data for audit purposes.
Inadequate Audit Trail Management
Effective audit trail management is crucial for demonstrating the accuracy and completeness of audit activities. Insufficient or poorly maintained audit trails can hinder the ability to track transactions, identify anomalies, and investigate potential fraud. This lack of traceability can hinder the investigation process and compromise the reliability of audit conclusions. Properly maintained audit trails provide a robust mechanism to track activities, enabling effective investigation and ensuring the integrity of audit findings.
Factors Contributing to Internal Audit Technology Risks and Mitigation Strategies
| Factor Contributing to Risk | Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|
| Inadequate Cybersecurity Measures | Implement robust security controls, including firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and regular security updates. Conduct regular security assessments and penetration testing. Provide comprehensive cybersecurity training to employees. |
| Lack of Employee Training and Awareness | Develop and implement comprehensive cybersecurity training programs for all employees. Conduct regular phishing simulations to test awareness levels. Establish clear communication channels for reporting security incidents. |
| Outdated or Poorly Maintained IT Systems | Regularly update and maintain IT systems with the latest security patches and upgrades. Implement a phased migration plan to newer, more secure systems where appropriate. Evaluate the security posture of legacy systems and implement necessary controls. |
| Poor Data Governance Practices | Establish clear data ownership, access controls, and data validation procedures. Implement data quality checks and monitoring to identify and correct data inconsistencies. Develop and enforce data retention policies. |
| Inadequate Audit Trail Management | Establish and maintain comprehensive audit trails for all critical transactions and activities. Implement robust logging mechanisms to record user actions and system events. Ensure regular review and analysis of audit trails to identify anomalies. |
Impact of Internal Audit Technology Risks
Internal audit functions increasingly rely on technology for efficiency and effectiveness. However, this reliance also introduces new vulnerabilities. Understanding the potential consequences of technology risks is crucial for mitigating their impact and safeguarding the organization. This section delves into the various facets of these consequences, from financial losses to reputational damage and operational disruptions.
Financial Consequences
Technology risks can translate into significant financial losses. Data breaches can lead to direct costs like notification expenses, legal fees, and regulatory fines. Lost revenue due to system downtime, compromised transactions, or reduced customer trust can also be substantial. Indirect costs, such as the cost of recovery and remediation, often exceed the initial damage. For example, a ransomware attack on a hospital’s system could halt critical operations, impacting patient care and resulting in substantial financial losses.
Reputational Damage
Technology-related breaches can severely damage an organization’s reputation. Public disclosure of data breaches, especially sensitive information like customer details or financial records, can erode trust and damage brand image. Loss of customer confidence can lead to decreased sales, lost contracts, and long-term negative effects on market perception. Consider the impact of the Equifax breach, where the exposure of millions of customer records resulted in a substantial drop in consumer confidence and a significant decline in the company’s stock price.
Operational Efficiency and Productivity
Technology risks can significantly disrupt operational efficiency and productivity. System outages, data breaches, or security incidents can lead to delays in critical processes, impacting production schedules and customer service delivery. The cost of recovery and remediation can also divert resources away from core business activities, further reducing productivity. For instance, a cyberattack on a manufacturing plant’s control systems could lead to production halts, supply chain disruptions, and significant financial losses.
Regulatory Non-Compliance
Technology risks can expose organizations to regulatory non-compliance issues. Failure to adhere to data protection regulations (like GDPR or CCPA) can lead to substantial penalties. Breaches of security standards or inadequate controls can result in regulatory fines, legal actions, and reputational damage. For example, a healthcare provider failing to comply with HIPAA regulations regarding patient data security could face significant fines and reputational harm.
Impact on Stakeholder Confidence and Trust, Internal audit technology risks
Technology risks can erode stakeholder confidence and trust. Investors, customers, and employees may lose faith in the organization’s ability to manage risk effectively. A data breach can lead to investor uncertainty, a decrease in stock price, and loss of customer loyalty. Employees may also lose confidence in the organization’s ability to protect their data and personal information.
This decline in trust can have long-term consequences, impacting the organization’s ability to attract and retain talent.
Impact of Technology Risks: Summary Table
| Impact Category | Description | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Financial | Direct costs (fines, notification) and indirect costs (recovery, lost revenue) | Ransomware attacks, data breaches, system downtime |
| Reputational | Damage to brand image, loss of customer trust, negative market perception | Data breaches exposing sensitive information, security incidents |
| Operational | Disruptions to processes, delays, reduced productivity, resource diversion | System outages, cyberattacks, security incidents |
| Regulatory | Non-compliance with data protection regulations, security standards | Breaches of GDPR, HIPAA, or other relevant regulations |
| Stakeholder | Loss of investor confidence, decreased customer loyalty, employee distrust | Data breaches, security incidents, lack of transparency |
Mitigation Strategies for Internal Audit Technology Risks
Internal audit functions are increasingly reliant on technology. This reliance, while offering efficiencies and new insights, also introduces new vulnerabilities. Effective mitigation strategies are crucial to safeguarding the integrity of audit processes and the organization’s data. Understanding and implementing these strategies is vital for maintaining trust and ensuring compliance.
Improving Data Security and Privacy Measures
Robust data security and privacy are paramount in the digital age. Implementing strong access controls, including multi-factor authentication and least privilege principles, is essential. Regular security audits and penetration testing help identify and address vulnerabilities. Data encryption, both in transit and at rest, is critical to protecting sensitive information. Furthermore, adherence to industry best practices and relevant regulations (e.g., GDPR, CCPA) is mandatory for protecting data privacy.
This comprehensive approach minimizes the risk of unauthorized access, data breaches, and privacy violations.
Enhancing System Security and Vulnerability Management
Proactive system security is key to mitigating technology risks. Implementing regular security patches and updates is a fundamental step. Employing intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDPS) can help identify and respond to malicious activity. Regular vulnerability assessments and penetration testing are crucial for identifying weaknesses in systems and promptly addressing them. Maintaining a robust incident response plan, outlining procedures for dealing with security breaches, is essential.
This structured approach ensures the organization can effectively react to and recover from security incidents.
Ensuring Proper Employee Training and Awareness
Employee training and awareness programs are critical to mitigating technology risks. Comprehensive training should cover phishing awareness, safe password practices, and recognizing suspicious emails or websites. Regular updates and refresher courses reinforce knowledge and address emerging threats. Empowering employees to report suspicious activities fosters a culture of security awareness. This proactive approach empowers employees to act as the first line of defense against cyber threats.
Implementing Robust Data Governance Practices
Effective data governance is vital for managing the increasing volume and complexity of data. Establishing clear data ownership and access policies ensures data is used appropriately and complies with regulations. Defining data retention policies and schedules helps organizations manage data lifecycles and comply with legal requirements. Developing robust data quality standards minimizes inconsistencies and errors. Regular data audits and compliance checks ensure adherence to policies and regulations.
This comprehensive framework ensures data is managed effectively, ethically, and securely.
Comparing Risk Mitigation Strategies and Effectiveness
| Mitigation Strategy | Description | Effectiveness (High/Medium/Low) | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Strong Access Controls | Implementing multi-factor authentication and least privilege | High | Requiring both a password and a code from a mobile device for login. |
| Regular Security Audits | Conducting penetration testing and vulnerability assessments | Medium | Using specialized tools to identify potential weaknesses in systems. |
| Employee Training | Providing regular training on phishing and security awareness | High | Simulated phishing exercises to test employee awareness. |
| Data Encryption | Encrypting data in transit and at rest | High | Using encryption protocols for sensitive data transmitted over networks. |
The effectiveness ratings are relative and can vary depending on the specific implementation and context.
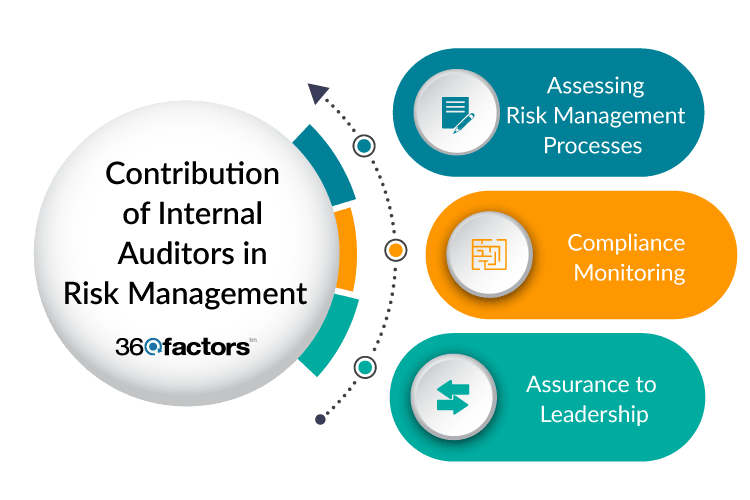
Role of a Strong Internal Audit Function in Mitigating Risks
A robust internal audit function plays a crucial role in mitigating technology risks. By evaluating the effectiveness of security controls, identifying vulnerabilities, and assessing the adequacy of risk management processes, internal auditors can provide valuable insights and recommendations. They can also assess the overall impact of technology risks on the organization and provide guidance on how to address them.
Internal auditors act as a safeguard, ensuring the organization’s systems and data are protected against vulnerabilities.
Case Studies of Internal Audit Technology Risks
Internal audit technology risks are not theoretical concerns; they have tangible impacts on organizations. Understanding real-world examples helps us grasp the severity and potential for losses associated with these risks. These case studies offer valuable insights into the importance of proactive risk management and mitigation strategies within the realm of internal audit.Technology-related risks are ever-evolving, and companies must adapt their internal audit procedures accordingly.
By studying successful and unsuccessful responses to technology-related audit risks, we can develop more robust strategies for protecting our organizations from similar threats in the future.
Case Study of a Major Data Breach
Target, a major US retailer, suffered a significant data breach in 2013. Hackers gained access to customer credit card information, compromising the personal data of millions. This breach highlighted vulnerabilities in Target’s security systems, including outdated technology and inadequate security protocols. The incident resulted in substantial financial losses due to credit card fraud, regulatory fines, and reputational damage.
The company’s response to the breach, while eventually effective, was perceived by many as slow and insufficient, compounding the negative impact.
Case Study of Successful Mitigation of a Technology-Related Audit Risk
A multinational bank implemented advanced fraud detection software. This technology proactively identified and flagged suspicious transactions, significantly reducing fraudulent activities. By integrating the software into its internal audit process, the bank strengthened its ability to detect and respond to potential fraud. This proactive approach prevented significant financial losses and maintained customer trust.
Impact of a Specific Technology Risk on Company Operations
A manufacturing company heavily reliant on a proprietary software system experienced a system outage. The outage lasted for several days, disrupting production schedules and supply chains. The company’s inability to access critical data led to significant delays in order fulfillment, impacting customer satisfaction and profitability. The incident exposed the critical role of data backups and disaster recovery plans in maintaining business continuity.
How Technology Risks Can Lead to Financial Losses
A small e-commerce company suffered a ransomware attack. The attackers encrypted the company’s critical data, demanding a substantial ransom to restore access. The company, lacking sufficient backup systems, paid the ransom, resulting in significant financial losses. Furthermore, the incident resulted in a loss of customer data, leading to regulatory penalties and further financial damage.
How a Company’s Reputation Suffered Due to Technology Risks
A social media platform experienced a security vulnerability that exposed user data. The incident resulted in a significant drop in user trust and confidence. The platform’s reputation was severely tarnished, leading to a decline in user engagement and advertising revenue. The incident highlighted the importance of prioritizing user data security and transparency in addressing technology-related risks.
Summary Table of Case Studies
| Case Study | Description | Lessons Learned |
|---|---|---|
| Target Data Breach | Target experienced a major data breach exposing millions of customer credit card details. | Outdated security systems and inadequate security protocols can lead to severe data breaches. A swift and transparent response is crucial in mitigating reputational damage. |
| Multinational Bank Fraud Mitigation | A bank implemented advanced fraud detection software, reducing fraudulent activities. | Proactive measures and robust technology solutions can significantly mitigate technology-related audit risks. |
| Manufacturing Company Outage | A manufacturing company experienced a system outage disrupting production and supply chains. | Data backups and disaster recovery plans are critical for business continuity in the face of technology failures. |
| E-commerce Ransomware Attack | An e-commerce company was victimized by a ransomware attack leading to data encryption and financial losses. | Robust backup systems and incident response plans are essential for mitigating ransomware attacks and ensuring business continuity. |
| Social Media Platform Data Breach | A social media platform suffered a data breach compromising user data. | Prioritizing user data security and maintaining transparency are essential for maintaining user trust and reputation. |
Future Trends in Internal Audit Technology Risks
The landscape of internal audit is rapidly evolving, driven by technological advancements. Emerging technologies introduce new avenues for risk, demanding a proactive and adaptive approach from internal audit teams. This necessitates a deep understanding of these emerging technologies and their potential impacts on audit processes. This exploration delves into the future of internal audit technology risks, focusing on emerging trends and their implications.
Emerging Technologies and Audit Risks
The constant innovation in technology creates new avenues for both opportunities and risks. Internal audit departments must be aware of these new technologies to ensure that their processes remain effective. The increasing complexity of interconnected systems necessitates a thorough understanding of how these technologies interact and potentially expose vulnerabilities. Failure to adapt to these trends can leave organizations exposed to significant risks.
Impact of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML)
AI and ML are transforming many industries, and internal audit is no exception. These technologies can automate tasks, identify anomalies, and enhance the efficiency of audit processes. However, concerns exist regarding the potential for bias in algorithms, the lack of transparency in decision-making, and the need for appropriate oversight. Internal audit professionals need to adapt their skills to effectively leverage these technologies while mitigating potential risks.
Impact of Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology offers opportunities for enhanced security and transparency in internal audit processes. By creating immutable records, blockchain can improve the traceability and reliability of audit trails. However, the complexity of blockchain technology and the need for specialized knowledge present challenges. Implementing blockchain requires careful planning and consideration of its potential impact on existing audit infrastructure.
Impact of the Internet of Things (IoT)
The proliferation of IoT devices introduces new risks related to data security, device vulnerabilities, and the management of vast amounts of data. Internal audit needs to assess the security and integrity of IoT systems to ensure that data remains protected and that operational processes are not compromised. Auditing IoT environments requires a shift in approach, focusing on the interconnectedness of devices and the potential for cascading failures.
Impact of Cloud Computing
The increasing adoption of cloud computing presents both opportunities and challenges for internal audit. Cloud-based systems can improve efficiency and accessibility but also introduce new security concerns related to data breaches and unauthorized access. Internal audit must assess the security controls implemented by cloud providers and evaluate the potential impact on audit processes.
Predictions for Future Technology Risks
| Technology | Potential Risk | Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Advanced Automation (Robotic Process Automation – RPA) | Loss of human oversight, potential for errors in complex processes, dependency on software maintenance | Establish clear oversight procedures, maintain human intervention points, and ensure ongoing testing and maintenance of automation tools. |
| Quantum Computing | Potential for breaking current encryption methods, increasing the complexity of risk assessment. | Invest in research and development of quantum-resistant encryption techniques, and continuously evaluate and update audit strategies to remain ahead of quantum computing’s impact. |
| Metaverse | Data security in virtual environments, fraud, and misrepresentation. | Develop new standards for data security in virtual environments, and proactively monitor for fraud and misrepresentation. |
| Cyber-physical systems | Increased attack surface from vulnerabilities in physical systems, potential for cascading failures. | Implement rigorous security measures in cyber-physical systems, and establish protocols for detecting and responding to potential vulnerabilities. |
Final Review
In conclusion, internal audit technology risks are an undeniable reality in the modern business world. By understanding the diverse types of risks, the factors that contribute to them, and the potential impacts, organizations can proactively implement robust mitigation strategies. The key is to recognize that these risks are dynamic and constantly evolving, requiring a proactive and adaptable approach to internal audit practices.
A strong internal audit function, combined with a commitment to cybersecurity and employee training, is paramount to mitigating these risks and ensuring long-term organizational success.
Helpful Answers
What are some common types of data breaches that internal audit technology risks can lead to?
Common data breaches related to internal audit technology risks include unauthorized access, data theft, ransomware attacks, and phishing scams. These breaches can have significant financial and reputational consequences for the organization.
How does employee training and awareness affect internal audit technology risks?
Employee training and awareness programs play a crucial role in mitigating technology risks. Educating employees about cybersecurity threats, data handling procedures, and the importance of strong passwords can significantly reduce the likelihood of successful attacks.
What is the role of a strong internal audit function in mitigating internal audit technology risks?
A robust internal audit function acts as a crucial safeguard against technology risks. They can conduct regular audits of IT systems, identify vulnerabilities, and ensure compliance with relevant regulations, significantly reducing the organization’s exposure to threats.
What are some emerging technologies that introduce new audit risks?
Emerging technologies like AI, machine learning, blockchain, and the Internet of Things (IoT) introduce new challenges to internal audit. These technologies often have complex structures and data flows that traditional audit methods might not fully encompass.
