
Roll Out Finance Automation with the Right Priorities
Roll out finance automation with the right priorities is crucial for any business aiming to optimize financial processes and gain a competitive edge. This involves careful planning, meticulous execution, and a clear understanding of the potential benefits and challenges. This guide will cover everything from defining finance automation to measuring success, providing a roadmap for a smooth and impactful implementation.
Understanding the different types of automation solutions, their features, costs, and implementation complexities is paramount. Prioritizing projects based on business value and feasibility, while addressing potential roadblocks, are essential steps. A robust roadmap, including stakeholder engagement, technology selection, and resource allocation, is critical for success.
Defining Finance Automation
Finance automation is revolutionizing how businesses manage their financial operations. It encompasses the use of technology to streamline, optimize, and automate various financial tasks, freeing up valuable time and resources for strategic initiatives. This approach leverages software, tools, and processes to improve accuracy, reduce errors, and enhance overall efficiency. The key benefits are clear: increased productivity, reduced costs, and improved decision-making capabilities.The core components of finance automation include automating tasks like invoice processing, expense reporting, reconciliation, and budgeting.
Modern systems often integrate with other business applications to provide a holistic view of financial data and streamline workflows. This seamless integration allows for real-time data updates and improved visibility across departments.
Types of Finance Automation Solutions
Finance automation solutions come in diverse forms, catering to various needs and budgets. These solutions range from simple, dedicated software tools to complex, enterprise-level platforms.
- Software solutions automate repetitive tasks, like data entry and report generation, improving accuracy and speed.
- Specialized tools automate specific financial functions, such as accounts payable or accounts receivable. These tools often integrate with existing accounting systems.
- Process automation involves re-engineering financial processes to leverage technology. This often includes workflow management systems and robotic process automation (RPA) to streamline and automate manual steps.
Impact on Business Functions
Finance automation impacts various business functions beyond just the finance department. Improved efficiency in financial processes translates to enhanced productivity across the entire organization. For example, timely expense reports allow for faster reimbursement cycles, freeing up cash flow. Automated invoice processing reduces delays in payments, which can strengthen supplier relationships.
Obtain a comprehensive document about the application of cima ethics confidentiality rules that is effective.
- Improved Cash Flow: Automated invoice processing and payment reconciliation can significantly reduce delays in payment processing, leading to a more efficient cash flow management cycle.
- Reduced Operational Costs: Automation reduces the need for manual data entry, reducing errors and freeing up personnel for more strategic tasks.
- Enhanced Decision Making: Real-time financial data enables better, more informed decisions, which in turn leads to increased profitability.
Comparison of Finance Automation Solutions
The table below provides a comparative analysis of different finance automation solutions based on their features, cost, and implementation complexity.
| Solution Type | Features | Cost | Implementation Complexity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Basic Accounting Software | Basic invoice processing, expense tracking, and reporting | Low to Medium | Low |
| Specialized Finance Tools | Automated accounts payable/receivable, bank reconciliation, and budget management | Medium to High | Medium |
| Enterprise-Level ERP Systems | Comprehensive financial management, integrated with other business functions | High | High |
Note: Cost and complexity can vary based on the specific features, integrations, and customization required.
Identifying Priorities for Rollout
Finance automation is no longer a “nice-to-have” but a critical component of modern financial operations. Successfully rolling out automation requires a meticulous approach, focusing on strategic priorities to maximize efficiency and ROI. This involves careful consideration of various factors, from assessing the business value of each process to mitigating potential challenges.A well-defined plan for finance automation, including clear priorities, significantly reduces the risk of failure and ensures that the investment yields substantial returns.
This approach ensures that the chosen automation initiatives align with the organization’s overall strategic goals, leading to a smoother implementation process.
Critical Factors in Planning a Finance Automation Rollout
Careful planning is crucial for a successful finance automation rollout. This involves a thorough evaluation of existing processes, identifying areas ripe for automation, and understanding the specific needs and limitations of the organization. The factors to consider extend beyond technical feasibility and encompass organizational culture, stakeholder engagement, and data quality.
- Process Analysis: A comprehensive analysis of existing financial processes is essential to identify opportunities for automation. This includes evaluating the steps involved, identifying bottlenecks, and assessing the potential for streamlining and optimization. For example, manual invoice processing can be significantly automated, freeing up valuable time for other tasks.
- Data Quality Assessment: The accuracy and completeness of data are critical for automation success. Inaccurate data will lead to flawed outputs and hinder the entire process. Assessing the quality of existing data, implementing data cleansing and validation procedures, and establishing data governance protocols are crucial.
- Stakeholder Engagement: Gaining buy-in from key stakeholders, including finance staff, management, and other departments affected by the automation, is essential. This involves clear communication, addressing concerns, and fostering collaboration throughout the process.
- Resource Allocation: Proper allocation of resources, including budget, personnel, and time, is vital. Identifying the necessary skills and expertise, procuring the required software or tools, and allocating time for training and support are all crucial elements.
Potential Challenges and Mitigation Strategies, Roll out finance automation with the right priorities
Implementing finance automation can present various challenges. Understanding these potential hurdles and developing mitigation strategies is crucial for a successful rollout. These challenges include resistance to change, integration issues, and data security concerns.
- Resistance to Change: Employees may resist changes in their routines and workflows. Addressing these concerns through proactive communication, training, and support is vital. A well-structured communication plan, addressing concerns and outlining the benefits, can help mitigate this resistance.
- Integration Issues: Integrating new automation systems with existing financial systems can be complex. Thorough planning, testing, and careful system selection can help minimize integration problems.
- Data Security Concerns: Protecting sensitive financial data is paramount. Implementing robust security measures, adhering to industry regulations, and ensuring data encryption are essential steps.
Prioritizing Automation Projects
A structured approach to prioritizing automation projects is essential. This prioritization should be based on both the potential business value and the feasibility of implementation.
- Business Value Assessment: Evaluate the potential return on investment (ROI) for each project. This includes quantifying the cost savings, increased efficiency, and improved decision-making that automation can provide.
- Feasibility Assessment: Consider the technical feasibility, resource availability, and potential impact on existing processes. This involves assessing the complexity of the automation, the availability of necessary skills and resources, and the potential disruption to existing workflows.
ROI Assessment Framework
A structured framework is essential for assessing the potential ROI of different automation initiatives.
| Automation Initiative | Estimated Cost | Estimated Savings | Estimated ROI | Feasibility Score | Priority Level |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Invoice Processing Automation | $10,000 | $20,000 | 200% | 9/10 | High |
| Payroll Automation | $5,000 | $15,000 | 300% | 8/10 | High |
| Accounts Payable Automation | $15,000 | $30,000 | 200% | 7/10 | Medium |
Establishing a Roadmap

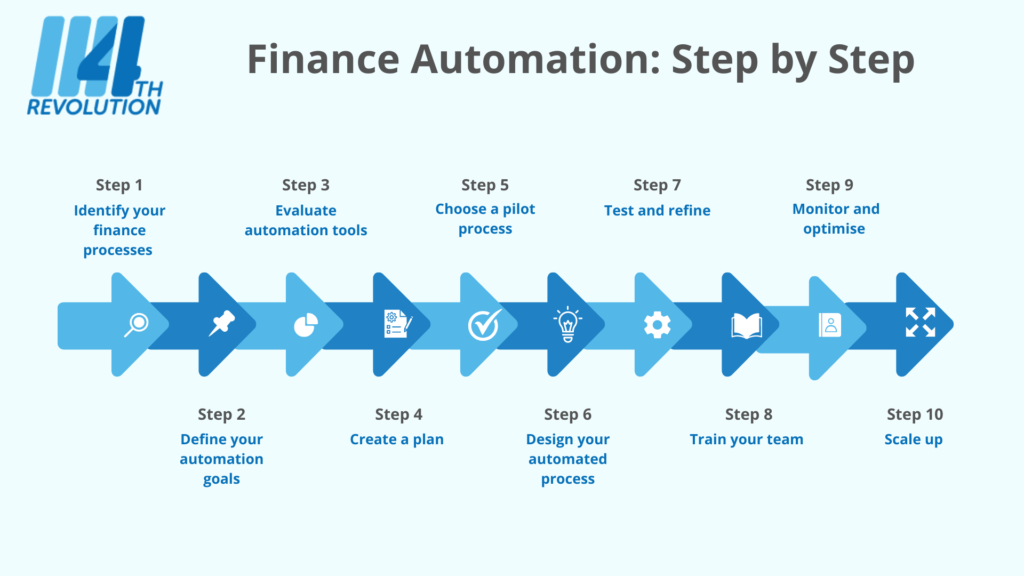
Finance automation isn’t a switch you flip; it’s a journey. A well-defined roadmap is crucial for navigating this journey successfully, ensuring alignment across teams and maximizing the ROI of your automation efforts. This roadmap should be a living document, adapting to changing needs and priorities as you progress.A robust finance automation roadmap acts as a blueprint, guiding your team through each phase of implementation, from initial planning to ongoing maintenance.
It details the specific steps, timelines, and resources required for a smooth and efficient rollout. It’s more than just a list of tasks; it’s a strategic framework for achieving your automation goals.
Step-by-Step Roadmap Development
Developing a finance automation roadmap is an iterative process. It starts with a clear understanding of your current state, followed by defining specific automation targets and then outlining the steps to reach those targets. This approach fosters a clear vision and sets realistic expectations for each stage of the process.
- Assessment and Gap Analysis: Begin by thoroughly evaluating your current finance processes. Identify bottlenecks, manual tasks, and areas prone to errors. This assessment will highlight opportunities for automation and help you understand the specific pain points that automation can address. A crucial element is to assess the current technology stack and its integration capabilities to understand the existing infrastructure and limitations.
- Define Automation Targets: Prioritize specific tasks and processes for automation based on the assessment. Focus on high-impact areas with the greatest potential for efficiency gains. These targets should be measurable, time-bound, and aligned with overall business objectives.
- Select Appropriate Technology and Vendors: Research and evaluate various automation tools and vendors. Consider factors like scalability, integration capabilities, security features, and vendor support. Thorough due diligence is essential to avoid unforeseen complications during implementation.
- Develop a Phased Implementation Plan: Divide the automation rollout into manageable phases. Start with pilot projects to test the chosen technology and processes in a controlled environment. Gradually expand automation to other areas as the system proves reliable. This phased approach mitigates risk and ensures a smooth transition.
- Establish a Project Timeline and Resource Allocation: Develop a detailed project timeline with milestones for each phase. Allocate resources – including personnel, budget, and technology – effectively for each stage of the implementation process. Identify critical paths and dependencies within the timeline to proactively address potential delays.
- Ongoing Monitoring and Evaluation: Establish metrics to track the success of the automation initiative. Regularly monitor system performance and make necessary adjustments to processes and technology as needed. This ongoing evaluation ensures that the automation remains effective and relevant over time.
Stakeholder Engagement
Stakeholder buy-in and active participation are critical for a successful finance automation rollout. Engaging key stakeholders from the beginning ensures that the automation aligns with their needs and expectations.
- Identify Key Stakeholders: Identify all individuals and departments who will be affected by or involved in the automation process. This includes finance teams, operations teams, and other relevant departments.
- Communicate Effectively: Clearly communicate the objectives, benefits, and potential impact of automation to all stakeholders. Address concerns and provide regular updates on the progress of the project.
- Seek Feedback and Input: Actively solicit feedback from stakeholders throughout the process. Incorporate their insights and suggestions to refine the automation strategy and ensure that it meets their needs.
- Foster Collaboration: Create opportunities for stakeholders to collaborate and work together to address challenges and optimize processes. This collaboration will improve the overall understanding of the process and encourage buy-in.
Technology Selection Considerations
Choosing the right technology and vendor is critical for a successful automation implementation. Careful consideration of various factors will lead to a smoother, more efficient process.
- Scalability and Flexibility: Select systems that can adapt to future growth and changing business needs. Assess the system’s ability to accommodate increasing data volumes and evolving requirements.
- Integration Capabilities: Ensure seamless integration with existing systems to avoid data silos and maintain data integrity. This includes evaluating the system’s compatibility with other financial applications, ERP systems, and data warehouses.
- Security and Compliance: Prioritize security features to protect sensitive financial data. Ensure that the chosen technology and vendor comply with relevant industry regulations and standards.
- Vendor Support and Expertise: Evaluate the vendor’s support capabilities and technical expertise. Look for a vendor with a proven track record and a strong support team.
Data Management and Integration
Finance automation thrives on accurate and reliable data. Without robust data management, the entire system crumbles. This crucial stage ensures the smooth operation and effectiveness of automated finance processes. This section delves into the essential aspects of data management, from quality and integrity to security, integration, and optimal structuring.
Importance of Data Quality and Integrity
High-quality data is the bedrock of reliable financial insights. Inaccurate or inconsistent data leads to flawed analyses, incorrect reporting, and ultimately, poor decision-making. Data integrity, meaning the accuracy and consistency of data over time, is paramount. Maintaining data quality and integrity requires establishing clear data validation rules, implementing data cleansing procedures, and regularly auditing data sources. Errors and inconsistencies, if left unaddressed, can propagate throughout the automated system, leading to significant inaccuracies and potentially impacting financial reporting and compliance.
Examine how positive outlook financial services work in europe can boost performance in your area.
Data Migration and Integration Process
A well-defined data migration and integration process is essential for a successful finance automation rollout. This process should include careful planning, data mapping, and testing. A phased approach is often the best strategy. Start with a pilot program to identify and address any potential issues. This enables a smooth transition to the full implementation.
Thorough data mapping is critical to ensure data from legacy systems seamlessly integrates with the new automated finance system. Data validation steps at each stage of the migration process are crucial for identifying and correcting any discrepancies before they affect the automated system. The migration process must be carefully documented and monitored throughout to identify and resolve any unforeseen issues.
Data Security and Compliance
Data security and compliance are paramount in automated finance systems. Protecting sensitive financial data is crucial for maintaining regulatory compliance and preventing fraud. Robust security measures, including encryption, access controls, and regular security audits, are essential. Compliance with relevant regulations, such as GDPR, CCPA, and SOX, is critical. Implementing these security protocols not only protects sensitive data but also safeguards the organization’s reputation and financial stability.
Data encryption, access controls with least privilege principles, and regular security audits are essential components of a robust security strategy.
Data Structuring for Optimal Use
Data structuring is critical for maximizing the value of the automated finance system. A well-structured data model ensures that data is easily accessible, usable, and analyzable. Standardizing data formats and implementing consistent naming conventions across the system is vital. A clear data dictionary, documenting the meaning and usage of each data element, is essential for maintaining data consistency and ensuring data is understood and used correctly.
Defining clear relationships between data entities and using appropriate data types will improve the efficiency of the automated system and reduce errors.
Training and Change Management
Finance automation is not just about implementing new software; it’s about transforming how your entire finance team works. A successful rollout hinges on a comprehensive training and change management strategy. Without proper preparation, even the most sophisticated automation tools can lead to frustration, resistance, and ultimately, failure to achieve the desired benefits. This phase is critical to ensure employees embrace the new processes and technology, maximizing the return on investment.Effective training and change management aren’t just nice-to-haves; they are essential components of a successful finance automation project.
They empower employees to adapt to new roles and responsibilities, fostering a culture of collaboration and innovation. This section delves into the crucial elements of creating a smooth transition, focusing on employee training, change management strategies, and ongoing communication.
Importance of Comprehensive Training
Employee buy-in is crucial for successful finance automation. Training programs should go beyond basic software operation. They should equip employees with the knowledge and skills needed to understand the underlying processes, leverage the automation tools to their maximum potential, and address potential challenges effectively. Comprehensive training not only increases proficiency but also boosts confidence and reduces anxiety around the new systems.
This confidence translates into faster adoption and a more efficient workflow.
Strategies for Managing Change and Minimizing Resistance
Resistance to change is a natural human response. To mitigate this, proactive change management is vital. This involves clearly communicating the reasons behind the automation, highlighting the benefits for individuals and the organization as a whole. For instance, demonstrating how automation frees up time for more strategic tasks or improves accuracy in reporting can help alleviate concerns.
Transparency and open communication channels are essential throughout the entire process. Employees should feel empowered to ask questions and voice concerns without fear of reprisal. Addressing concerns promptly and providing solutions proactively helps foster a supportive and collaborative environment. This strategy builds trust and acceptance of the new processes.
Designing and Delivering Effective Training Programs
Training programs must be tailored to different roles and skill levels within the finance team. Junior analysts will require different training than senior managers. A blended learning approach, combining online modules, hands-on workshops, and one-on-one coaching, can cater to diverse learning styles and preferences. Interactive simulations, allowing employees to practice new procedures in a risk-free environment, are highly effective.
This practical application reinforces learning and builds confidence. Providing regular feedback and opportunities for ongoing support, such as online forums or dedicated help desks, is essential for sustaining knowledge and addressing any emerging issues. The key is to make the training engaging, relevant, and easily accessible.
Communication Plan
A clear and consistent communication plan is critical for keeping stakeholders informed throughout the rollout. This includes regular updates on project progress, timelines, and any potential roadblocks. Open forums, newsletters, and dedicated intranet pages can keep everyone informed. This transparency reduces speculation and anxiety, fostering a shared understanding of the goals and benefits of the automation. Regular Q&A sessions with key stakeholders, including finance leadership, can address concerns and answer questions in real-time.
This active engagement builds trust and creates a collaborative atmosphere.
Continuous Improvement
Finance automation isn’t a one-time project; it’s a journey of continuous refinement. A robust system requires ongoing monitoring, evaluation, and adaptation to stay aligned with evolving business needs and market dynamics. This phase focuses on building a sustainable, high-performing automation engine, ensuring long-term value.Effective finance automation isn’t static; it requires a proactive approach to improvement. A well-defined plan for ongoing maintenance and support is crucial to sustaining the benefits of automation.
This includes mechanisms for identifying areas for improvement and implementing adjustments to the system over time.
Monitoring and Evaluating Performance
Regular monitoring and evaluation of the finance automation system are essential to identify potential issues and opportunities for improvement. Key performance indicators (KPIs) should be established to track system efficiency, accuracy, and cost-effectiveness. These metrics could include processing time, error rates, and resource utilization. Tracking these metrics over time allows for the identification of trends and patterns, revealing areas needing attention.
Remember to click how to clearly communicate feedback and expectations to understand more comprehensive aspects of the how to clearly communicate feedback and expectations topic.
This continuous observation ensures the system’s continued effectiveness.
Identifying Areas for Improvement and Optimization
Regular reviews and analysis of performance data are critical to identify bottlenecks and areas for optimization. Reviewing user feedback, system logs, and performance reports can reveal issues like data inconsistencies, inefficient workflows, or underutilized functionalities. This data-driven approach ensures that the system is always performing at its best. Analyzing user feedback and system logs will provide valuable insights into user experience and technical performance.
Adapting and Refining the Automation System
The business landscape is constantly evolving. The finance automation system must adapt to accommodate new business requirements, regulatory changes, and technological advancements. Flexibility is key; the system should be designed to accommodate future needs and allow for easy adjustments to processes or data flows. Examples include updating data sources or integrating new financial systems. This proactive approach prevents the system from becoming obsolete and maintains its value proposition.
Ongoing System Maintenance and Support
A robust maintenance plan ensures the continued functionality and reliability of the automation system. This plan should encompass regular system checks, updates, and backups. A dedicated support team or individual should be responsible for addressing issues, resolving problems, and providing assistance to users. This proactive approach will mitigate downtime and maintain user confidence in the system’s reliability.A comprehensive support documentation should be readily available, guiding users on how to troubleshoot common problems and utilize the system effectively.
Security and Compliance: Roll Out Finance Automation With The Right Priorities
Finance automation, while offering significant benefits, introduces heightened security risks. Robust security measures are crucial to protect sensitive financial data and maintain compliance with relevant regulations. This section details the importance of security and compliance in a finance automation system, emphasizing the need for proactive measures to mitigate risks.
Importance of Robust Security Measures
A finance automation system handles highly sensitive financial data, making robust security measures paramount. Compromised data can lead to significant financial losses, reputational damage, and legal repercussions. Protecting this data requires a layered approach, encompassing multiple security controls. A strong security posture prevents unauthorized access, data breaches, and manipulation of financial records, safeguarding the integrity of the entire financial ecosystem.
Regulatory Compliance Requirements
Various regulatory bodies dictate compliance standards for handling financial data. These regulations aim to protect consumers and maintain the stability of the financial system. Specific requirements vary based on jurisdiction and the type of financial institution. Examples include the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe and the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) for organizations handling credit card information.
Adherence to these regulations is crucial for avoiding penalties and maintaining operational efficiency.
Data Encryption and Access Controls
Data encryption and robust access controls are essential elements of a secure finance automation system. Data encryption converts readable data into an unreadable format, preventing unauthorized access even if data is intercepted. Access controls define who can access specific data and what actions they can perform. Implementing granular access control lists limits the potential damage from unauthorized access or insider threats.
Examples include encrypting sensitive data at rest and in transit, implementing multi-factor authentication, and regularly reviewing and updating access privileges.
Security Protocols and Best Practices
A comprehensive security strategy requires implementing and maintaining robust security protocols and best practices. This involves regular security assessments, vulnerability scanning, penetration testing, and incident response planning. For example, regularly patching software vulnerabilities is a critical practice to prevent attackers from exploiting known weaknesses. Security awareness training for employees is also essential, as human error is a significant factor in data breaches.
Implementing a zero-trust security model, where every user and device is treated as a potential threat, enhances security posture.
Measuring Success
Finance automation isn’t just about implementing new software; it’s about achieving tangible results. A successful rollout requires meticulous tracking and analysis to ensure the investment delivers the expected return and improves overall financial processes. This phase focuses on establishing clear metrics to gauge the effectiveness of the automation, not just the technology itself.Effective measurement allows for adjustments and optimizations throughout the implementation, making the automation process more efficient and ultimately benefiting the organization.
Regular monitoring and reporting ensure that the automation continues to meet business objectives and provide the desired value.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
To assess the success of finance automation, a comprehensive set of KPIs must be defined and tracked. These metrics should reflect the specific goals of the automation project, encompassing efficiency gains, accuracy improvements, and cost savings.
- Processing Time Reduction: Tracking the time taken to complete various financial tasks, such as invoice processing or expense reporting, provides a direct measure of efficiency gains. For example, if invoice processing time decreases from 5 days to 2 days, this indicates a significant improvement in efficiency.
- Error Rate Reduction: Monitoring the number of errors detected in financial transactions before and after automation provides valuable insight into the accuracy of the automated processes. A reduction in errors, for instance, from 1% to 0.5% signals improved accuracy.
- Cost Savings: Identifying and quantifying cost reductions achieved through automation is crucial. This can include reductions in labor costs, material costs, or other operational expenses. For instance, a company might save $50,000 annually by automating accounts payable processes.
- User Adoption Rate: Assessing the rate at which finance professionals are using the new automated tools is critical. High adoption rates indicate the tool is user-friendly and valuable to the team. For instance, 90% of finance team members utilizing the new software demonstrates high adoption.
Return on Investment (ROI)
Calculating the ROI of finance automation allows for a quantitative assessment of its value to the organization. This involves comparing the benefits derived from the automation against the costs of implementation.
ROI = (Benefits – Costs) / Costs
The benefits encompass cost savings, efficiency gains, and improved accuracy. The costs include software licensing fees, implementation costs, training expenses, and potential disruption during the transition period. By accurately estimating both the benefits and costs, a realistic ROI can be calculated and used to justify the investment.
Impact on Efficiency, Accuracy, and Cost Savings
Measuring the impact of finance automation on these crucial areas is essential to demonstrate its value. This requires a comparative analysis of pre- and post-automation performance data.
- Efficiency: Assess the time taken to complete specific tasks before and after automation. A significant reduction in processing time indicates an improvement in efficiency. For example, comparing the time spent on month-end closing procedures before and after automation reveals the impact.
- Accuracy: Track the number of errors in financial data before and after the automation implementation. A decrease in error rates demonstrates increased accuracy. For example, a company might reduce data entry errors by 30% post-implementation.
- Cost Savings: Calculate the cost reductions realized by automating tasks. This includes savings in labor costs, material costs, and other operational expenses. For example, a company might see a reduction in staff required for data entry, thus saving on salaries and benefits.
Tracking and Reporting
Regular tracking and reporting are essential for monitoring the effectiveness of finance automation. Reports should be tailored to the specific needs and priorities of the organization.
- Establish a reporting schedule: Regular reports, such as weekly or monthly summaries, allow for ongoing monitoring of progress and identification of potential issues.
- Use dashboards and visualizations: Data visualization tools enable quick and easy understanding of key performance indicators. These tools can be particularly helpful for spotting trends and anomalies.
- Communicate findings: Share insights and data with relevant stakeholders. This ensures everyone understands the impact of the automation and can contribute to its ongoing improvement.
Ultimate Conclusion

In conclusion, a successful finance automation rollout requires a comprehensive approach that considers various factors, from defining automation types to continuous improvement and measuring success. By carefully planning, prioritizing, and managing the entire process, businesses can leverage automation to streamline financial operations, improve accuracy, and boost profitability. The key is to understand the importance of data management, security, and training throughout the process.
