China Accounting Evolving Trends A Deep Dive
China accounting evolving trends are rapidly reshaping the financial landscape. From the historical context of accounting practices in China to the influence of globalization and technological advancements, this exploration delves into the key developments. We’ll examine current standards, evolving financial reporting methods, and the impact of these changes on Chinese businesses. The journey includes case studies, highlighting the innovative approaches adopted by companies navigating this dynamic environment.
This in-depth analysis provides a comprehensive overview of China’s accounting evolution, touching upon key milestones, challenges, and opportunities. Understanding these trends is crucial for anyone looking to engage with the Chinese business world or international accounting practices.
Historical Context of Accounting in China: China Accounting Evolving Trends
China’s accounting practices have a rich history, evolving from traditional methods to sophisticated modern standards. This journey reflects not only China’s economic development but also its interaction with global accounting principles. Understanding this historical context is crucial for appreciating the current state of accounting in the country.Traditional Chinese accounting systems, rooted in Confucian values and a focus on ethical conduct, initially differed significantly from the more formalized approaches of the West.
The adoption of international accounting standards has brought about significant changes, but the historical underpinnings continue to influence present-day practices.
Early Accounting Practices
Early Chinese accounting practices were primarily focused on recording transactions for taxation and administrative purposes. These systems, often employing a dual-entry bookkeeping system, were quite sophisticated for their time. Records were kept using a variety of mediums, including bamboo slips, silk scrolls, and later, paper. These practices were crucial for managing the complex financial operations of the imperial court and large commercial enterprises.
Evolution of Accounting Standards and Regulations
The evolution of accounting standards in China has been a gradual process, marked by increasing influence from international best practices. Initially, accounting standards were primarily based on domestic regulations, reflecting the country’s unique economic and cultural context. However, as China integrated into the global economy, the need for convergence with international standards became increasingly apparent.
Significant Accounting Scandals and Controversies
While China has made significant strides in improving its accounting practices, past accounting scandals and controversies highlight the challenges of maintaining transparency and accountability. These instances, often involving fraudulent reporting or manipulation of financial data, have served as crucial learning experiences, prompting regulatory reforms and increased oversight. Examples include instances of inflated revenue or assets, and instances of improper accounting treatment for investments.
Comparison with International Standards
Chinese accounting practices, historically, have exhibited differences compared to international standards, particularly in areas like the recognition of assets and liabilities, and the treatment of specific transactions. These differences stem from a combination of cultural influences, historical context, and unique economic circumstances. The adoption of international financial reporting standards (IFRS) has been a key step toward aligning Chinese accounting practices with global standards.
Key Dates and Developments in Chinese Accounting History
| Date | Event | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Early Dynasties (e.g., Shang, Zhou) | Rudimentary accounting methods emerge | Foundation for future development, focused on administrative and tax purposes. |
| Song Dynasty (960-1279) | Increased commercial activity leads to more complex accounting | Emergence of specialized accounting practices within trade and commerce. |
| 1949 | Establishment of People’s Republic of China | Significant shifts in economic policy, affecting accounting regulations and practices. |
| 1980s | Economic reforms open China to international trade | Increased interaction with global accounting practices, prompting discussions about standardization. |
| 2000s | Adoption of International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) | A significant step towards international harmonization. |
Current Accounting Standards and Regulations

Navigating the complex world of accounting in China requires understanding the interplay of local and international standards. China’s unique regulatory framework, while increasingly aligning with global best practices, still presents some key distinctions from international standards. This section delves into the specifics of China’s current accounting standards, regulations, and key principles.China’s accounting landscape is governed by a combination of local Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) and, increasingly, International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS).
Understanding these standards and their application is crucial for businesses operating in or with Chinese entities.
Current Accounting Standards in China
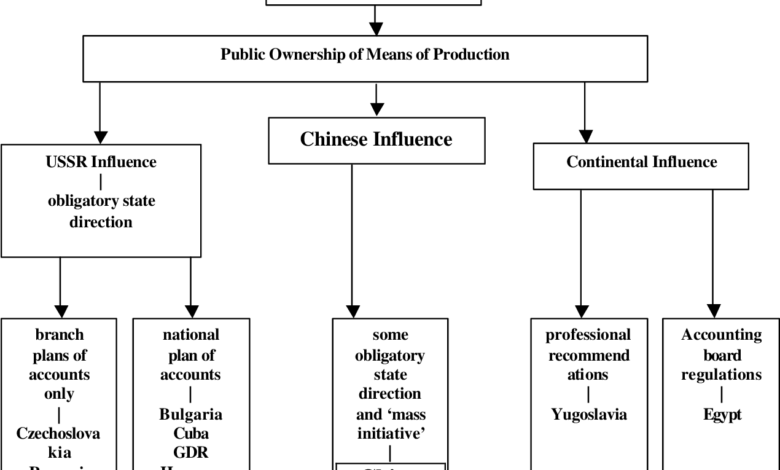
China’s accounting standards are primarily based on its own GAAP, known as Chinese Accounting Standards (CAS). These standards have been gradually converging with IFRS, although a complete adoption is not yet in place. This convergence reflects China’s growing integration into the global economy and its desire to enhance the transparency and comparability of financial reporting for international investors.
Key Differences Between Chinese and International Standards
Significant differences exist between Chinese Accounting Standards (CAS) and IFRS. One key distinction lies in the treatment of certain assets and liabilities. For example, the accounting for intangible assets or financial instruments might vary considerably. Another area of divergence is in the recognition and measurement of revenue. Chinese GAAP might have specific requirements for revenue recognition that differ from the more general IFRS framework.
These differences can impact the financial reporting of Chinese companies and necessitate careful consideration for investors and analysts.
Regulatory Bodies Governing Accounting Practices
The Ministry of Finance (MOF) and the China Securities Regulatory Commission (CSRC) play pivotal roles in regulating accounting practices in China. The MOF primarily oversees the development and implementation of accounting standards for all businesses. The CSRC, on the other hand, focuses on ensuring compliance with accounting standards for publicly listed companies. These two bodies, alongside other relevant authorities, maintain a framework that balances domestic needs with global trends.
Key Accounting Principles Used in China
Several key accounting principles underpin financial reporting in China. These principles include the accrual basis of accounting, the historical cost principle, and the prudence concept. The accrual basis ensures that revenues and expenses are recognized when they are earned or incurred, regardless of cash flow. The historical cost principle requires assets to be recorded at their original cost.
The prudence concept dictates that financial statements should be prepared conservatively, recognizing potential losses but not necessarily unrealized gains.
Major Accounting Standards and Their Relevant Regulations in China
| Accounting Standard | Relevant Regulation |
|---|---|
| Chinese Accounting Standards for Business Enterprises (CAS) | Ministry of Finance (MOF) |
| Chinese Accounting Standards for Financial Institutions | China Banking Regulatory Commission (CBRC) |
| IFRS Adoption Guidance (issued by the MOF) | Ministry of Finance (MOF) |
These standards and regulations ensure consistency and comparability in financial reporting, promoting transparency and efficiency within the Chinese market.
Discover how dennis johnson cfo qlik urgency for growth has transformed methods in this topic.
Evolving Trends in Financial Reporting
China’s financial reporting landscape is undergoing a dynamic transformation, driven by global pressures, technological advancements, and a growing emphasis on corporate social responsibility. This evolution reflects a move towards more transparent and sustainable practices, while also grappling with the challenges of maintaining competitiveness in a rapidly changing global market.
Sustainability Reporting
China is increasingly recognizing the importance of sustainability reporting, mirroring global trends. This shift is fueled by growing investor demand for information on environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors. Companies are recognizing that incorporating ESG considerations into their financial reporting can enhance their long-term value and attract responsible investors. The government is also encouraging this trend, issuing guidelines and regulations that compel companies to disclose more information about their environmental impact and social contributions.
This increased transparency is essential for stakeholders to assess a company’s overall performance and long-term viability.
Corporate Social Responsibility
Corporate social responsibility (CSR) is gaining significant traction as a key aspect of accounting practices in China. Companies are recognizing that their social and environmental impact is a crucial factor for investor confidence and public perception. This rising importance of CSR is evident in the growing number of companies that incorporate CSR reports alongside their financial statements, providing stakeholders with a comprehensive view of the company’s performance.
This holistic approach demonstrates a commitment to ethical business practices and long-term value creation, extending beyond the traditional focus on profit maximization.
Influence of Technological Advancements
Technological advancements are fundamentally reshaping accounting procedures in China. The adoption of cloud-based accounting software, big data analytics, and artificial intelligence (AI) is streamlining processes, improving data accuracy, and enabling more insightful financial analysis. Automation is reducing manual tasks, leading to increased efficiency and reduced operational costs. The implementation of these technologies is also enhancing the speed and accuracy of financial reporting, thereby allowing for faster decision-making and more responsive business strategies.
Innovative Financial Reporting Methods
Several Chinese companies are embracing innovative financial reporting methods to enhance transparency and stakeholder engagement. For example, some companies are integrating blockchain technology into their accounting processes, ensuring greater security and immutability of transactions. Others are using data visualization tools to present complex financial data in a user-friendly format, making it easier for stakeholders to understand the company’s performance.
These initiatives underscore the growing need for adapting accounting practices to the demands of a digital age.
Examples of Companies Implementing Innovative Methods
Numerous companies in China are pioneering new approaches to financial reporting. For example, Alibaba Group has integrated sustainability reporting into its annual financial statements, showcasing its commitment to environmental and social responsibility. Similarly, Tencent Holdings has utilized data visualization tools to present its financial performance in a clear and easily understandable manner. These examples demonstrate how Chinese companies are proactively adapting to the evolving financial reporting landscape.
Comparison of Financial Reporting Practices
| Characteristic | China | Other Countries (e.g., US, EU) |
|---|---|---|
| Sustainability Reporting | Increasingly important, driven by government guidelines and investor demand. | Well-established practice, with mandatory disclosures and standards. |
| Corporate Social Responsibility | Growing recognition, with increasing integration into financial reporting. | Common practice, often with separate CSR reports alongside financial statements. |
| Technological Advancements | Rapid adoption of cloud-based accounting, big data analytics, and AI. | Significant adoption of these technologies, but at varying levels of maturity. |
| Transparency | Continuously improving, though still evolving compared to advanced economies. | Generally high level of transparency, with established standards and regulations. |
Technological Advancements in Accounting
The accounting landscape in China is rapidly evolving, driven by technological advancements. These innovations are transforming traditional accounting practices, increasing efficiency, and enhancing the accuracy and transparency of financial reporting. The integration of technology is reshaping the role of accountants, requiring them to adapt and acquire new skills to effectively utilize these tools.Automation, big data analytics, cloud computing, and artificial intelligence (AI) are fundamentally changing how accounting tasks are performed in China.
This shift is not only streamlining processes but also opening up new avenues for analysis and insight, ultimately contributing to more informed business decisions.
Discover the crucial elements that make finance departments evolving while bracing for coronavirus second wave the top choice.
Impact of Automation on Accounting Tasks in China
Automation is significantly impacting accounting tasks in China. From basic data entry to complex calculations, automated systems are streamlining procedures and reducing human error. Software applications are automating routine tasks such as invoice processing, accounts payable and receivable management, and general ledger maintenance. This automation frees up accounting professionals to focus on more strategic and analytical work, such as financial forecasting and risk management.
Big Data Analytics in Chinese Accounting
Big data analytics is being increasingly used in Chinese accounting to gain deeper insights into financial data. Companies are leveraging vast amounts of data, including transaction records, market trends, and customer behavior, to identify patterns, predict future outcomes, and make more informed business decisions. For instance, big data analysis can help identify potential fraud or irregularities in financial transactions, enabling proactive risk management.
Role of Cloud Computing in Accounting Processes
Cloud computing is playing a pivotal role in transforming accounting processes in China. Cloud-based accounting software allows for real-time data access, collaboration among teams, and enhanced security. This accessibility facilitates remote work and improves communication and data sharing across different departments and locations. Furthermore, cloud solutions often offer scalability and cost-effectiveness, especially for smaller businesses.
Use of AI and Machine Learning in Accounting Audits
AI and machine learning are increasingly used in accounting audits in China. AI-powered systems can analyze large volumes of data to identify anomalies and potential risks more efficiently than traditional methods. Machine learning algorithms can also be trained to detect patterns indicative of fraud or financial irregularities, providing early warning signals to auditors. These tools are helping to automate parts of the audit process, potentially reducing costs and increasing audit efficiency.
Table: Transforming Accounting Procedures in China
| Technology | Transformation in Accounting Procedures |
|---|---|
| Automation | Streamlining routine tasks like invoice processing, accounts payable/receivable, and general ledger maintenance. Reduced human error, increased efficiency. |
| Big Data Analytics | Identifying patterns in financial data, predicting future outcomes, proactive risk management, improved business decisions. |
| Cloud Computing | Real-time data access, enhanced collaboration, improved security, remote work facilitation, scalability, cost-effectiveness. |
| AI/Machine Learning | Analyzing large volumes of data for anomalies and potential risks, detecting fraud/irregularities, automating parts of the audit process, increasing audit efficiency. |
Impact of Globalization on Accounting Practices
Globalization has profoundly reshaped accounting practices worldwide, and China is no exception. The increasing interconnectedness of economies, fueled by international trade and investment, necessitates a harmonization of accounting standards to facilitate cross-border transactions and ensure transparency. This has led to significant adaptations in Chinese accounting methods, reflecting the pressures and opportunities presented by a globalized marketplace.
Obtain direct knowledge about the efficiency of global cfo survey rebuild revenue streams through case studies.
Influence of International Trade and Investment
International trade and investment have driven a demand for consistent accounting practices across borders. Companies engaged in global trade need a common language to report their financial performance. This demand has directly impacted the evolution of accounting standards in China. The growing presence of multinational corporations within China and Chinese companies expanding globally has amplified the need for standardized accounting principles.
This pressure has spurred the adoption of international accounting standards, though the pace of adoption has been gradual.
Impact of Cross-Border Transactions on Accounting Standards
Cross-border transactions necessitate a shared understanding of financial reporting. Different countries often have distinct accounting standards, leading to potential discrepancies and complexities when companies report financial data from various locations. This has created a pressing need for harmonization. The challenge lies in balancing the unique economic and cultural contexts of different countries with the requirements for international comparability.
Adaptation of Chinese Accounting Practices to Global Standards
China has progressively adopted international accounting standards, particularly for publicly listed companies. This adoption reflects the growing need for transparency and comparability in financial reporting, as well as the increasing participation of Chinese companies in global markets. However, the transition has not been seamless, and Chinese accounting practices still exhibit some unique characteristics. The ongoing dialogue and alignment with international standards are essential to fostering trust and investment in the Chinese market.
Comparison of Globalization’s Impact on Accounting in China and Other Countries
| Characteristic | China | Other Countries (e.g., US, UK) |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Accounting Framework | Historically based on Chinese national standards, gradually transitioning towards international standards. | Often developed and maintained a longer history of specific standards. |
| Pace of Adoption | Relatively faster in recent years, driven by market pressures. | May vary across countries depending on their specific economic and political context. |
| Unique Cultural Factors | Traditional Chinese business practices and cultural values influence accounting standards. | Different national contexts affect how accounting standards are interpreted and applied. |
| Impact on International Trade | Enhances transparency and fosters trust in cross-border transactions. | Facilitates comparison of financial performance, driving investment and trade. |
| Governmental Role | Government regulations and policies significantly influence the direction of accounting standards. | Governmental influence may vary across countries. |
Challenges and Opportunities for Chinese Accounting
Navigating the dynamic landscape of global commerce presents unique challenges and opportunities for Chinese accounting practices. The interplay of evolving international standards, technological advancements, and the increasing interconnectedness of the global economy necessitates a careful examination of the strengths and weaknesses of the Chinese accounting system. This examination allows for proactive adaptation and strategic planning, ultimately bolstering the competitiveness of Chinese businesses in the global market.
Challenges Faced by Chinese Accountants
The adoption of new international accounting standards, such as IFRS, necessitates a significant shift in the existing Chinese accounting framework. Accountants face the challenge of acquiring new knowledge and skills to comply with these standards. This transition demands a commitment to ongoing professional development and a willingness to embrace new methodologies. Furthermore, the increasing complexity of financial transactions in a globalized market necessitates advanced analytical skills.
Accountants need to be equipped with sophisticated tools and techniques to manage and interpret the intricate financial data generated by these transactions. The growing use of technology in accounting also presents a challenge, requiring accountants to adapt to new software and systems. The ability to leverage technology effectively for enhanced efficiency and accuracy is paramount.
Opportunities Presented by Evolving Trends
The evolution of accounting practices presents significant opportunities for Chinese businesses. The adoption of international standards enhances the comparability of financial statements, fostering trust and attracting foreign investment. This increased transparency facilitates smoother international collaborations and partnerships. The embrace of technology, like cloud-based accounting software, enables greater efficiency and cost savings. This can translate into improved profitability and a competitive edge in the market.
Technological advancements also create opportunities for automation of routine tasks, freeing up accountants to focus on higher-value activities, such as strategic analysis and financial planning.
Need for Professional Development in Chinese Accounting
Continuous professional development is crucial for Chinese accountants to effectively navigate the challenges and capitalize on the opportunities presented by evolving trends. Training programs focusing on international accounting standards, technological advancements, and data analysis skills are essential. These programs should be tailored to meet the specific needs of different industries and roles within the accounting profession. Institutions offering these programs need to prioritize practical application and real-world scenarios to equip accountants with the skills necessary to tackle complex financial challenges.
Importance of Ethical Considerations in Accounting, China accounting evolving trends
Maintaining high ethical standards in accounting practices is paramount, regardless of the specific accounting standards or technologies used. Ethical considerations must be woven into the fabric of accounting education and professional development. Promoting a culture of integrity and accountability in the Chinese accounting profession is critical for building trust and maintaining the credibility of financial information. Accountants must be aware of and adhere to the relevant ethical codes and regulations to ensure the accuracy, objectivity, and reliability of financial reporting.
This commitment to ethical conduct ultimately strengthens the reputation of Chinese businesses and promotes responsible financial practices.
Challenges and Opportunities in Chinese Accounting
| Area | Challenges | Opportunities |
|---|---|---|
| Adoption of IFRS | Requires significant retraining for accountants and adapting existing systems. Difficulties in translating and interpreting complex standards. | Increased comparability of financial statements, attracting foreign investment and fostering international collaborations. Improved understanding of international financial markets. |
| Technological Advancements | Requires investment in new software and training for staff. Potential for job displacement due to automation. Cybersecurity concerns. | Enhanced efficiency and accuracy in data processing. Improved data analysis capabilities. Greater accessibility and cost savings for businesses of all sizes. |
| Globalization | Adapting to diverse international accounting standards and practices. Increased complexity of financial transactions. Navigating cross-border regulatory compliance. | Increased opportunities for international collaborations and partnerships. Enhanced competitiveness in global markets. Access to wider investment opportunities. |
| Ethical Considerations | Maintaining high ethical standards in a rapidly changing environment. Potential for fraud and misconduct. Pressure to compromise ethical principles for profit. | Building trust and credibility with investors and stakeholders. Promoting a positive reputation for Chinese businesses. Enhancing the overall stability and integrity of the financial system. |
Illustrative Case Studies of Evolving Accounting Practices
China’s accounting landscape is dynamic, constantly adapting to economic shifts and technological advancements. This evolution is exemplified by numerous companies embracing innovative accounting practices. These case studies highlight how companies are leveraging new methods to enhance financial transparency, improve efficiency, and ultimately, achieve greater success.The following case studies illustrate how companies in China are adapting their accounting practices to the evolving regulatory environment and technological landscape.
Each example showcases a unique approach, demonstrating the impact on financial performance and highlighting the differences in approach compared to competitors.
Evolving Practices in Online Retail
Chinese online retail giants are pioneering new methods of revenue recognition and inventory valuation, reflecting the unique characteristics of their business models.
- JD.com, a major online retailer, has implemented a sophisticated system for recognizing revenue based on the point of sale, rather than simply on the order date. This allows for more accurate reflection of sales performance and better forecasting. JD.com also utilizes advanced inventory management techniques, employing predictive analytics to minimize carrying costs and ensure optimal inventory levels.
This proactive approach has resulted in increased efficiency and reduced losses from obsolete inventory. They have also implemented more transparent reporting on fulfillment costs and logistics, offering a deeper understanding of their operational performance. This level of detail allows investors to better assess their overall business strategy.
- Alibaba, another dominant player in the e-commerce sector, has adopted sophisticated accounting methods for its diverse portfolio of businesses. This includes using complex models for recognizing revenue from its various platforms, including its payment systems and cloud computing services. Their accounting practices prioritize transparency in disclosing the performance of different divisions, which helps investors assess the contribution of each segment to the overall financial health of the company.
Their approach contrasts with competitors by emphasizing detailed segment reporting, allowing for a more nuanced understanding of performance across various business units. This allows for a more holistic evaluation of the company’s performance, as opposed to a simple top-down view.
Adapting to the Sharing Economy
The rise of the sharing economy has presented unique accounting challenges.
- Didi Chuxing, a prominent ride-hailing service, has implemented sophisticated accounting methods for driver payments and commission structures. They have developed complex algorithms for calculating driver payouts, ensuring accurate and timely financial settlements. Their accounting approach also encompasses transparent reporting on transaction volumes and usage patterns. This has facilitated more effective cost management and improved investor confidence in their ability to manage the complexities of a highly dynamic and growing market.
This contrasts with traditional taxi companies, which may have simpler accounting methods for driver compensation and revenue recognition. The complexity of Didi’s model necessitates a more intricate and adaptable approach.
Advancements in Technology
Chinese companies are increasingly adopting technology to improve their accounting processes.
- BYD, a leading manufacturer of electric vehicles and other technologies, uses advanced software and automation to streamline its accounting operations. Their systems automate many routine tasks, such as data entry and reconciliation. BYD’s approach has reduced operational costs and improved accuracy, allowing for faster financial reporting cycles. This level of automation is more common in companies operating in sectors where data volumes are high and efficiency is critical.
Summary Table
| Company | Key Accounting Practices | Impact on Financial Performance | Comparison with Competitors | Key Insights |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JD.com | Revenue recognition at point of sale, advanced inventory management | Improved forecasting accuracy, reduced inventory losses | More detailed reporting than some competitors, providing a clearer picture of sales performance. | Innovative approach to e-commerce accounting. |
| Alibaba | Complex revenue recognition models for diverse businesses | Enhanced transparency in segment performance, improved investor confidence | Emphasis on segment reporting differentiates it from competitors focusing on a top-down view. | Demonstrates adaptability to diverse business models. |
| Didi Chuxing | Sophisticated accounting for driver payments and commissions | Improved cost management, enhanced investor confidence | More intricate approach than traditional taxi companies, reflecting the complexities of the sharing economy. | Adaptability to a novel business model. |
| BYD | Automation of accounting processes | Reduced operational costs, improved accuracy, faster reporting | Automation is a common practice in sectors with high data volumes, but the specific implementation varies. | Technology integration for efficiency and accuracy. |
Closing Summary
In conclusion, China’s accounting landscape is undergoing a significant transformation. The convergence of traditional practices with international standards, coupled with technological advancements, presents both challenges and opportunities. As China continues its global integration, its evolving accounting practices will undoubtedly influence international financial reporting standards. This analysis underscores the importance of staying informed about these developments for businesses and professionals alike.