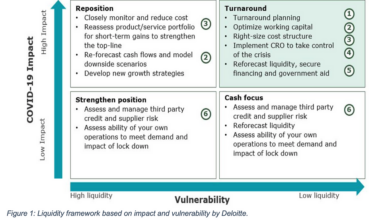
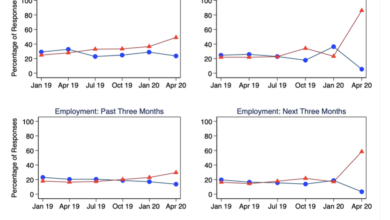
UK Regulators Respond to COVID-19 Policy Changes
UK regulators set policy changes amid coronavirus disruption, responding to the unprecedented challenges posed by the pandemic. This involved significant shifts across various sectors, impacting businesses and consumers in profound ways. The changes, driven by the need to adapt to the evolving crisis, are examined in detail, exploring their rationale, impact, and potential long-term effects. The analysis also looks at international comparisons and illustrative case studies, offering a comprehensive picture of the regulatory landscape during this period.
This article delves into the specifics of the policy changes, providing a clear overview of the adjustments made by UK regulators. It explores the rationale behind these modifications, considering the challenges faced by businesses and consumers alike. The aim is to offer a balanced perspective on the effectiveness of the regulatory responses, drawing comparisons with other countries’ approaches.
The discussion will also analyze the short and long-term impacts on the UK economy, potentially offering valuable insights into future policy directions.
Policy Changes Overview
The COVID-19 pandemic significantly disrupted various sectors, prompting UK regulators to implement policy changes to mitigate the crisis’s impact and ensure economic stability. These changes aimed to support businesses, protect consumers, and maintain essential services. Understanding the specific adjustments and their rationale is crucial for navigating the evolving regulatory landscape.
Summary of Policy Changes
The UK government and regulatory bodies, including the Financial Conduct Authority (FCA), the Competition and Markets Authority (CMA), and the Health and Safety Executive (HSE), introduced numerous policy changes to address the economic and social challenges presented by the pandemic. These adjustments covered areas such as financial markets, consumer protection, and business operations.
Key Sectors Affected
The policy changes had a significant impact on several sectors, including financial services, retail, healthcare, and energy. The adjustments varied in nature, encompassing temporary waivers, relaxed compliance standards, and targeted support measures.
Rationale Behind Regulatory Adjustments
The rationale behind these regulatory changes stemmed from the urgent need to address the unprecedented challenges posed by the pandemic. The aim was to provide temporary relief to businesses and consumers, maintain essential services, and facilitate a swift recovery. This involved assessing the risks and vulnerabilities of different sectors and implementing targeted interventions. Many changes were intended to support the economy during a period of high uncertainty.
Policy Changes Table
| Sector | Change Description | Rationale |
|---|---|---|
| Financial Services | Temporary reduction in capital requirements for banks, relaxed lending criteria for small businesses, and support for vulnerable consumers. | To mitigate the financial strain on businesses and individuals, ensuring access to credit remained available during the pandemic. |
| Retail | Relaxation of some trading regulations, allowing for more flexible operating hours and adaptation to changing consumer behaviour, including temporary measures for online safety. | To support businesses in adapting to the shift in consumer behaviour and maintain essential services, whilst also mitigating the risk to consumer safety. |
| Healthcare | Prioritisation of healthcare resources, relaxed regulations for the rapid production of essential medical supplies, and increased flexibility in staffing levels. | To ensure continued access to healthcare services and enable a rapid response to the pandemic’s demands. |
| Energy | Temporary waivers on energy efficiency standards for businesses, and support for vulnerable households with energy bills. | To support energy-intensive businesses during the economic downturn and mitigate the impact on vulnerable households, ensuring continued access to essential services. |
Impact on Businesses
The UK’s coronavirus-era policy changes significantly reshaped the business landscape. These alterations, while intended to mitigate the pandemic’s economic fallout, presented both opportunities and challenges for businesses across various sectors. Understanding these impacts is crucial for evaluating the long-term effects of the pandemic’s response.The policy changes, encompassing everything from financial aid packages to social distancing measures, affected businesses differently based on their size, industry, and adaptability.
While some companies flourished by pivoting to new models, others struggled to adjust to the rapidly evolving situation. The subsequent analysis examines the varied impacts on different businesses and the specific strategies used to navigate these changes.
Positive Impacts on Businesses
The pandemic-era policies, though initially disruptive, fostered innovative solutions and opportunities. Many businesses recognized the need for rapid adaptation and embraced digital transformation. This shift led to increased efficiency and new revenue streams for many organizations.
- E-commerce Boom: Retailers accelerated their online presence, capitalizing on the increased demand for online shopping. This resulted in the growth of online platforms and increased sales for numerous businesses. Companies that had already invested in e-commerce platforms experienced significant gains.
- Remote Work Adoption: Policies enabling remote work forced many companies to adopt new technologies and work processes. This led to increased flexibility and efficiency for many companies, particularly those in sectors like IT and consulting.
- Increased Government Support: Government initiatives, like grants and loans, provided critical support to struggling businesses, particularly small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). This assistance helped many companies maintain operations and navigate the economic downturn.
Negative Impacts on Businesses
Despite the positive impacts, the policy changes had considerable negative consequences for many businesses. Supply chain disruptions, reduced consumer spending, and lockdowns directly impacted many sectors.
- Supply Chain Disruptions: Global lockdowns and restrictions on movement severely disrupted supply chains, causing shortages and delays for businesses. This led to increased costs and production issues for companies across many sectors.
- Reduced Consumer Spending: Lockdowns and economic uncertainty reduced consumer spending, leading to decreased revenue for many businesses, especially those reliant on in-person interactions. Restaurants, entertainment venues, and tourism-related businesses were particularly affected.
- Increased Operational Costs: Implementing safety protocols, such as social distancing and enhanced hygiene measures, significantly increased operational costs for businesses. This burden was particularly heavy for small businesses with limited resources.
Industries Experiencing Significant Shifts
Certain industries experienced more significant shifts than others. The tourism, hospitality, and retail sectors faced particularly challenging conditions.
- Tourism and Hospitality: International travel restrictions and lockdowns severely impacted businesses in the tourism and hospitality sector. Hotels, restaurants, and airlines suffered substantial revenue losses. Examples include the closure of many hotels and restaurants for extended periods.
- Retail: The retail sector experienced a significant shift towards online sales. Brick-and-mortar stores faced challenges adapting to the new environment, leading to store closures and significant financial difficulties for some companies.
- Manufacturing: Manufacturing industries faced disruptions in their supply chains and reduced demand, causing challenges in production and distribution.
Business Strategies for Adaptation
Businesses employed various strategies to adapt to the new regulations.
- Digital Transformation: Many companies invested in digital tools and platforms to support remote work and online sales. This included the development of e-commerce platforms and online ordering systems.
- Cost Reduction Strategies: Businesses implemented cost-cutting measures to mitigate the impact of reduced revenue and increased operational costs. Examples include reducing staff, renegotiating contracts, and streamlining operations.
- Innovation and Diversification: Some businesses explored new markets and product lines to diversify their revenue streams. This included offering new services or products to cater to changing customer needs.
Impact on Small and Large Businesses
The impact of the policy changes varied significantly between small and large businesses.
- Small Businesses: Small businesses often lacked the resources to adapt quickly to the new regulations. They were frequently more vulnerable to disruptions in supply chains and reduced consumer spending. Government support programs were often crucial for their survival.
- Large Businesses: Large businesses, with greater financial resources and established networks, often had more flexibility to adapt to the new regulations. They could invest more heavily in digital transformation and diversification strategies.
Consumer Implications: Uk Regulators Set Policy Changes Amid Coronavirus Disruption
The UK’s regulatory response to the coronavirus pandemic significantly impacted consumers. Policy changes, while often aimed at mitigating economic hardship, created a complex web of benefits and drawbacks for various consumer groups. Understanding these implications is crucial for assessing the overall impact of the pandemic on the UK’s consumer landscape.Policy changes aimed at supporting businesses also inadvertently influenced consumer behavior and choices.
These changes, while well-intentioned, introduced new considerations for consumers, ranging from altered purchasing patterns to adjustments in service access. Understanding these shifts is key to comprehending the long-term effects of the crisis on the UK’s consumer market.
Consumer Protection Measures
Government interventions, such as temporary business support schemes, had knock-on effects for consumers. These included discounts, promotions, and access to financial relief measures, all designed to alleviate financial burdens during the pandemic. These policies often manifested in various forms, including grants, subsidies, and flexible repayment options for loans.
Specific Consumer Disadvantages
Despite the supportive measures, some consumers faced challenges. Reduced access to certain services, like in-person financial advice or specific healthcare provisions, limited options for consumers. Supply chain disruptions also resulted in product shortages and price hikes, impacting consumer affordability and choice.
Impact on Different Consumer Groups
The policy changes’ impact varied significantly across different consumer demographics and those deemed vulnerable. These variations are critical to understanding the broader implications of the crisis.
| Consumer Group | Potential Benefits | Potential Drawbacks |
|---|---|---|
| Vulnerable groups (e.g., low-income households) | Access to financial aid, reduced burdens on essential goods | Limited access to specific services, disproportionate impact from supply chain issues |
| Young adults | Job support programs, access to training schemes | Difficulties in accessing stable employment, high youth unemployment |
| Older adults | Simplified access to government support packages | Difficulties adapting to digital platforms, reduced access to in-person support services |
| Families with children | Increased support for childcare, flexibility in working arrangements | Strain on household finances, increased pressure on childcare arrangements |
| Small business owners | Access to grants and loans | Difficulty adapting to remote working or online sales, increased financial burdens |
Regulatory Responses and Coordination
Navigating the unprecedented disruption of the coronavirus pandemic required swift and adaptable regulatory responses. UK regulators, across diverse sectors, faced the challenge of balancing public health concerns with the need to maintain economic stability. This involved adapting existing frameworks, introducing temporary measures, and coordinating actions to mitigate the pandemic’s impact. This analysis explores the regulatory responses in different sectors, examining instances of coordination and highlighting the effectiveness of various approaches.Regulatory bodies had to swiftly adjust their approaches to address the immediate challenges posed by the pandemic.
This involved implementing new rules, adapting existing ones, and potentially altering enforcement strategies. The effectiveness of these changes is dependent on the sector and the specific challenges faced.
Regulatory Responses Across Sectors
Different sectors experienced varying degrees of disruption and required distinct regulatory responses. The financial sector, for example, saw a need for interventions to maintain market stability, while the healthcare sector was confronted with the urgent need to manage the surge in demand for essential goods and services. The hospitality sector faced a unique set of challenges as lockdowns and restrictions dramatically impacted business operations.
These differences in sector-specific challenges influenced the nature and scope of regulatory actions.
- Financial Sector: The Bank of England and the Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) implemented measures to support the financial system, including reducing capital requirements and providing liquidity support. This was crucial to prevent a systemic crisis and ensure market stability.
- Healthcare Sector: The Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency (MHRA) accelerated the approval processes for COVID-19 treatments and vaccines. This rapid response was critical to ensure timely access to effective therapies and prevent further spread of the virus.
- Hospitality Sector: The hospitality sector was significantly impacted by lockdowns and restrictions. The UK government and regulators focused on providing financial support, such as business grants and loans, to help businesses weather the crisis. The focus was on mitigating the impact of reduced consumer spending.
Coordination Between Regulators
The effectiveness of regulatory responses often hinged on the level of coordination between different UK regulators. A lack of clear communication channels or differing priorities could hinder the overall impact of the response. Ideally, coordinated action across multiple sectors would ensure consistency in policies and avoid conflicting directives.
- Coordination Challenges: Instances of conflicting directives or unclear communication between regulators were reported in some sectors. This highlighted the need for improved communication channels and a clearer framework for inter-agency collaboration. For example, inconsistencies in the interpretation of government guidelines among different regulatory bodies could have led to confusion among businesses trying to comply.
- Examples of Coordination: However, there were instances of effective collaboration. The FCA and the Bank of England, for example, worked closely to ensure financial stability during the pandemic. This demonstrated the potential for effective coordination when there is a shared understanding of the risks and the need for joint action.
Effectiveness of Regulatory Approaches
The effectiveness of regulatory responses varied depending on the sector and the specific approach adopted. Some measures were highly effective in mitigating the crisis’s impact, while others may have been less successful or even counterproductive in certain situations. A careful assessment of the various approaches can provide insights into the most effective strategies for future crises.
- Positive Outcomes: The swift action taken by the MHRA in accelerating vaccine approvals demonstrated a highly effective regulatory response to a critical public health need. This rapid action had a direct positive impact on the pandemic’s trajectory.
- Areas for Improvement: The hospitality sector’s experience highlighted the need for more targeted and timely financial support measures. The initial response to the pandemic, in this sector, revealed the need for a more comprehensive and nuanced approach to support businesses.
Regulatory Frameworks Before the Disruption
Understanding the regulatory frameworks in place before the pandemic provides context for assessing the effectiveness of responses. Existing regulations often had gaps or limitations, which became apparent during the crisis. This underscores the importance of ongoing review and adaptation of regulatory frameworks to anticipate and respond to future crises.
- Strengths and Weaknesses: The existing frameworks in place prior to the disruption were varied in their robustness and adaptability. Some sectors had well-established frameworks for dealing with specific risks, while others relied on more ad hoc or less adaptable approaches. These differences influenced the sector-specific responses during the crisis.
- Lessons Learned: The pandemic highlighted areas where existing regulatory frameworks could be strengthened, including improved communication protocols and a more proactive approach to adapting regulations to emerging challenges. Lessons learned are vital to improve future crisis responses.
Long-Term Effects

The UK’s regulatory landscape is undergoing a significant transformation in response to the coronavirus disruption. These changes are not merely temporary fixes but are likely to reshape the future regulatory environment, impacting businesses, consumers, and the economy as a whole. Understanding the potential long-term consequences is crucial for navigating this evolving regulatory landscape.
Potential Long-Term Consequences on the UK Economy
The coronavirus disruption has accelerated pre-existing trends and introduced new challenges for the UK economy. Policy changes in response to the crisis are likely to have long-lasting effects on various sectors. For example, increased government intervention in the economy, like support packages for businesses and job security measures, could lead to a more interventionist regulatory environment in the future.
This might include greater scrutiny of industries deemed essential or vulnerable, with potential long-term impacts on competitiveness.
Reshaping Future Regulatory Actions
The coronavirus crisis has highlighted vulnerabilities and exposed gaps in existing regulations. These experiences will undoubtedly shape future regulatory actions. For example, the speed and scale of regulatory responses to the pandemic demonstrate a potential shift towards more agile and adaptable regulatory frameworks. The increased use of digital tools and technologies in regulatory processes could lead to greater transparency and efficiency in the future.
Furthermore, the crisis has brought to light the interconnectedness of various sectors and the need for better coordination between regulators.
Examples of Potential Future Policy Directions, Uk regulators set policy changes amid coronavirus disruption
The disruption has underscored the need for resilience and adaptability in the regulatory system. Potential future policy directions include a focus on strengthening supply chains to reduce reliance on single points of failure, like what was seen during the initial pandemic lockdowns. Another direction might involve prioritizing digitalization in regulatory processes to enhance efficiency and transparency. For example, the use of data analytics in assessing risks and ensuring compliance could become more prominent.
Furthermore, there’s a potential shift toward more targeted regulations that address specific vulnerabilities rather than blanket regulations applicable to all sectors.
Comparison of Pre- and Post-Disruption Regulatory Landscapes
| Characteristic | Pre-Disruption | Post-Disruption |
|---|---|---|
| Regulatory Agility | Relatively slow and incremental | Potentially faster and more adaptable |
| Focus of Regulation | Sector-specific and often broad-based | More targeted and sector-specific, focusing on vulnerabilities |
| Regulatory Coordination | Potential for gaps and inconsistencies | Emphasis on better coordination between regulators |
| Technological Integration | Limited use of technology in regulatory processes | Increased use of digital tools and technologies in regulatory processes |
This table highlights the potential differences between the pre- and post-disruption regulatory landscapes. The post-disruption environment suggests a move towards greater agility, more targeted regulations, improved coordination, and a stronger emphasis on technological integration.
International Comparisons
Navigating the unprecedented challenges of the coronavirus pandemic required swift and adaptable regulatory responses worldwide. Comparing these responses offers valuable insights into effective strategies, potential pitfalls, and the long-term impacts on businesses and consumers. Examining international approaches provides a lens through which to assess the UK’s regulatory actions and identify potential areas for future improvement.Understanding how different countries approached the crisis reveals not only the similarities but also the unique adaptations driven by specific contexts and priorities.
This comparison reveals best practices, highlighting successful strategies employed by other nations and drawing parallels to the UK’s efforts. It also allows us to analyze the effectiveness of specific regulatory tools and policies, providing a broader perspective on the UK’s response.
Regulatory Approaches in Different Countries
Different countries adopted various strategies to manage the economic and social disruptions caused by the pandemic. Some nations prioritized public health measures, while others focused on mitigating the economic fallout. This diversity of approaches reflects differing cultural values, economic structures, and political priorities.
Similarities in Regulatory Responses
Several common themes emerged in the regulatory responses across various countries. A shared concern for the well-being of citizens and the stability of the economy led many nations to implement financial support programs for businesses and individuals. These programs often involved grants, loans, and tax relief measures. International collaborations and information sharing also became crucial, as countries learned from each other’s experiences.
Differences in Regulatory Responses
Despite the common ground, differences in regulatory approaches were significant. The speed and scope of government interventions varied considerably across nations. Some countries adopted a more cautious approach, focusing on targeted interventions, while others embraced a more expansive and comprehensive strategy. Cultural norms and economic structures also played a role in shaping regulatory responses, leading to varied levels of public trust and acceptance of the interventions.
Best Practices Observed in Other Countries
Some countries demonstrated commendable practices in managing the economic impact of the pandemic. The swift implementation of targeted financial assistance programs for small businesses, coupled with effective communication strategies, proved highly effective in some instances. These successful strategies demonstrated how clear communication and coordinated efforts can mitigate economic anxieties and bolster public trust. Examples include proactive measures taken in certain European countries to stabilize their financial markets.
International Regulatory Initiatives Inspired by the UK
While the UK’s regulatory response during the pandemic was noteworthy, it’s important to acknowledge that some countries have not publicly referenced the UK’s approach as a source of inspiration. However, the UK’s experience in areas like supporting specific sectors and managing the flow of vital resources could serve as a benchmark for future responses to similar crises. In the realm of financial regulation, the UK’s actions were closely watched by other countries, influencing their own approaches to preserving financial stability.
Illustrative Case Studies
Navigating the economic fallout of the pandemic required regulators to adapt quickly. Policy changes, often enacted with unprecedented speed, had profound effects on various sectors. These case studies illustrate how specific businesses and industries responded to these changes, highlighting the complex interplay between regulatory action and business resilience.
Retail Sector Adjustments
The retail sector experienced significant disruption as consumers shifted purchasing habits. Brick-and-mortar stores faced closures and adapted to online sales, while e-commerce companies experienced unprecedented growth. Regulatory responses, including those related to online marketplaces and consumer protection, played a crucial role in managing the transition.
- Example 1: A Large Department Store Chain: Faced declining foot traffic and store closures. Regulatory support for business continuity, including aid packages and temporary relief from certain regulations, allowed the company to maintain operations and adapt to the online market. The transition required significant investment in online infrastructure and a restructuring of their workforce.
- Example 2: A Smaller, Independent Bookstore: Depended heavily on in-person sales. The sudden shift to online sales was challenging, but the company leveraged social media and community engagement to create a loyal online following and explore local partnerships. Regulatory actions regarding digital commerce and small business support helped mitigate losses.
“Government support programs were crucial in helping retail businesses, both large and small, adapt to the changing landscape.”
Restaurant Industry’s Transformation
The restaurant industry faced challenges with dine-in restrictions, impacting revenue streams. Regulatory actions on food safety, delivery services, and outdoor dining spaces shaped the industry’s adaptation.
- Example 1: A High-End Restaurant: Experienced significant revenue losses due to dine-in restrictions. They successfully pivoted to offering high-quality meal kits and online ordering, leveraging their reputation for quality ingredients. Regulatory support in this case focused on facilitating the use of delivery services and compliance with food safety regulations.
- Example 2: A Casual Family Restaurant: Focused on takeout and delivery, creating partnerships with local delivery platforms and adjusting their menu to meet demand. Regulatory changes regarding food safety and hygiene standards were critical for maintaining customer trust.
“Regulatory support for food safety and hygiene standards was vital for maintaining consumer trust in the restaurant industry.”
Impact on the Tourism Sector
Travel restrictions and lockdowns severely impacted the tourism sector. Regulatory responses focused on supporting businesses and mitigating economic losses.
- Example 1: A Large Hotel Chain: Faced significant revenue losses due to travel restrictions. The company implemented cost-cutting measures, furloughed staff, and explored new revenue streams such as corporate bookings. Regulatory support programs for businesses, including loan guarantees and tax breaks, were instrumental in maintaining operations.
- Example 2: A Small Boutique Hotel: Successfully adapted by focusing on local and regional tourism. The hotel created unique packages and partnered with local businesses, capitalizing on the need for domestic travel. Regulatory actions aimed at supporting small businesses and local tourism were crucial to their survival.
“Regulatory support for tourism businesses was essential in mitigating the devastating effects of travel restrictions.”
Illustrative Visuals
Understanding the evolution of policy changes and the diverse regulatory responses during the coronavirus disruption requires visual aids. These visuals will help contextualize the data and highlight key trends, making the information more accessible and impactful.
Evolution of Policy Changes Over Time
This graph displays the timeline of key policy changes enacted in response to the pandemic. The x-axis represents time (e.g., months or quarters), and the y-axis plots the number or type of policies implemented. The graph shows a sharp increase in the number of policies in the initial months of the crisis, followed by a period of consolidation and adjustment.
 The graph illustrates a rapid escalation in policy interventions in the early months of the pandemic, highlighting the urgency and scale of the initial responses. The subsequent period shows a decrease in the rate of new policy announcements, suggesting a shift towards refining existing measures and evaluating their effectiveness. This visual representation aids in understanding the dynamic nature of policy responses during this period.
The graph illustrates a rapid escalation in policy interventions in the early months of the pandemic, highlighting the urgency and scale of the initial responses. The subsequent period shows a decrease in the rate of new policy announcements, suggesting a shift towards refining existing measures and evaluating their effectiveness. This visual representation aids in understanding the dynamic nature of policy responses during this period.
Comparison of Regulatory Approaches Across the UK
A crucial aspect of understanding the policy landscape is comparing different regulatory approaches across various sectors in the UK. The following chart provides a visual representation of different approaches used by government agencies, highlighting the nuances and variations in regulatory strategies.  The chart presents a comparison of regulatory approaches across various UK sectors. Different regulatory agencies may have adopted different approaches to similar problems. For instance, some sectors might have seen more stringent rules on business operations, while others focused on consumer protection measures. This variability in approaches is a key feature of the overall regulatory response, reflecting the diverse needs and complexities of different sectors. Each sector had specific characteristics and required unique regulatory interventions.
The chart presents a comparison of regulatory approaches across various UK sectors. Different regulatory agencies may have adopted different approaches to similar problems. For instance, some sectors might have seen more stringent rules on business operations, while others focused on consumer protection measures. This variability in approaches is a key feature of the overall regulatory response, reflecting the diverse needs and complexities of different sectors. Each sector had specific characteristics and required unique regulatory interventions.
Final Conclusion

In conclusion, the UK’s response to the coronavirus crisis through policy changes by regulators underscores the need for adaptability and swift action in times of unprecedented disruption. The analysis of these changes reveals both successes and areas for improvement in the regulatory framework. Looking forward, the lessons learned from this period will undoubtedly shape future regulatory approaches, ensuring a more resilient and responsive system for navigating future crises.
The comprehensive nature of this analysis, encompassing policy changes, business impacts, consumer implications, and international comparisons, provides a rich understanding of the challenges faced and the strategies employed.