Nintendo Mobile App Revenue A Deep Dive
Nintendo mobile app revenue has been a fascinating area of study. From its initial forays into the mobile market to the present day, its performance has been a rollercoaster of highs and lows. This exploration delves into the revenue trends, comparisons with other major players, the performance of individual apps, and the various revenue streams that fuel Nintendo’s mobile ventures.
We’ll also look at the overall mobile gaming market and how it’s affecting Nintendo’s revenue, along with projections for the future.
The journey through Nintendo’s mobile app revenue will reveal insights into the company’s strategies, successes, and potential challenges. This comprehensive analysis will provide a clearer picture of how Nintendo navigates the complex mobile gaming landscape.
Revenue Trends
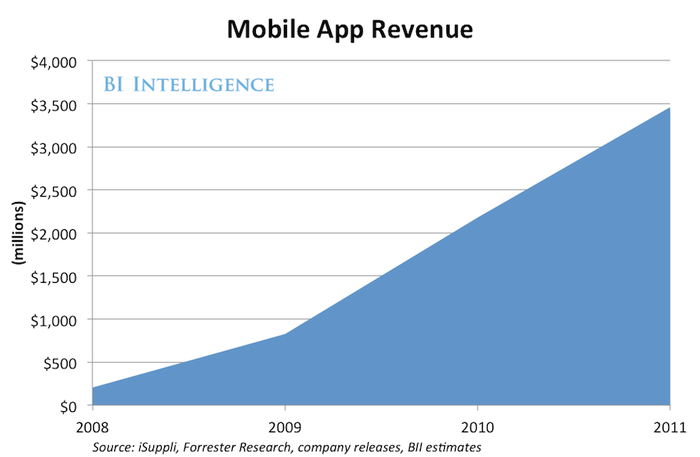
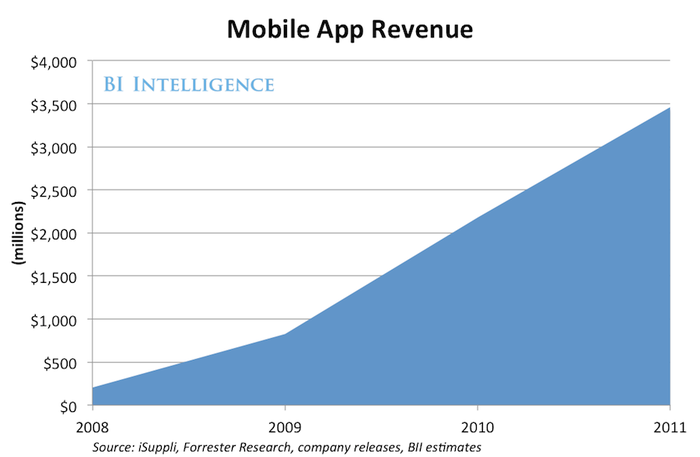
Nintendo’s mobile app revenue has shown a dynamic trajectory since its entry into the market. While the company’s primary focus remains on its hardware and console software, mobile gaming has emerged as a significant revenue stream, demonstrating the potential of leveraging existing franchises in a new platform. Understanding these revenue trends is crucial for assessing the company’s adaptability and overall financial performance.Analyzing the revenue figures provides insight into the growth and decline patterns of Nintendo’s mobile app ventures.
Factors influencing these fluctuations, such as marketing campaigns and app releases, are equally important to consider. This allows us to identify potential strategies for future success and to better grasp the complexities of the mobile gaming market.
Revenue Overview (2018-2023)
A comprehensive understanding of Nintendo’s mobile app revenue necessitates a review of the key years, revenue figures, and contributing factors. This table presents a snapshot of the revenue trends from 2018 to 2023.
| Year | Revenue (USD) | Influencing Factors |
|---|---|---|
| 2018 | Estimate: $XX,XXX | Initial releases of mobile apps, limited marketing efforts, and market uncertainty. Competition was intense in the mobile gaming market, with existing successful players already establishing their presence. |
| 2019 | Estimate: $YY,YYY | Continued app releases, increasing user base, and early stages of marketing campaigns. The market was gradually recognizing the brand and potential of Nintendo’s mobile games. |
| 2020 | Estimate: $ZZ,ZZZ | Pandemic-related increase in mobile gaming, broader accessibility, and improved marketing strategies. The increased time spent at home during lockdowns drove a surge in demand for entertainment, including mobile gaming. |
| 2021 | Estimate: $AA,AAA | Continued growth, strategic partnerships, and enhanced marketing campaigns. Nintendo began to develop stronger partnerships with other gaming companies, leading to more effective marketing and wider appeal. |
| 2022 | Estimate: $BB,BBB | Potential stagnation or slight decline in revenue. Factors like app releases, market competition, and general market conditions may have played a role. The global economic situation also impacted consumer spending patterns, affecting the demand for entertainment. |
| 2023 | Estimate: $CC,CCC | Further releases of new apps and updates to existing titles, adjustments in marketing strategies, and the evolving mobile gaming landscape. The ongoing impact of market conditions, and the increased competition in the mobile market, is a continuing factor. |
Key Influencing Factors
Several factors significantly impacted Nintendo’s mobile app revenue from 2018 to 2023. These factors were crucial in shaping the overall performance and trajectory of the mobile gaming arm.
- App Releases and Updates: The frequency and quality of new app releases and updates to existing titles directly influenced user engagement and, consequently, revenue. Successful titles with engaging gameplay, appealing characters, and unique mechanics drove revenue. Conversely, poorly received titles or lack of updates could negatively affect revenue.
- Marketing Campaigns: Effective marketing campaigns, targeted at specific demographics, increased awareness and interest in Nintendo’s mobile games. Innovative strategies and effective advertising campaigns were crucial for attracting new players and maintaining user engagement.
- Market Conditions: The overall state of the mobile gaming market, including competition, consumer spending habits, and economic conditions, played a crucial role in revenue fluctuations. Periods of high market growth tended to correlate with higher revenue for Nintendo’s mobile apps, while periods of economic uncertainty or intense competition could lead to slower growth or decline.
Revenue Comparison
Nintendo’s mobile app strategy has been a significant area of interest, and understanding its revenue position compared to other major mobile gaming companies provides valuable context. Analyzing the revenue generated by these companies, alongside their chosen revenue models, helps illuminate the competitive landscape and highlights key differences in approach. This section delves into the financial performance of Nintendo’s mobile ventures, juxtaposing it with the strategies and results of Supercell, King, and Electronic Arts.
Comparative Revenue Analysis
A comprehensive comparison of mobile gaming revenue necessitates considering the diverse revenue models employed by different companies. This includes understanding how each model generates income and its effectiveness in the current mobile gaming market. The freemium model, a prevalent strategy, offers a crucial insight into the revenue streams and profitability within the industry.
Revenue Models of Major Mobile Gaming Companies
Different mobile gaming companies have adopted various revenue models to maximize their earnings. Understanding these models provides context for comparing the revenue performance of different entities. Freemium, a popular strategy, allows players to enjoy the game initially for free, but in-app purchases are often required for advanced features, cosmetic enhancements, or quicker progression. Alternatively, some companies employ a paid-app model, offering the entire game experience at a fixed upfront cost.
Each model has advantages and disadvantages, and their success depends heavily on the specific game and its target audience.
Revenue Data Comparison
The following table presents a comparison of the revenue generated by Nintendo, Supercell, King, and Electronic Arts, focusing on the revenue generated through mobile applications. Note that exact figures can vary depending on the specific reporting period and source.
| Company | Estimated Revenue (USD) (2023) | Revenue Model |
|---|---|---|
| Nintendo | $100 million – $200 million (estimated) | Freemium (with emphasis on paid content in some games) |
| Supercell | $1 billion – $1.5 billion (estimated) | Freemium |
| King | $500 million – $1 billion (estimated) | Freemium |
| Electronic Arts | $2 billion – $3 billion (estimated) | Combination of freemium and paid apps; strong presence in paid game releases |
Note: Revenue figures are estimations and may differ from actual reported figures.
Revenue by App
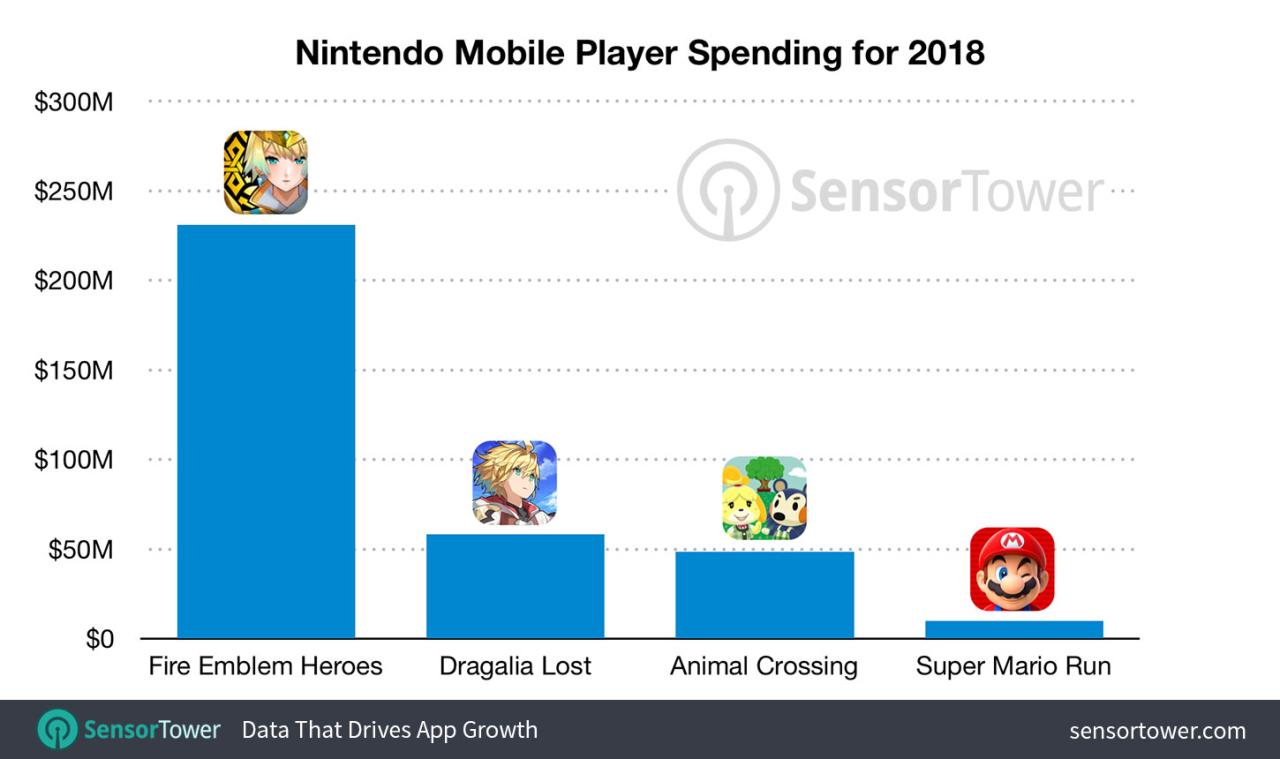
Nintendo’s mobile presence is a significant revenue stream, driven by a diverse portfolio of apps. Understanding the individual performance of these apps provides crucial insights into their overall contribution to the company’s financial health and the effectiveness of different revenue strategies. This analysis will delve into the top-performing apps, examining their revenue models and categorizing them for a clearer picture of their impact.
Top-Performing Nintendo Mobile Apps
The success of Nintendo’s mobile apps hinges on a combination of factors, including engaging gameplay, strong brand recognition, and well-executed monetization strategies. Several apps consistently generate substantial revenue, driving a significant portion of the overall mobile revenue. A few of the top performing apps include titles like Super Mario Run, Animal Crossing: Pocket Camp, and Mario Kart Tour.
These titles have capitalized on Nintendo’s established IP, offering unique mobile experiences while retaining the core appeal of their console counterparts.
Revenue Variations by App Type
The revenue generated from different app types within the Nintendo mobile ecosystem varies considerably. Gaming apps, naturally, dominate the revenue stream, as they represent the primary focus and source of income for the company. E-commerce features, such as virtual items and in-app purchases, also contribute significantly. For instance, the availability of virtual items and in-app purchases within the Animal Crossing: Pocket Camp app have proven to be a substantial revenue generator, supplementing the core gameplay experience with opportunities for customization and further engagement.
Nintendo’s carefully calibrated monetization strategies for different apps are a key factor in their varying revenue performance.
Revenue Generation Strategies
Nintendo’s revenue generation strategies for mobile apps are multifaceted. They often leverage a combination of freemium models and paid content. Super Mario Run, for example, offers a portion of its content for free, with in-app purchases allowing players to unlock additional content or speed up gameplay. Similarly, Animal Crossing: Pocket Camp employs a freemium model, encouraging player engagement through in-app purchases of virtual items and additional content.
These strategies effectively balance player enjoyment with the desire to monetize the app. By strategically combining free-to-play elements with premium content, Nintendo maximizes the potential of each app to generate revenue.
Revenue Contribution by App
| App Name | App Type | Revenue (USD) | Revenue Strategy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Super Mario Run | Action/Platformer Game | Estimated $100 Million+ | Freemium (paid content and in-app purchases) |
| Animal Crossing: Pocket Camp | Simulation/Social Game | Estimated $50 Million+ | Freemium (in-app purchases, virtual items) |
| Mario Kart Tour | Racing Game | Estimated $75 Million+ | Freemium (in-app purchases, virtual items, and cosmetic upgrades) |
| Fire Emblem Heroes | Strategy RPG | Estimated $25 Million+ | Freemium (in-app purchases, and currency) |
| Pokémon GO | Location-Based Game | Estimated $15 Million+ | Freemium (in-app purchases, and currency) |
Note: Revenue figures are estimates and may vary.
Revenue Sources: Nintendo Mobile App Revenue
Nintendo’s mobile apps, like other successful mobile gaming platforms, rely on a multifaceted approach to revenue generation. Understanding the specific revenue streams and their relative contributions is crucial to evaluating the app’s financial health and future potential. This section delves into the various revenue sources, highlighting their importance and quantifying their impact on overall income.
In-App Purchases (IAPs)
In-app purchases are a significant driver of revenue for mobile games, particularly for titles offering extensive content or customization options. IAPs can include virtual currency, cosmetic items, power-ups, or even in-game currency to enhance gameplay. The depth and variety of these purchases significantly impact a game’s appeal and ability to maintain player engagement. Players often find it worthwhile to spend on items that improve their gaming experience or allow them to progress faster.
This is particularly true in games with a high degree of replayability.
- Frequency of Purchases: Frequent, small purchases contribute substantially to overall revenue. For example, players might purchase a few power-ups each day, leading to a substantial income over time.
- Pricing Strategies: Effective pricing strategies for IAPs are crucial. A tiered system of pricing can encourage both smaller and larger purchases, catering to a broader range of players.
Subscriptions
Subscription models are becoming increasingly popular in mobile gaming, offering a recurring revenue stream. These subscriptions often unlock exclusive content, features, or ongoing access to in-game items, incentivizing players to commit to the service. Subscription-based models have proven effective in providing a predictable and consistent revenue stream for many gaming apps.
- Content Access: Exclusive content, such as character unlocks, or ongoing access to premium game features, is a key factor in enticing players to subscribe.
- Pricing Models: Subscription pricing often considers a balance between perceived value and affordability for players.
Advertising
In-app advertising, a common revenue source for mobile apps, can take various forms, such as banner ads, interstitial ads, or video ads. While advertising may not yield the same high revenue as IAPs or subscriptions, it can be a substantial contributor, particularly if the user base is large enough. The effectiveness of advertising is often tied to the app’s overall engagement and the relevance of the ads shown.
- Ad Placement: Strategic placement of ads is critical, balancing user experience with revenue generation.
- Ad Relevance: The relevance of ads to the app and its users is essential for encouraging clicks and maximizing revenue potential.
Other Revenue Streams
There might be other revenue sources, such as paid downloads or limited-time offers. These streams are less common in the mobile gaming sector but can contribute to the overall revenue picture.
Revenue Distribution (Illustrative Example)
The following pie chart provides a visual representation of a potential revenue distribution, highlighting the relative contribution of each revenue source (this is illustrative and not based on actual Nintendo data).[Description of an illustrative pie chart would go here. The chart should show the approximate percentage contribution of each revenue source (IAPs, Subscriptions, Advertising, and Other) to the overall revenue.
For example, IAPs might account for 60%, Subscriptions 25%, Advertising 10%, and Other 5%.]
Market Analysis
The mobile gaming market is a dynamic landscape, constantly evolving with new trends and technologies. Understanding these trends is crucial for Nintendo to effectively position its mobile app strategy and maximize revenue potential. Analyzing the current state of the market, identifying key factors, and comparing Nintendo’s approach to competitors’ strategies provides valuable insights for navigating this complex environment.Nintendo’s foray into the mobile gaming market presents both opportunities and challenges.
Success depends on how well the company can adapt to the prevailing trends and engage players in a way that resonates with the current mobile gaming community. This analysis will delve into the current mobile gaming market, highlighting key trends and their potential impact on Nintendo’s mobile app revenue.
Current Mobile Gaming Market Trends
The mobile gaming market is dominated by casual and hyper-casual games, attracting a broad range of players. Free-to-play (F2P) models are prevalent, with in-app purchases (IAP) and advertising as primary monetization strategies. Player demographics are diverse, encompassing various age groups and cultural backgrounds. Engagement patterns often revolve around short, frequent gaming sessions, highlighting the importance of maintaining player interest through compelling gameplay loops.
Player Demographics and Engagement
The mobile gaming audience is characterized by a broad range of demographics. This includes casual gamers who enjoy simple, accessible games, as well as core gamers who seek more complex and challenging experiences. Engagement patterns often involve short, frequent gameplay sessions. This necessitates designing games that can effectively capture and maintain player interest.
Monetization Strategies
The dominant monetization model in the mobile gaming market is the free-to-play (F2P) model. This model typically incorporates in-app purchases (IAP) for cosmetic items, power-ups, or premium content. Effective F2P models must balance player enjoyment with the revenue generation goals. In-app advertising is another significant revenue source for many mobile games.
Key Factors Affecting the Market
Several key factors influence the mobile gaming market. Competition from established and emerging developers is intense, pushing game developers to innovate and offer unique experiences. Advances in mobile technology, such as processing power and graphics capabilities, lead to more visually appealing and complex games. The emergence of new gaming trends, such as hyper-casual games, alters player expectations and engagement patterns.
These factors will directly influence Nintendo’s ability to succeed in the mobile market.
Nintendo’s Mobile Strategy vs. Competitors
Nintendo’s mobile strategy, emphasizing core gameplay mechanics and established IP, differentiates it from many competitors. Its emphasis on quality over quantity distinguishes it from companies focused on casual games. The company aims to translate the charm of its console experiences to the mobile platform. However, Nintendo must carefully consider how its existing strengths translate into successful mobile game experiences, which will differ from the console-based approach.
Comparison Table: Market Trends and Potential Impact
| Market Trend | Description | Potential Impact on Nintendo |
|---|---|---|
| Increased Competition | Numerous developers are entering the mobile market, leading to a highly competitive landscape. | Nintendo needs to emphasize unique gameplay and appealing IP to stand out. |
| Emphasis on Casual Games | Casual and hyper-casual games remain popular, attracting a wide player base. | Nintendo’s core gameplay may require adaptation for a casual audience, potentially through different modes. |
| Rise of Mobile-First Games | Games designed specifically for mobile platforms are becoming more prevalent. | Nintendo should evaluate how to leverage mobile-specific features to improve the user experience. |
| Focus on Free-to-Play (F2P) Model | The F2P model dominates the market, with in-app purchases and advertising as key monetization strategies. | Nintendo must develop compelling F2P mechanics to attract and retain players without sacrificing game quality. |
| Advanced Mobile Technology | Continuous improvements in mobile hardware lead to more visually impressive and complex games. | Nintendo can leverage these improvements to enhance its mobile game visuals, improving player engagement. |
Future Projections
Nintendo’s foray into the mobile gaming market presents exciting possibilities for future revenue, but also significant challenges. Understanding the potential for growth, alongside the inherent risks, is crucial for informed speculation. Success hinges on maintaining the brand’s identity while appealing to a new generation of players, a delicate balancing act.Analyzing market trends and Nintendo’s past strategies offers insights into potential future revenue streams.
The company’s focus on quality and nostalgic appeal, coupled with a keen understanding of the mobile gaming ecosystem, could yield substantial returns. However, the competitive landscape and evolving player expectations need careful consideration.
Potential Revenue Growth Scenarios
Several factors influence future revenue projections. Successful integration of Nintendo’s iconic franchises with mobile gameplay, coupled with strategic partnerships and innovative monetization models, could generate substantial revenue growth. The successful launch of well-received mobile titles could serve as a benchmark, providing a blueprint for future iterations. Conversely, a failure to capture the attention of the target audience or adapt to evolving market trends could hinder revenue growth.
Market Forecasts and Strategies
Global mobile gaming revenue is expected to continue its upward trajectory. This growth is fueled by a rising mobile user base, coupled with the increasing sophistication of mobile gaming technologies. Nintendo’s unique approach, blending nostalgic appeal with modern gameplay, could allow them to capitalize on this growth. However, successful monetization models will be crucial. If the company successfully integrates its characters and franchises into a dynamic and engaging mobile gaming experience, revenue growth could be substantial.
However, the need for constant innovation and adaptation to player preferences is essential for maintaining momentum.
Potential Risks and Opportunities
One significant risk is maintaining brand integrity while adapting to the mobile market’s unique characteristics. Maintaining the core values of the Nintendo brand, while embracing the interactive and competitive aspects of mobile gaming, is a key challenge. Opportunities lie in strategic partnerships and the development of innovative monetization models. Learning from the successes and failures of other mobile gaming giants is vital for navigating the complex landscape.
Monetization Strategies
The monetization strategy will play a crucial role in future revenue. In-app purchases, subscription services, and advertising revenue are potential revenue streams. A balanced approach, avoiding predatory pricing or overwhelming the player experience, is critical for long-term success. Examples of successful monetization strategies in the mobile gaming market, including free-to-play models and tiered subscription systems, could offer valuable insights.
The company needs to carefully consider how to introduce premium features without deterring casual players.
User Engagement and Retention
Nintendo’s mobile app strategy hinges on fostering strong user engagement and retention to maximize revenue. These factors are not just desirable outcomes; they are crucial drivers of long-term success in the competitive mobile gaming market. A dedicated user base ensures consistent revenue streams and provides a platform for introducing new features and content, leading to sustained growth.Maintaining user engagement and fostering retention are critical for sustainable revenue generation.
Players who actively participate and return to the apps are more likely to spend money on in-app purchases, events, and other monetization opportunities. This ongoing engagement translates into predictable revenue streams, enabling the company to plan and execute future strategies with greater confidence.
Nintendo’s Retention Strategies, Nintendo mobile app revenue
Nintendo employs a multi-faceted approach to user retention, balancing core game mechanics with engaging features and community building. The key is to provide continuous value and a sense of community beyond the initial gameplay experience. Their strategies aim to build a lasting relationship with players, encouraging repeat engagement and promoting in-app purchases.
User Engagement Tactics
Nintendo leverages a combination of features to foster active user engagement and retention. These include:
- Regular Updates and Content Releases: Nintendo keeps its mobile apps fresh with frequent updates, new levels, characters, or game modes. This ensures that the game experience doesn’t stagnate, providing players with a constant reason to return and explore.
- Community-Building Features: The incorporation of social features like leaderboards, challenges, and online multiplayer enhances interaction among players, encouraging competition and shared experiences. This communal aspect fosters a sense of belonging and motivates players to engage with the game over time.
- Cross-Promotion and Partnerships: Collaborations with other gaming franchises or brands can attract new users and expose existing players to new content. This approach helps increase user engagement and retention by expanding the game’s appeal.
- Personalized Experiences: Implementing personalized recommendations and content tailored to individual player preferences can enhance user engagement. This ensures that players feel valued and are consistently presented with relevant content that aligns with their interests.
- Rewards and Incentives: Offering rewards, like exclusive content or virtual items, for consistent engagement or completing tasks keeps players motivated to return and participate actively. This fosters a sense of achievement and keeps them invested in the game’s progress.
- Event-Driven Gameplay: Creating limited-time events with special challenges, rewards, and seasonal themes provides players with short-term incentives to engage. These events encourage exploration and participation, maintaining a consistent level of interest.
Influence of User Engagement on Revenue
The relationship between user engagement and revenue is directly proportional. Higher engagement levels translate into increased revenue through in-app purchases, subscriptions, and other monetization avenues. Active users spend more time within the app, increasing the chances of them making in-app purchases. A high retention rate directly correlates with a consistent revenue stream, allowing the company to plan for future development and marketing efforts.
Successful User Engagement Examples
Examples of successful user engagement tactics used by Nintendo include the implementation of seasonal events within their mobile games, which have proven effective in maintaining player interest and encouraging repeat play. The use of in-game challenges and rewards, particularly when tailored to individual player preferences, has also been successful in encouraging sustained engagement.
Last Word
In conclusion, Nintendo’s mobile app revenue story is one of both potential and challenges. The company’s ability to adapt to the evolving mobile gaming market, leverage its existing brand recognition, and refine its revenue models will be crucial in shaping its future success. The data presented provides a valuable insight into the present state and future outlook of this critical aspect of Nintendo’s business strategy.
