
Boosting Workplace Learning
Increase learning in the workplace is crucial for a thriving organization. This exploration delves into various methods, from hands-on training to innovative approaches like gamification, to create a culture of continuous improvement. We’ll examine the different types of learning, the factors that impact it, and the metrics for assessing success. It’s all about making learning an integral part of the work experience.
Understanding different learning styles and creating a supportive environment are key components of a successful workplace learning strategy. We’ll discuss how leadership can foster a culture of continuous learning and how to address diverse needs and styles within a company. We’ll also examine the critical role of technology in modern learning and the importance of employee feedback in program optimization.
Defining Learning in the Workplace
Learning in the workplace is a multifaceted process crucial for individual and organizational growth. It transcends simple knowledge acquisition; it encompasses a wide range of activities and methods that equip employees with the skills and expertise needed to excel in their roles and contribute to the overall success of the company. Understanding these various forms of learning, from formal training to informal mentorship, is vital for fostering a culture of continuous improvement.Effective learning in the workplace is not just about accumulating facts but also about applying them, adapting to new challenges, and contributing to a positive work environment.
A company that prioritizes employee learning fosters innovation, improves productivity, and strengthens its competitive advantage in the long run.
Different Forms of Workplace Learning
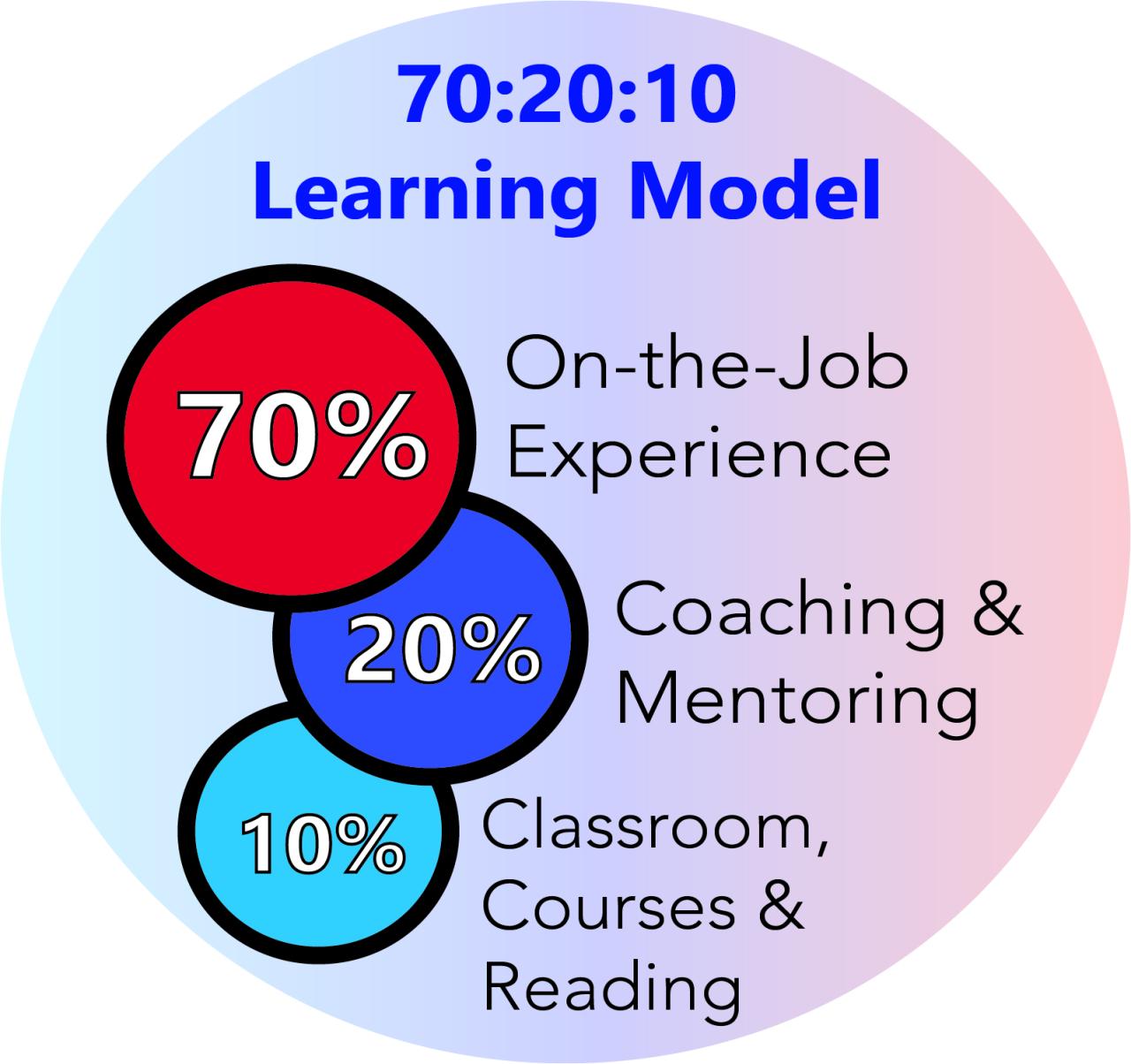
Various methods contribute to employee development in a professional setting. On-the-job training, mentorship, and formal courses are key components of a comprehensive learning strategy. Each approach offers unique benefits and caters to different learning styles and needs.
- On-the-Job Training (OJT): OJT is a practical, hands-on approach where employees learn by doing. It involves observing experienced colleagues, performing tasks under supervision, and receiving feedback. This method is particularly effective for developing practical skills and fostering a strong understanding of company procedures and processes. For example, a junior accountant learning bookkeeping procedures by assisting a senior accountant is a clear instance of OJT.
- Mentorship: Mentorship involves pairing experienced employees (mentors) with less experienced ones (mentees). Mentors guide mentees through challenges, share their expertise, and provide valuable insights into industry trends and professional development. This approach fosters a supportive learning environment and promotes knowledge transfer across generations of employees. A seasoned marketing executive mentoring a junior marketing associate on social media campaigns is an example of mentorship.
- Formal Courses: Formal courses, workshops, and training programs provide structured learning opportunities. These programs often cover specific skills, knowledge, or industry best practices. They are beneficial for imparting specialized knowledge and ensuring a consistent level of competency across teams. A company offering a series of workshops on project management methodologies to all project managers is an example of utilizing formal courses.
Implicit vs. Explicit Learning
Learning in the workplace can be categorized into implicit and explicit forms. Implicit learning is often subconscious, occurring naturally through experience and observation. Explicit learning, on the other hand, is deliberate and intentional, often involving structured programs and formal instruction.
- Implicit Learning: Implicit learning happens organically, often without conscious effort. It’s the accumulation of knowledge and skills through everyday work experiences, interactions with colleagues, and exposure to company culture. This type of learning can be invaluable in developing a deep understanding of organizational procedures and unspoken rules.
- Explicit Learning: Explicit learning is a conscious, deliberate process. It typically involves formal training programs, structured courses, or mentorship programs designed to impart specific skills or knowledge. This approach provides a structured framework for acquiring new skills and knowledge.
Successful Learning Initiatives
Examples of successful learning initiatives across various industries demonstrate the positive impact of focused learning programs.
- Technology Sector: Companies like Google and Amazon invest heavily in internal training programs to keep their employees updated with the latest technological advancements. These initiatives equip employees with the skills needed to adapt to the rapid pace of innovation in the industry.
- Healthcare Sector: Hospitals and clinics often implement comprehensive training programs to ensure that healthcare professionals have the most up-to-date knowledge and skills. This is crucial to patient safety and quality care. Examples of this can be seen in continuous medical education programs.
- Financial Sector: Banks and financial institutions regularly update their employees on compliance and regulatory changes. This is vital for maintaining ethical standards and avoiding potential legal issues. Ongoing compliance training for financial advisors is an example.
Framework for Classifying Learning Activities
A structured framework for classifying learning activities can help organizations track and evaluate their effectiveness. A classification system can ensure consistency in learning methodologies and allow for better monitoring of progress.
| Category | Description | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Skill-Based Learning | Focuses on developing practical skills and competencies. | Project management, communication, problem-solving |
| Knowledge-Based Learning | Aims to increase understanding of specific topics and concepts. | Industry regulations, company policies, technical procedures |
| Behavioral Learning | Focuses on improving attitudes, behaviors, and work ethics. | Conflict resolution, teamwork, customer service |
Factors Affecting Learning
Learning in the workplace is a complex process influenced by a multitude of factors. Understanding these factors is crucial for creating effective learning programs that foster employee growth and organizational success. From the leadership style employed to the prevailing company culture and the individual motivations of employees, each aspect plays a role in shaping the learning experience.A well-designed learning environment recognizes and addresses these factors to maximize the potential for knowledge acquisition and skill development.
This approach leads to more engaged employees, higher productivity, and a more adaptable workforce capable of navigating the evolving demands of the modern workplace.
Leadership Styles and Learning
Effective leadership is essential for creating a positive learning environment. Transformational leadership, characterized by inspiring vision, intellectual stimulation, and individualized consideration, fosters a culture of continuous learning and development. In contrast, a laissez-faire approach, while appearing permissive, can hinder learning by failing to provide adequate guidance and support. Autocratic leadership styles, although potentially efficient in the short term, often stifle creativity and limit employee participation in the learning process.
Company Culture and Learning
Company culture significantly impacts employee learning. A supportive and collaborative culture encourages knowledge sharing, peer-to-peer learning, and the willingness to experiment and take risks. Conversely, a rigid or competitive culture may discourage employees from seeking out new knowledge or participating in training initiatives. A culture that values learning and growth creates an atmosphere where employees feel empowered to learn and contribute to the organization.
Employee Motivation and Learning
Employee motivation is intrinsically linked to learning. Employees who are motivated to learn are more likely to engage actively in training programs and apply new knowledge to their work. Factors like compensation, recognition, and career development opportunities influence motivation and, consequently, learning outcomes. A clear understanding of individual employee needs and motivations is crucial for tailoring learning experiences to enhance engagement and maximize impact.
Technology in Workplace Learning
Technology plays a crucial role in enhancing workplace learning. Online learning platforms, virtual reality simulations, and collaborative tools offer flexible and engaging learning experiences. These tools can be adapted to accommodate diverse learning styles and deliver content in accessible formats. Effective use of technology leverages digital resources to support a dynamic and adaptable learning environment. For instance, online courses allow employees to learn at their own pace, while virtual reality training can simulate complex scenarios, offering practical experience without physical risks.
Learning Styles in the Workforce
Different learning styles exist among employees, with each style best suited to certain learning environments and materials. Visual learners thrive on diagrams, presentations, and images, while auditory learners benefit from lectures and discussions. Kinesthetic learners, on the other hand, prefer hands-on activities and practical exercises. Recognizing these diverse learning styles is crucial for creating learning programs that cater to a broad spectrum of preferences.
This ensures the effectiveness and accessibility of training initiatives, thereby maximizing employee engagement and skill development. For example, a training program might incorporate visual aids for visual learners, group discussions for auditory learners, and hands-on workshops for kinesthetic learners.
Employee Feedback and Learning Optimization
Collecting and analyzing employee feedback is critical for optimizing workplace learning programs. Regular surveys, focus groups, and one-on-one discussions provide valuable insights into the effectiveness of training initiatives. Feedback allows for adjustments to content, delivery methods, and program design to better meet the needs and preferences of the workforce. By actively seeking and incorporating employee feedback, organizations can continuously improve the quality and impact of their learning programs.
This feedback-driven approach ensures that learning initiatives are tailored to the specific needs and expectations of employees.
Methods for Increasing Workplace Learning
Boosting employee knowledge and skills is crucial for organizational success in today’s dynamic environment. Effective learning strategies empower employees, enhance productivity, and foster a culture of continuous improvement. A well-structured learning program translates into a more engaged and adaptable workforce.Investing in employee learning isn’t just about acquiring new skills; it’s about creating a culture of continuous development. This translates into a more agile and adaptable organization capable of responding to evolving market demands.
This approach not only benefits individual employees but also strengthens the overall performance and resilience of the company.
Effective Learning Methods
A diverse range of methods can be employed to facilitate learning in the workplace. From traditional workshops to cutting-edge online resources, organizations can tailor their approaches to meet specific needs and maximize impact. These methods must be carefully selected and implemented to optimize their effectiveness.
- Workshops: Structured workshops, delivered by experienced professionals, offer focused training in specific areas. These sessions can cover a variety of topics, from technical skills to soft skills like communication and leadership. Workshops provide an opportunity for active learning through interactive exercises and group discussions. Examples include workshops on project management methodologies, data analysis techniques, or conflict resolution strategies.
- Online Courses: Online learning platforms provide flexible and accessible training opportunities. Employees can access courses at their own pace and convenience, making it easier to integrate learning into existing schedules. They can also access a vast library of content, covering a wide range of subjects. This flexibility is crucial in today’s work environment where employees often have multiple responsibilities.
For example, a company might offer online courses on industry-specific software or compliance regulations.
- Simulations: Simulations provide realistic scenarios for employees to practice new skills without the risk of real-world consequences. This hands-on experience can build confidence and refine abilities in a safe environment. This is particularly valuable for roles requiring complex decision-making or technical expertise. Examples include financial modeling simulations for investment professionals or emergency response simulations for first responders.
Creating a Learning Culture
Cultivating a learning culture within a company goes beyond simply offering training programs. It requires a fundamental shift in mindset, fostering a climate where learning is valued and encouraged.
- Leadership Commitment: Leaders must champion the importance of learning and development. This includes actively supporting training initiatives and demonstrating a commitment to continuous improvement themselves. If leaders don’t value learning, it’s unlikely to become a company priority.
- Open Communication: Open communication channels allow employees to share their learning needs and experiences. This helps identify areas where training is needed and allows for a more personalized learning approach. This fosters a sense of shared responsibility for professional growth.
- Recognition and Rewards: Recognizing and rewarding employees for their efforts in learning and development demonstrates their value to the organization. This could include bonuses, promotions, or public acknowledgments. This positive reinforcement strengthens the learning culture.
Innovative Approaches to Boost Employee Learning
Several innovative approaches can further enhance employee learning and development.
- Gamification: Incorporating game mechanics into learning activities can make training more engaging and motivating. Points, badges, leaderboards, and challenges can increase employee participation and knowledge retention. This approach is particularly effective for younger generations.
- Peer-to-Peer Learning: Creating opportunities for employees to learn from each other can foster collaboration and knowledge sharing. Mentorship programs, peer coaching, and group projects can encourage informal learning and support. This builds a sense of community and support within the organization.
Implementing a New Learning Initiative
A well-defined process is essential for successfully launching a new learning initiative.
Browse the multiple elements of global cfo survey rebuild revenue streams to gain a more broad understanding.
- Needs Assessment: Identify specific training needs based on organizational goals and employee roles. Analyze existing skill gaps and identify areas for improvement.
- Program Design: Develop a detailed learning program that aligns with identified needs. Consider various learning methods and resources. Ensure the program is accessible and engaging.
- Implementation and Support: Execute the program, providing adequate support and resources to employees. This includes clear communication, access to materials, and ongoing guidance.
- Evaluation and Feedback: Monitor the program’s effectiveness and gather feedback from participants. Adjust the program based on evaluation results.
Measuring the Impact of Learning Initiatives
Knowing whether your workplace learning programs are effective is crucial for continuous improvement. Measuring their impact goes beyond simply tracking participation; it involves understanding how these programs translate into tangible results for the organization. A robust evaluation process helps identify what’s working, what needs adjustments, and how to maximize the return on investment in employee development.Effective measurement of learning initiatives involves a multi-faceted approach, moving beyond simple satisfaction surveys to examine the actual impact on performance and business outcomes.
This requires careful planning and execution to collect meaningful data and derive actionable insights.
Methods for Evaluating Learning Program Effectiveness
Various methods can be employed to gauge the effectiveness of workplace learning programs. These methods should be tailored to the specific goals of the program and the nature of the learning outcomes. A combination of methods often provides the most comprehensive picture.
- Surveys: Employee feedback is invaluable. Surveys can assess learner satisfaction, understanding of the material, and perceived usefulness of the training. Well-designed surveys, with clear and concise questions, can uncover areas where the program excels and where improvements are needed. Quantitative data collected through surveys allows for statistically significant comparisons and trends over time. For instance, a survey might ask employees to rate their confidence in using a new software tool before and after a training program.
This comparison allows for a clear assessment of learning outcomes.
- Performance Assessments: A critical aspect of evaluating learning is examining its impact on job performance. Performance assessments, such as performance reviews, 360-degree feedback, and project evaluations, can reveal how effectively employees apply the skills and knowledge gained through the learning program. For instance, if the learning program aimed to improve customer service skills, observing customer interactions or evaluating sales figures post-training can offer insights into the program’s effectiveness.
- Learning Progress Tracking: Monitoring learner progress during and after the training is vital. This can involve tracking completion rates, participation in online discussions, and scores on quizzes and assessments. Tools such as learning management systems (LMS) can facilitate this process, providing real-time data on learner engagement and progress. For example, tracking the completion rate of online modules and the scores on quizzes can provide valuable insights into the effectiveness of the learning material and the learners’ understanding.
Measuring Impact on Business Outcomes
Evaluating the impact of learning initiatives on business outcomes is crucial for demonstrating the program’s value. Connecting learning activities to quantifiable business results provides concrete evidence of their impact.
- Metrics for Different Sectors: Metrics for assessing learning effectiveness vary depending on the industry and the nature of the learning program. For instance, in a customer service sector, improvements in customer satisfaction scores, reduced customer complaints, and increased sales conversions could indicate a positive impact. In a technical sector, metrics might include fewer errors in production, higher productivity rates, and a decrease in product defects.
- Examples of Metrics: Examples of specific metrics used in various sectors include:
- Customer satisfaction scores (CSAT)
- Employee retention rates
- Productivity gains
- Reduced errors and defects
- Increased sales conversions
- Improved product quality
Identifying Areas for Improvement
Identifying areas for improvement in workplace learning programs is essential for continuous improvement. Feedback from various sources, including learners, managers, and stakeholders, is crucial for identifying potential weaknesses.
- Analysis of Data: A systematic analysis of data collected from various sources, including surveys, performance assessments, and learning progress tracking, can reveal patterns and trends that point towards areas requiring attention. This data analysis should focus on identifying any gaps between learning objectives and actual outcomes.
- Seeking Feedback: Collecting feedback from employees who have participated in the learning program is vital. This feedback can help identify areas where the program could be more engaging, relevant, or effective. Managers’ observations on how employees are applying the learned skills are also essential.
Learning Resources and Tools
Unlocking the potential of your workforce hinges on providing effective learning resources. Beyond structured training programs, a rich ecosystem of tools and platforms empowers employees to continuously develop their skills and knowledge. This empowers employees to stay ahead of industry trends, fostering a culture of growth and innovation within the organization.
Online Learning Platforms
A plethora of online platforms cater to various learning needs, from simple e-learning modules to comprehensive courses. These platforms offer flexibility and accessibility, allowing employees to learn at their own pace and convenience. They are particularly beneficial for remote or hybrid work environments. Examples include Coursera, Udemy, LinkedIn Learning, and company-specific learning management systems.
Libraries and Industry Publications
Access to relevant libraries and industry publications is crucial for keeping abreast of the latest advancements and best practices. Companies can partner with local libraries or subscribe to industry-specific journals, magazines, and online resources. This access fosters a culture of continuous learning, enabling employees to expand their knowledge base and stay updated on the evolving landscape of their field.
This can be facilitated through designated intranet pages or dedicated reading lists.
Mentorship and Coaching Programs
Mentorship and coaching programs play a vital role in fostering knowledge transfer and skill development. Experienced employees act as mentors, guiding junior colleagues through challenges and sharing their expertise. Coaches, on the other hand, provide focused support and guidance, helping individuals identify learning gaps and develop strategies for skill improvement. These programs are invaluable for cultivating leadership potential and building a supportive learning environment.
A mentor’s role is to provide guidance, support, and experience-based insights, while a coach helps identify learning goals and create action plans.
Learning Management Systems (LMS)
Learning Management Systems (LMS) are centralized platforms for managing and delivering training materials. Choosing the right LMS depends heavily on the size and structure of the company. Smaller companies might benefit from user-friendly, affordable options like Moodle or Google Classroom. Larger corporations with extensive training needs may require more robust platforms like Cornerstone OnDemand or Saba. The LMS should be scalable to accommodate future growth and adapt to the evolving needs of the organization.
| Company Size | Suitable LMS | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| Small | Moodle, Google Classroom | Ease of use, affordability, basic features |
| Medium | TalentLMS, Absorb | Scalability, customization, reporting features |
| Large | Cornerstone OnDemand, Saba | Advanced features, comprehensive reporting, integration with HR systems |
Comparing Learning Platforms
Different learning platforms offer distinct features and capabilities. Platforms like Coursera and edX provide access to a vast library of courses from top universities and institutions, fostering specialized skill development. Meanwhile, LinkedIn Learning emphasizes industry-specific skills and professional development, focusing on practical application. A company needs to carefully assess its learning objectives to determine the most suitable platform.
For example, a company focusing on technical skills might choose a platform specializing in coding bootcamps, whereas a company focused on soft skills might select a platform offering leadership and communication training.
Designing a Learning Strategy
Crafting a robust learning strategy is crucial for any organization aiming to cultivate a skilled and adaptable workforce. A well-defined strategy provides a roadmap for employee development, ensuring that learning initiatives align with the company’s overall goals and contribute to its success. This strategy will Artikel how employees acquire new knowledge and skills, ultimately boosting productivity and performance.A comprehensive learning strategy goes beyond simply offering training courses.
It encompasses a holistic approach that considers various learning styles, identifies specific skill gaps, and measures the impact of learning interventions on the company’s bottom line. This process involves meticulous planning, consistent evaluation, and a commitment to continuous improvement.
Key Considerations for a Successful Learning Program
A successful workplace learning program requires careful consideration of various factors. These factors are crucial for ensuring that the program resonates with employees and effectively meets the organization’s needs. The following considerations will help to create a program that is engaging and impactful.
You also can understand valuable knowledge by exploring cima ethics confidentiality rules.
- Identifying Learning Needs: A thorough analysis of existing skill gaps and future skill requirements is essential. This process involves assessing current employee capabilities, analyzing job roles, and forecasting industry trends to predict future needs. For instance, a company experiencing rapid technological advancements may need to prioritize training in emerging technologies to remain competitive.
- Defining Learning Objectives: Clearly defined learning objectives ensure that training initiatives directly address specific knowledge and skill gaps. These objectives must be measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART). Examples include improving customer service skills by 15% within six months or enhancing data analysis proficiency by 20% over the next year.
- Selecting Appropriate Learning Methods: A variety of learning methods, such as online courses, workshops, mentorship programs, and on-the-job training, should be considered. Selecting the most suitable methods will maximize engagement and learning outcomes. For instance, a hands-on workshop might be ideal for developing practical skills, while online courses could be more efficient for delivering theoretical knowledge.
- Ensuring Accessibility and Inclusivity: Learning initiatives should be accessible to all employees, regardless of their learning styles, backgrounds, or physical limitations. This may involve offering multiple learning formats and providing accommodations for diverse needs. Consider incorporating different learning styles such as visual, auditory, and kinesthetic to ensure all employees benefit from the training.
Aligning Learning Initiatives with Business Goals
Aligning learning initiatives with business goals ensures that training investments directly contribute to the organization’s overall success. This alignment is crucial for demonstrating the value of learning and fostering a culture of continuous improvement.
Finish your research with information from how to clearly communicate feedback and expectations.
- Strategic Planning: Integrating learning goals into the organization’s strategic plan ensures that training initiatives support business objectives. This process involves aligning learning initiatives with key performance indicators (KPIs) and quantifiable metrics.
- Performance Improvement: Identifying performance gaps and designing learning interventions to address these gaps is essential. Learning initiatives should directly address areas where employees are struggling, leading to improved performance and efficiency.
- Growth and Innovation: Investing in employee development fosters a culture of innovation and growth within the organization. Employees with enhanced skills and knowledge are better equipped to adapt to changes and contribute to new ideas.
Potential Challenges in Implementing a Workplace Learning Strategy, Increase learning in the workplace
Implementing a workplace learning strategy can present several challenges. Understanding and proactively addressing these challenges is crucial for successful implementation.
- Resistance to Change: Some employees may resist new learning initiatives, either due to fear of the unknown or a lack of understanding of the benefits. Open communication, clear expectations, and showcasing the benefits of the learning initiatives can mitigate this challenge.
- Budgetary Constraints: Funding learning initiatives can be challenging, especially in organizations with limited budgets. Identifying cost-effective learning methods and securing funding through various sources can overcome this issue.
- Maintaining Engagement: Keeping employees engaged throughout the learning process is essential for maximizing the impact of training. Employing interactive and engaging methods, incorporating real-world scenarios, and ensuring ongoing support can boost employee engagement.
Creating a Supportive Learning Environment
A supportive learning environment is crucial for maximizing employee development and organizational growth. It goes beyond simply providing training resources; it fosters a culture where learning is valued, encouraged, and integrated into daily work. This environment empowers employees to acquire new skills, contribute more effectively, and ultimately drive business success.A thriving learning culture isn’t built overnight. It requires deliberate effort, consistent reinforcement, and a clear commitment from leadership at all levels.
Creating a supportive learning environment requires a multifaceted approach, focusing on leadership, inclusivity, diverse learning styles, and knowledge sharing. This approach ensures that all employees feel empowered to learn and contribute their best work.
The Role of Leadership in Fostering Continuous Learning
Leadership plays a pivotal role in establishing a culture of continuous learning. Leaders who champion learning are not just managers; they are facilitators and role models. They demonstrate a commitment to personal and professional growth, thereby inspiring similar behavior in their teams. This leadership commitment sets the tone for the entire organization.Effective leaders create opportunities for learning, whether through formal training programs, mentorship initiatives, or encouraging knowledge sharing within teams.
They actively encourage employees to seek out new skills and knowledge relevant to their roles and the organization’s goals. This approach creates a virtuous cycle of continuous improvement. Furthermore, leaders must actively remove obstacles that hinder learning, such as heavy workloads or lack of time allocation.
Creating an Inclusive and Accessible Learning Environment
An inclusive learning environment welcomes all employees, regardless of their background, experience, or learning style. It actively addresses potential barriers to learning, ensuring that all individuals have equal opportunities to succeed. This inclusive approach benefits the organization by tapping into the diverse skills and perspectives of all employees.Implementing accessibility features, such as providing materials in different formats (audio, visual, written), accommodating different learning paces, and offering flexible learning schedules, are vital components of an inclusive environment.
This approach fosters a sense of belonging and encourages participation from every employee. By implementing accessibility features, the organization is showing its commitment to equity and inclusion.
Addressing Diverse Learning Styles and Needs
Employees have varying learning styles, preferences, and needs. Some learn best through hands-on experiences, while others thrive in collaborative settings. Acknowledging and accommodating these diverse learning styles is crucial for effective training.Providing a variety of learning methods, such as workshops, online courses, simulations, and peer-to-peer mentoring, caters to a broader range of learning preferences. Organizations should also recognize individual learning needs, such as providing support for employees with disabilities or those who require more personalized attention.
Flexibility in learning approaches is essential to fostering a truly inclusive environment. Furthermore, regular feedback mechanisms help identify and address specific learning needs, allowing for targeted interventions.
Building a Culture of Knowledge Sharing and Collaboration
A culture of knowledge sharing and collaboration encourages employees to learn from each other. This approach promotes a sense of community and teamwork, leading to improved problem-solving and innovation.Establishing platforms for knowledge sharing, such as internal wikis, knowledge bases, and online forums, facilitates the exchange of information and best practices. Encouraging peer-to-peer learning through mentorship programs and cross-functional teams fosters collaboration and allows employees to learn from each other’s expertise.
By actively promoting these platforms and fostering a culture of trust and openness, organizations can ensure the sharing of critical information and valuable knowledge. This sharing of knowledge leads to faster learning and problem-solving for everyone.
Case Studies of Successful Learning Programs: Increase Learning In The Workplace
Learning in the workplace isn’t just about training; it’s about creating a culture of continuous improvement and adaptation. Successful learning programs go beyond theoretical knowledge, impacting employee performance, organizational growth, and ultimately, bottom-line results. Examining real-world examples illuminates the strategies, implementation, and factors that drive these positive outcomes.Examining successful learning programs reveals key strategies and implementation methods that can be adapted and replicated in diverse organizational contexts and industries.
Understanding these successes offers invaluable insights into creating impactful learning initiatives within your own organization.
Examples of Successful Learning Initiatives
Successful learning programs are not one-size-fits-all. Different organizations, with varying needs and cultures, implement diverse strategies to achieve their learning goals. These examples highlight successful approaches, emphasizing the importance of tailoring programs to specific contexts.
- Google’s Project Oxygen: This program, focusing on effective leadership and team dynamics, involved employee feedback and data analysis. Results included improved team performance and increased employee satisfaction, demonstrating the value of a data-driven approach to learning. The key to success was its comprehensive feedback mechanisms and emphasis on fostering a positive work environment.
- Microsoft’s Learning Culture Initiative: Microsoft implemented a comprehensive approach, integrating learning into daily workflows. This involved providing accessible learning resources, promoting knowledge sharing, and encouraging continuous learning through mentorship programs. Results included increased innovation, improved employee engagement, and better skill development. This success highlights the importance of embedding learning into the fabric of the organization.
- Salesforce’s focus on customer-centricity: Salesforce integrated customer service training directly into the sales process. This involved simulations, role-playing, and ongoing feedback to enhance customer interaction skills. The measurable results were improved customer satisfaction ratings, increased sales conversions, and a demonstrably more effective sales team. This exemplifies the importance of linking learning directly to business outcomes.
Key Factors Contributing to Program Success
Several key factors consistently contribute to the success of workplace learning programs. Understanding these elements is crucial for creating effective and impactful initiatives.
- Alignment with Business Objectives: Successful programs are directly linked to organizational goals. This ensures that learning efforts are strategic and contribute directly to achieving desired outcomes. For example, a sales team’s training should directly address improving conversion rates, not just general sales skills.
- Employee Engagement and Participation: Active employee participation and engagement are crucial for knowledge retention and application. Learning programs should be interactive, relevant, and provide opportunities for employees to apply new skills immediately.
- Measurable Outcomes and Feedback: Successful programs track progress and measure impact. This allows for adjustments and improvements based on real-time feedback, ensuring the program’s effectiveness and relevance.
Adapting Successful Models to Specific Contexts
Adapting successful learning models to specific organizational contexts is crucial. Understanding the unique needs of each organization is essential for tailoring the approach to achieve the desired results.
- Consider Organizational Culture: The learning program should resonate with the existing organizational culture. A program that values individual learning may not be effective in a highly collaborative environment.
- Identify Specific Skill Gaps: Tailor the learning program to address specific skill gaps within the organization. A program focused on project management skills would be beneficial in a project-oriented team but not necessarily in a sales team.
- Utilize Available Resources: Effective programs leverage existing resources within the organization, such as internal experts or existing training materials. Leveraging internal expertise creates credibility and saves costs.
Replicating Successful Programs Across Industries
Replicating successful learning programs across industries requires careful consideration. While core principles remain consistent, adapting the specifics to the unique demands of different industries is critical.
- Industry-Specific Content: The content and delivery methods need to be tailored to the specific industry and its unique challenges. For example, healthcare professionals require different training than software developers.
- Technology Integration: Effective programs often integrate technology to enhance accessibility, engagement, and scalability. The specific technologies used might vary significantly across industries.
- Regulatory Compliance: Industry regulations can significantly impact the design and delivery of learning programs. Understanding and adhering to industry-specific regulations is crucial.
Illustrative Examples of Learning Initiatives

Learning in the workplace is not a one-size-fits-all endeavor. Effective programs consider the specific needs and context of the organization and its employees. This section presents illustrative examples of learning initiatives designed to address different aspects of professional development, from technical skills to leadership qualities.
Simulated Workplace Learning Program
A simulated workplace learning program immerses employees in realistic scenarios. This approach allows them to practice skills and make decisions in a safe environment, mimicking actual work situations. A key feature of this type of program is the use of interactive simulations. For example, a company selling software could create a simulated customer service environment where employees handle various customer complaints and resolve technical issues.
The simulation would track their responses, providing feedback and identifying areas needing improvement. Another example involves a healthcare company simulating a patient emergency situation, allowing employees to practice teamwork and decision-making under pressure. This simulated environment, complete with realistic challenges and outcomes, provides valuable experience that translates directly into improved performance in the real workplace. Benefits include enhanced problem-solving abilities, quicker adaptation to real-world situations, and improved decision-making.
Gamification in Workplace Learning
Gamification employs game mechanics and design principles to make learning more engaging and motivating. This approach transforms learning activities into interactive challenges, quests, and rewards. A retail company, for example, could use a gamified platform to train new sales associates on product knowledge and sales techniques. Employees earn points for correct answers, completing challenges, and exceeding sales targets.
Leaderboards and badges recognize top performers, fostering healthy competition and encouraging continued engagement. Another example involves a software development company using a gamified platform to train developers on new coding languages or frameworks. The program could involve challenges like completing coding tasks within a time limit or solving complex coding puzzles. This interactive format makes learning more enjoyable and encourages active participation, which leads to greater knowledge retention.
Leadership Development Program
Leadership development programs aim to enhance managerial skills and foster leadership qualities. A leadership program might include modules on communication, delegation, conflict resolution, and strategic thinking. A key component is mentoring, where experienced leaders guide and support aspiring leaders. This program could include workshops, coaching sessions, and real-world projects where participants apply their newly acquired skills in a practical context.
For instance, a company could have a program where managers lead small teams in projects, evaluating their approach and providing feedback. Such programs help managers effectively manage their teams, build trust, and drive performance.
Learning Path for a Sales Representative
| Phase | Activities | Learning Objectives |
|---|---|---|
| Phase 1: Foundational Knowledge | Product knowledge training, sales process overview, customer relationship management (CRM) basics | Understanding company products, comprehending the sales process, and using CRM tools effectively. |
| Phase 2: Skill Development | Negotiation techniques, objection handling, closing strategies, effective communication | Mastering negotiation techniques, handling objections professionally, closing deals successfully, and communicating effectively with customers. |
| Phase 3: Practical Application | Role-playing exercises, simulated sales scenarios, feedback sessions, mentorship | Applying learned skills in real-world scenarios, receiving feedback on performance, and gaining support from mentors. |
| Phase 4: Advanced Strategies | Advanced sales techniques, strategic account management, team collaboration | Implementing advanced sales techniques, managing strategic accounts, and collaborating effectively with the sales team. |
This table Artikels a structured learning path for a sales representative, encompassing different phases and activities. This learning path provides a clear roadmap for skill development, from foundational knowledge to advanced strategies, empowering sales representatives to excel in their roles.
Final Thoughts
In conclusion, fostering a learning environment within a company is not just beneficial for employees; it directly impacts business outcomes. By implementing a comprehensive learning strategy that aligns with business goals, organizations can create a culture of continuous improvement, enhance employee skills, and drive overall success. The key is understanding the multifaceted nature of learning, implementing effective methods, and measuring the impact of these initiatives.
From identifying learning styles to utilizing technology, every element plays a vital role in a successful workplace learning program.
